Hua Jin
Cross-Sample Augmented Test-Time Adaptation for Personalized Intraoperative Hypotension Prediction
Dec 12, 2025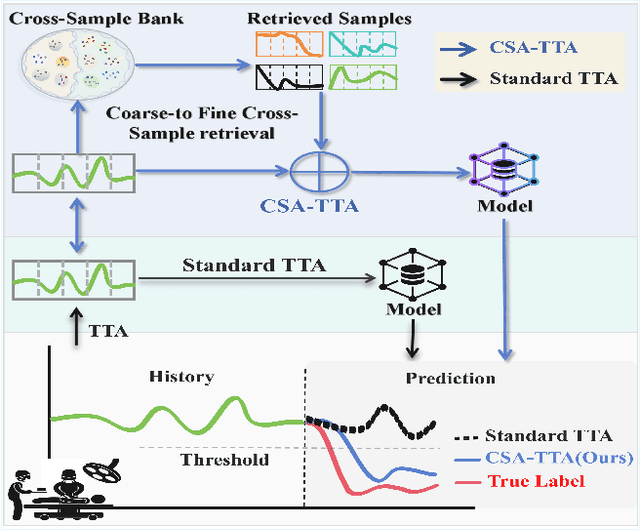
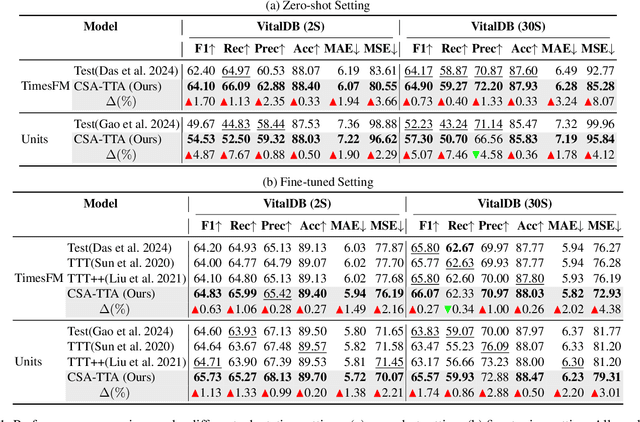
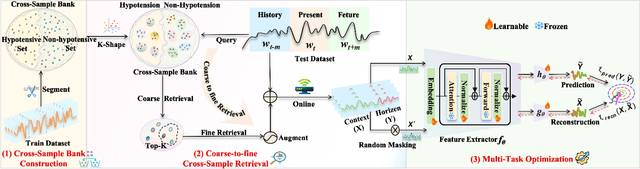
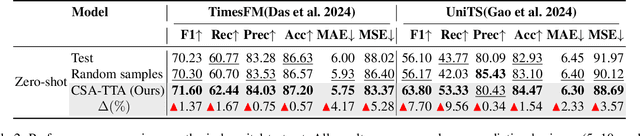
Abstract:Intraoperative hypotension (IOH) poses significant surgical risks, but accurate prediction remains challenging due to patient-specific variability. While test-time adaptation (TTA) offers a promising approach for personalized prediction, the rarity of IOH events often leads to unreliable test-time training. To address this, we propose CSA-TTA, a novel Cross-Sample Augmented Test-Time Adaptation framework that enhances training by incorporating hypotension events from other individuals. Specifically, we first construct a cross-sample bank by segmenting historical data into hypotensive and non-hypotensive samples. Then, we introduce a coarse-to-fine retrieval strategy for building test-time training data: we initially apply K-Shape clustering to identify representative cluster centers and subsequently retrieve the top-K semantically similar samples based on the current patient signal. Additionally, we integrate both self-supervised masked reconstruction and retrospective sequence forecasting signals during training to enhance model adaptability to rapid and subtle intraoperative dynamics. We evaluate the proposed CSA-TTA on both the VitalDB dataset and a real-world in-hospital dataset by integrating it with state-of-the-art time series forecasting models, including TimesFM and UniTS. CSA-TTA consistently enhances performance across settings-for instance, on VitalDB, it improves Recall and F1 scores by +1.33% and +1.13%, respectively, under fine-tuning, and by +7.46% and +5.07% in zero-shot scenarios-demonstrating strong robustness and generalization.
AnesBench: Multi-Dimensional Evaluation of LLM Reasoning in Anesthesiology
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:The application of large language models (LLMs) in the medical field has gained significant attention, yet their reasoning capabilities in more specialized domains like anesthesiology remain underexplored. In this paper, we systematically evaluate the reasoning capabilities of LLMs in anesthesiology and analyze key factors influencing their performance. To this end, we introduce AnesBench, a cross-lingual benchmark designed to assess anesthesiology-related reasoning across three levels: factual retrieval (System 1), hybrid reasoning (System 1.x), and complex decision-making (System 2). Through extensive experiments, we first explore how model characteristics, including model scale, Chain of Thought (CoT) length, and language transferability, affect reasoning performance. Then, we further evaluate the effectiveness of different training strategies, leveraging our curated anesthesiology-related dataset, including continuous pre-training (CPT) and supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Additionally, we also investigate how the test-time reasoning techniques, such as Best-of-N sampling and beam search, influence reasoning performance, and assess the impact of reasoning-enhanced model distillation, specifically DeepSeek-R1. We will publicly release AnesBench, along with our CPT and SFT training datasets and evaluation code at https://github.com/MiliLab/AnesBench.
Towards Training A Chinese Large Language Model for Anesthesiology
Mar 05, 2024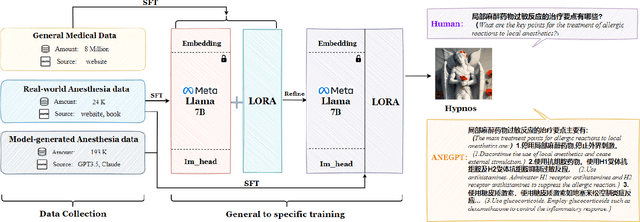
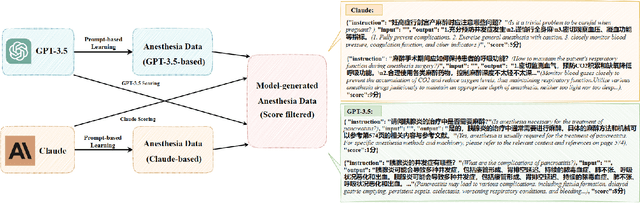
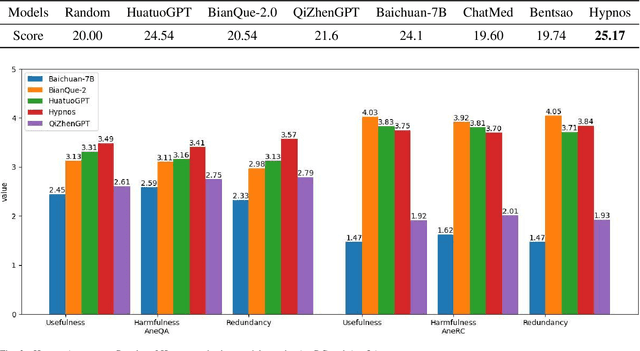
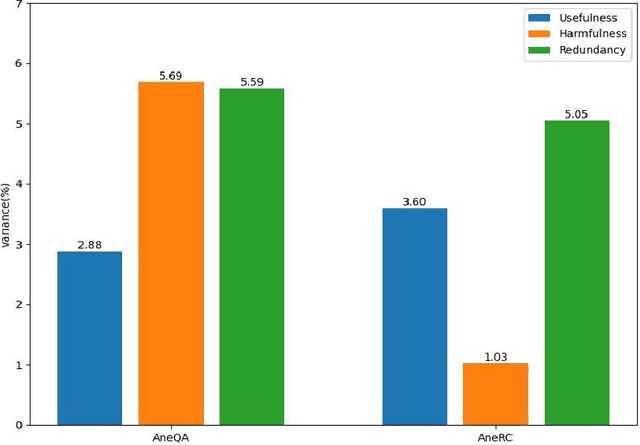
Abstract:Medical large language models (LLMs) have gained popularity recently due to their significant practical utility. However, most existing research focuses on general medicine, and there is a need for in-depth study of LLMs in specific fields like anesthesiology. To fill the gap, we introduce Hypnos, a Chinese Anesthesia model built upon existing LLMs, e.g., Llama. Hypnos' contributions have three aspects: 1) The data, such as utilizing Self-Instruct, acquired from current LLMs likely includes inaccuracies. Hypnos implements a cross-filtering strategy to improve the data quality. This strategy involves using one LLM to assess the quality of the generated data from another LLM and filtering out the data with low quality. 2) Hypnos employs a general-to-specific training strategy that starts by fine-tuning LLMs using the general medicine data and subsequently improving the fine-tuned LLMs using data specifically from Anesthesiology. The general medical data supplement the medical expertise in Anesthesiology and enhance the effectiveness of Hypnos' generation. 3) We introduce a standardized benchmark for evaluating medical LLM in Anesthesiology. Our benchmark includes both publicly available instances from the Internet and privately obtained cases from the Hospital. Hypnos outperforms other medical LLMs in anesthesiology in metrics, GPT-4, and human evaluation on the benchmark dataset.
Knowledge Graph Augmented Network Towards Multiview Representation Learning for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis
Jan 13, 2022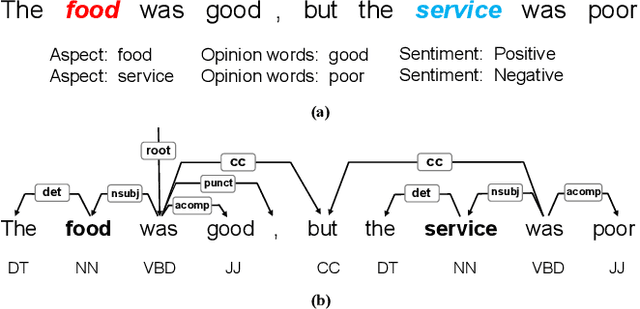

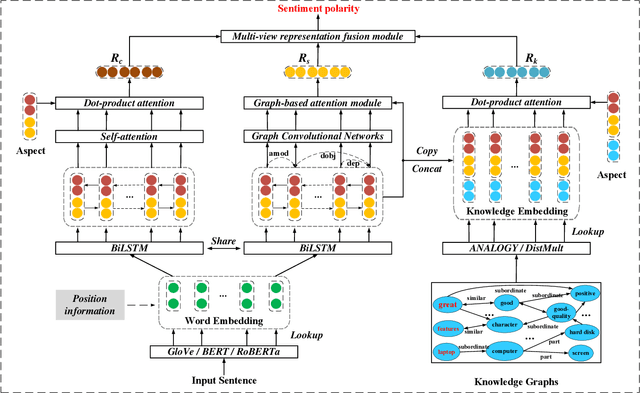

Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) is a fine-grained task of sentiment analysis. To better comprehend long complicated sentences and obtain accurate aspect-specific information, linguistic and commonsense knowledge are generally required in this task. However, most methods employ complicated and inefficient approaches to incorporate external knowledge, e.g., directly searching the graph nodes. Additionally, the complementarity between external knowledge and linguistic information has not been thoroughly studied. To this end, we propose a knowledge graph augmented network (KGAN), which aims to effectively incorporate external knowledge with explicitly syntactic and contextual information. In particular, KGAN captures the sentiment feature representations from multiple different perspectives, i.e., context-, syntax- and knowledge-based. First, KGAN learns the contextual and syntactic representations in parallel to fully extract the semantic features. Then, KGAN integrates the knowledge graphs into the embedding space, based on which the aspect-specific knowledge representations are further obtained via an attention mechanism. Last, we propose a hierarchical fusion module to complement these multiview representations in a local-to-global manner. Extensive experiments on three popular ABSA benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our KGAN. Notably, with the help of the pretrained model of RoBERTa, KGAN achieves a new record of state-of-the-art performance.
Unified Instance and Knowledge Alignment Pretraining for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis
Oct 26, 2021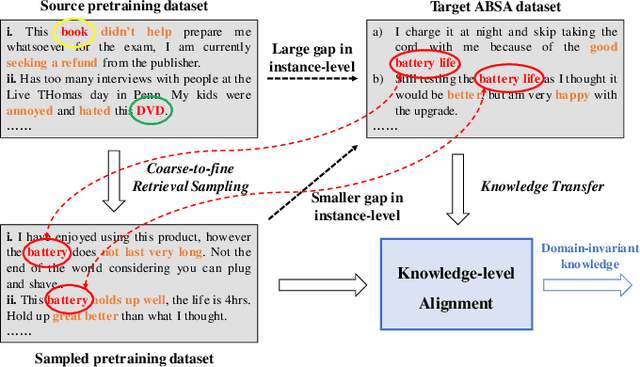
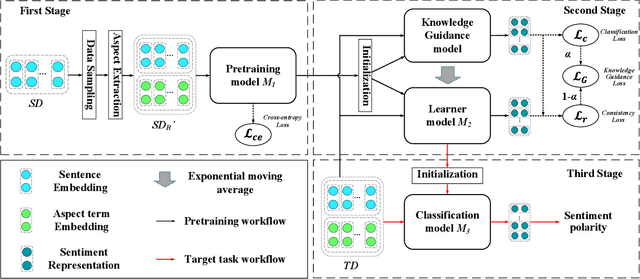
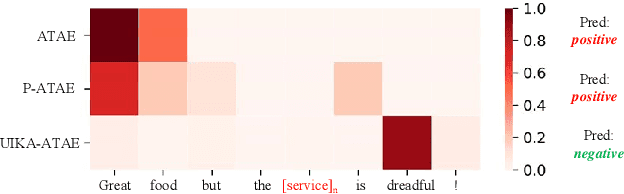
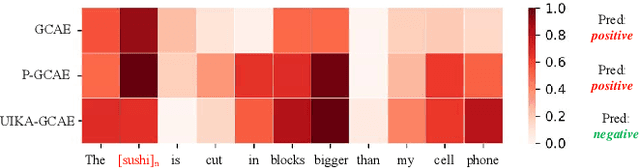
Abstract:Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) aims to determine the sentiment polarity towards an aspect. Because of the expensive and limited labelled data, the pretraining strategy has become the de-facto standard for ABSA. However, there always exists severe domain shift between the pretraining and downstream ABSA datasets, hindering the effective knowledge transfer when directly finetuning and making the downstream task performs sub-optimal. To mitigate such domain shift, we introduce a unified alignment pretraining framework into the vanilla pretrain-finetune pipeline with both instance- and knowledge-level alignments. Specifically, we first devise a novel coarse-to-fine retrieval sampling approach to select target domain-related instances from the large-scale pretraining dataset, thus aligning the instances between pretraining and target domains (\textit{First Stage}). Then, we introduce a knowledge guidance-based strategy to further bridge the domain gap at the knowledge level. In practice, we formulate the model pretrained on the sampled instances into a knowledge guidance model and a learner model, respectively. On the target dataset, we design an on-the-fly teacher-student joint fine-tuning approach to progressively transfer the knowledge from the knowledge guidance model to the learner model (\textit{Second Stage}). Thereby, the learner model can maintain more domain-invariant knowledge when learning new knowledge from the target dataset. In the \textit{Third Stage,} the learner model is finetuned to better adapt its learned knowledge to the target dataset. Extensive experiments and analyses on several ABSA benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and universality of our proposed pretraining framework. Notably, our pretraining framework pushes several strong baseline models up to the new state-of-the-art records. We release our code and models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge