Nino Cauli
Human-Centric Artificial Intelligence Architecture for Industry 5.0 Applications
Mar 21, 2022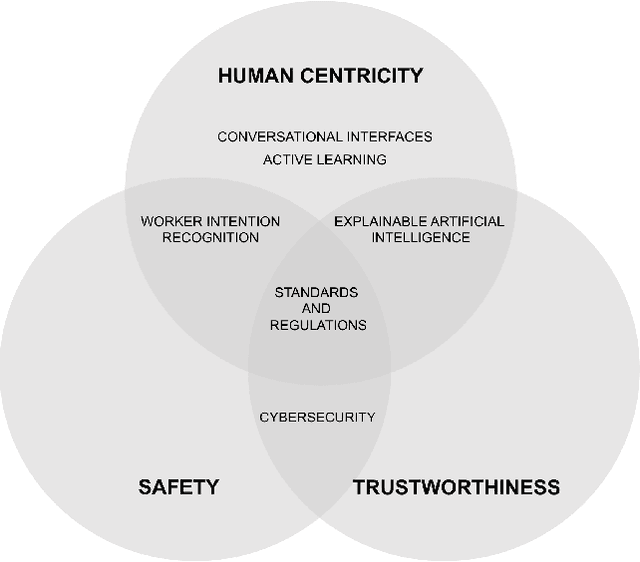
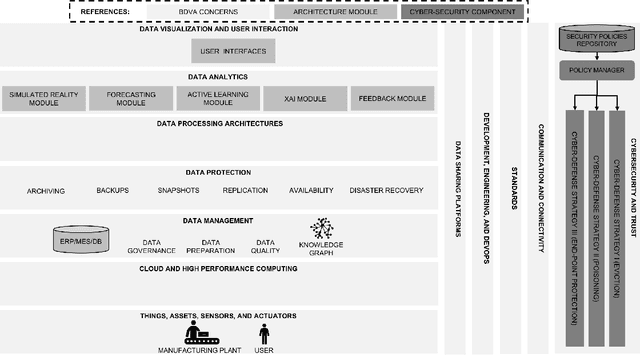
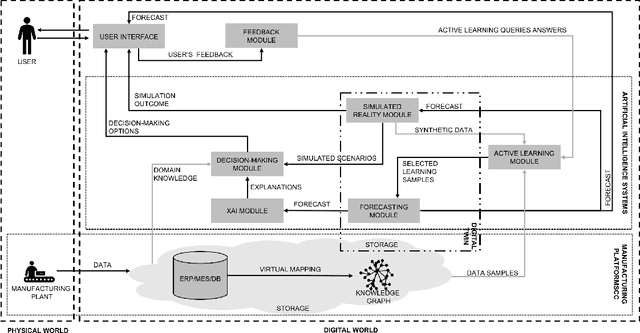

Abstract:Human-centricity is the core value behind the evolution of manufacturing towards Industry 5.0. Nevertheless, there is a lack of architecture that considers safety, trustworthiness, and human-centricity at its core. Therefore, we propose an architecture that integrates Artificial Intelligence (Active Learning, Forecasting, Explainable Artificial Intelligence), simulated reality, decision-making, and users' feedback, focusing on synergies between humans and machines. Furthermore, we align the proposed architecture with the Big Data Value Association Reference Architecture Model. Finally, we validate it on two use cases from real-world case studies.
STARdom: an architecture for trusted and secure human-centered manufacturing systems
Apr 02, 2021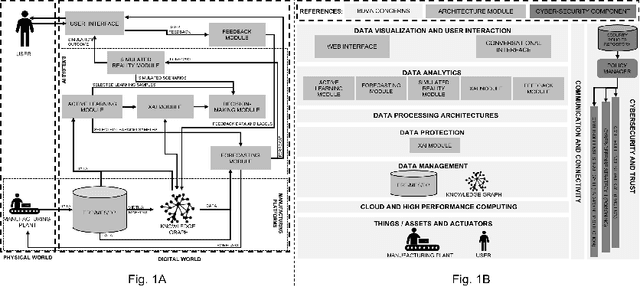
Abstract:There is a lack of a single architecture specification that addresses the needs of trusted and secure Artificial Intelligence systems with humans in the loop, such as human-centered manufacturing systems at the core of the evolution towards Industry 5.0. To realize this, we propose an architecture that integrates forecasts, Explainable Artificial Intelligence, supports collecting users' feedback, and uses Active Learning and Simulated Reality to enhance forecasts and provide decision-making recommendations. The architecture security is addressed as a general concern. We align the proposed architecture with the Big Data Value Association Reference Architecture Model. We tailor it for the domain of demand forecasting and validate it on a real-world case study.
Cleaning tasks knowledge transfer between heterogeneous robots: a deep learning approach
Mar 13, 2019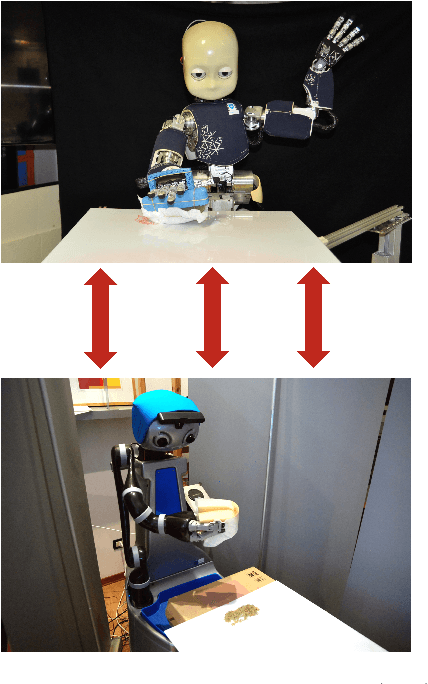
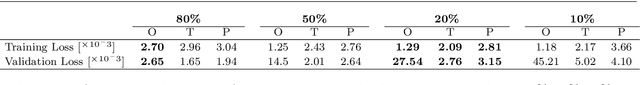
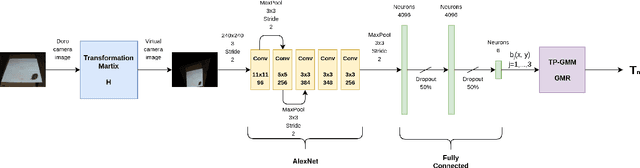

Abstract:Nowadays, autonomous service robots are becoming an important topic in robotic research. Differently from typical industrial scenarios, with highly controlled environments, service robots must show an additional robustness to task perturbations and changes in the characteristics of their sensory feedback. In this paper a robot is taught to perform two different cleaning tasks over a table, using a learning from demonstration paradigm. However, differently from other approaches, a convolutional neural network is used to generalize the demonstrations to different, not yet seen dirt or stain patterns on the same table using only visual feedback, and to perform cleaning movements accordingly. Robustness to robot posture and illumination changes is achieved using data augmentation techniques and camera images transformation. This robustness allows the transfer of knowledge regarding execution of cleaning tasks between heterogeneous robots operating in different environmental settings. To demonstrate the viability of the proposed approach, a network trained in Lisbon to perform cleaning tasks, using the iCub robot, is successfully employed by the DoRo robot in Peccioli, Italy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge