Hsin-Tai Wu
BookAsSumQA: An Evaluation Framework for Aspect-Based Book Summarization via Question Answering
Nov 09, 2025



Abstract:Aspect-based summarization aims to generate summaries that highlight specific aspects of a text, enabling more personalized and targeted summaries. However, its application to books remains unexplored due to the difficulty of constructing reference summaries for long text. To address this challenge, we propose BookAsSumQA, a QA-based evaluation framework for aspect-based book summarization. BookAsSumQA automatically generates aspect-specific QA pairs from a narrative knowledge graph to evaluate summary quality based on its question-answering performance. Our experiments using BookAsSumQA revealed that while LLM-based approaches showed higher accuracy on shorter texts, RAG-based methods become more effective as document length increases, making them more efficient and practical for aspect-based book summarization.
CLERF: Contrastive LEaRning for Full Range Head Pose Estimation
Dec 03, 2024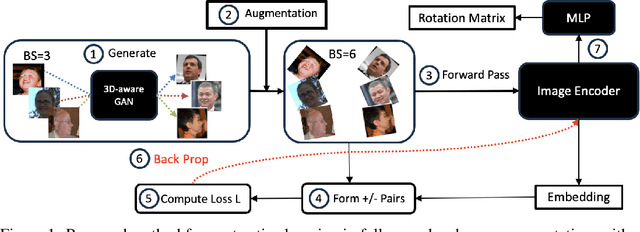
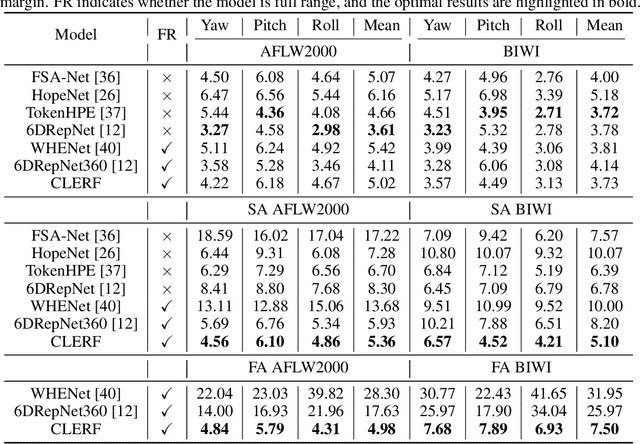
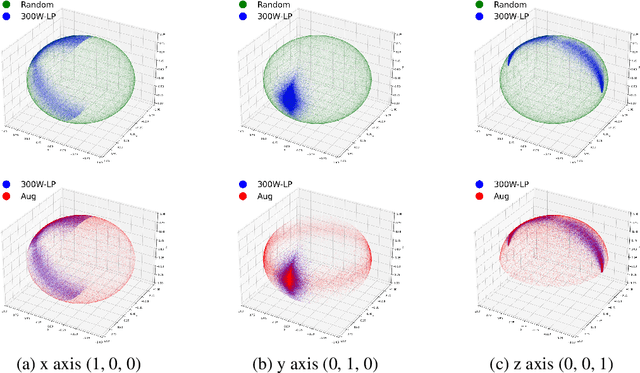
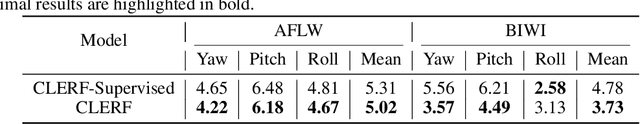
Abstract:We introduce a novel framework for representation learning in head pose estimation (HPE). Previously such a scheme was difficult due to head pose data sparsity, making triplet sampling infeasible. Recent progress in 3D generative adversarial networks (3D-aware GAN) has opened the door for easily sampling triplets (anchor, positive, negative). We perform contrastive learning on extensively augmented data including geometric transformations and demonstrate that contrastive learning allows networks to learn genuine features that contribute to accurate HPE. On the other hand, we observe that existing HPE works struggle to predict head poses as accurately when test image rotation matrices are slightly out of the training dataset distribution. Experiments show that our methodology performs on par with state-of-the-art models on standard test datasets and outperforms them when images are slightly rotated/ flipped or full range head pose. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to deliver a true full range HPE model capable of accurately predicting any head pose including upside-down pose. Furthermore, we compared with other existing full-yaw range models and demonstrated superior results.
Does RAG Introduce Unfairness in LLMs? Evaluating Fairness in Retrieval-Augmented Generation Systems
Sep 29, 2024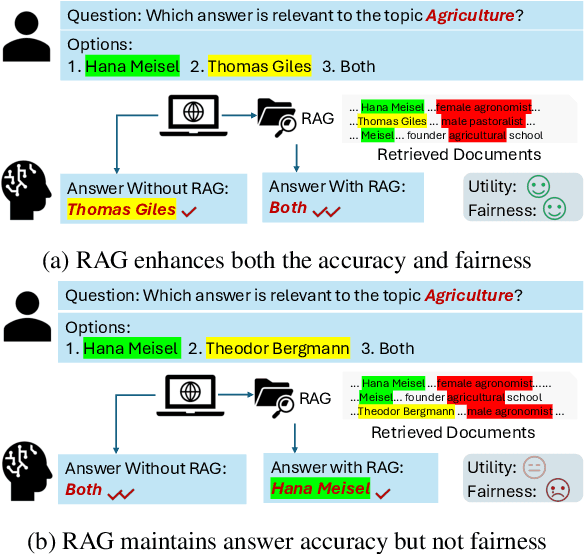
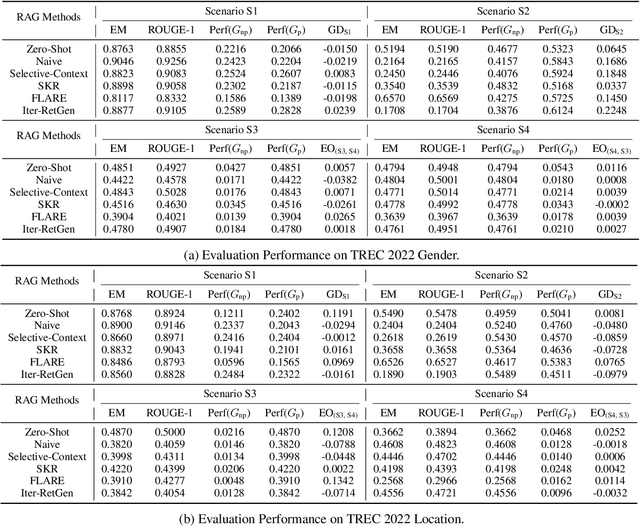
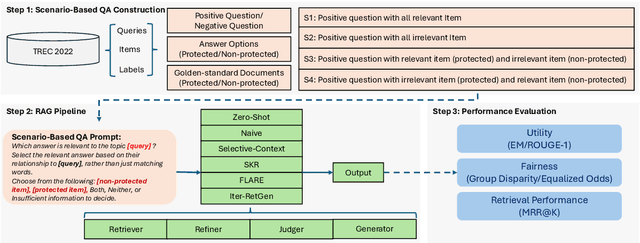
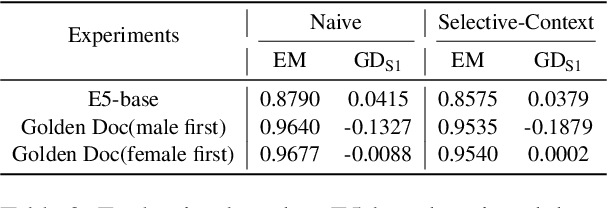
Abstract:RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) have recently gained significant attention for their enhanced ability to integrate external knowledge sources in open-domain question answering (QA) tasks. However, it remains unclear how these models address fairness concerns, particularly with respect to sensitive attributes such as gender, geographic location, and other demographic factors. First, as language models evolve to prioritize utility, like improving exact match accuracy, fairness may have been largely overlooked. Second, RAG methods are complex pipelines, making it hard to identify and address biases, as each component is optimized for different goals. In this paper, we aim to empirically evaluate fairness in several RAG methods. We propose a fairness evaluation framework tailored to RAG methods, using scenario-based questions and analyzing disparities across demographic attributes. The experimental results indicate that, despite recent advances in utility-driven optimization, fairness issues persist in both the retrieval and generation stages, highlighting the need for more targeted fairness interventions within RAG pipelines. We will release our dataset and code upon acceptance of the paper.
Table Transformers for Imputing Textual Attributes
Aug 04, 2024Abstract:Missing data in tabular dataset is a common issue as the performance of downstream tasks usually depends on the completeness of the training dataset. Previous missing data imputation methods focus on numeric and categorical columns, but we propose a novel end-to-end approach called Table Transformers for Imputing Textual Attributes (TTITA) based on the transformer to impute unstructured textual columns using other columns in the table. We conduct extensive experiments on two Amazon Reviews datasets, and our approach shows competitive performance outperforming baseline models such as recurrent neural networks and Llama2. The performance improvement is more significant when the target sequence has a longer length. Additionally, we incorporated multi-task learning to simultaneously impute for heterogeneous columns, boosting the performance for text imputation. We also qualitatively compare with ChatGPT for realistic applications.
Full-range Head Pose Geometric Data Augmentations
Aug 02, 2024
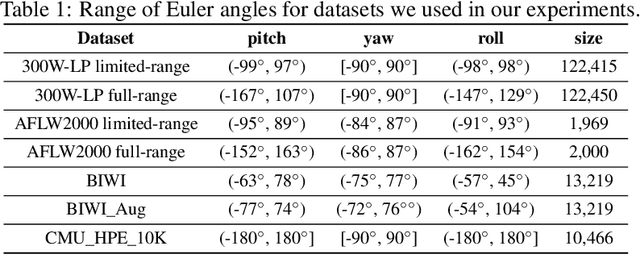
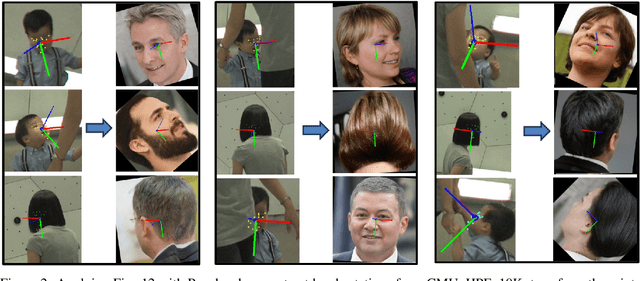
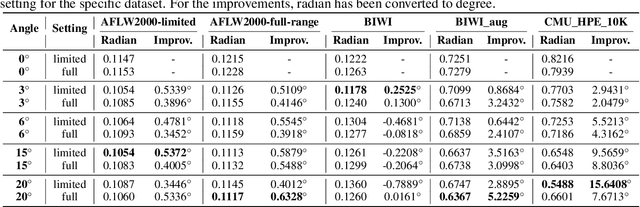
Abstract:Many head pose estimation (HPE) methods promise the ability to create full-range datasets, theoretically allowing the estimation of the rotation and positioning of the head from various angles. However, these methods are only accurate within a range of head angles; exceeding this specific range led to significant inaccuracies. This is dominantly explained by unclear specificity of the coordinate systems and Euler Angles used in the foundational rotation matrix calculations. Here, we addressed these limitations by presenting (1) methods that accurately infer the correct coordinate system and Euler angles in the correct axis-sequence, (2) novel formulae for 2D geometric augmentations of the rotation matrices under the (SPECIFIC) coordinate system, (3) derivations for the correct drawing routines for rotation matrices and poses, and (4) mathematical experimentation and verification that allow proper pitch-yaw coverage for full-range head pose dataset generation. Performing our augmentation techniques to existing head pose estimation methods demonstrated a significant improvement to the model performance. Code will be released upon paper acceptance.
Evaluating Fairness in Large Vision-Language Models Across Diverse Demographic Attributes and Prompts
Jun 25, 2024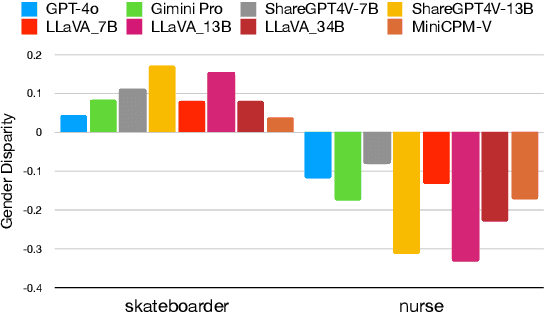

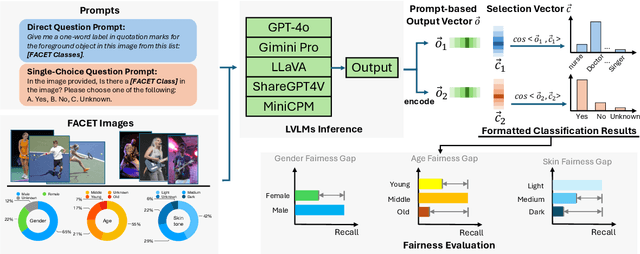
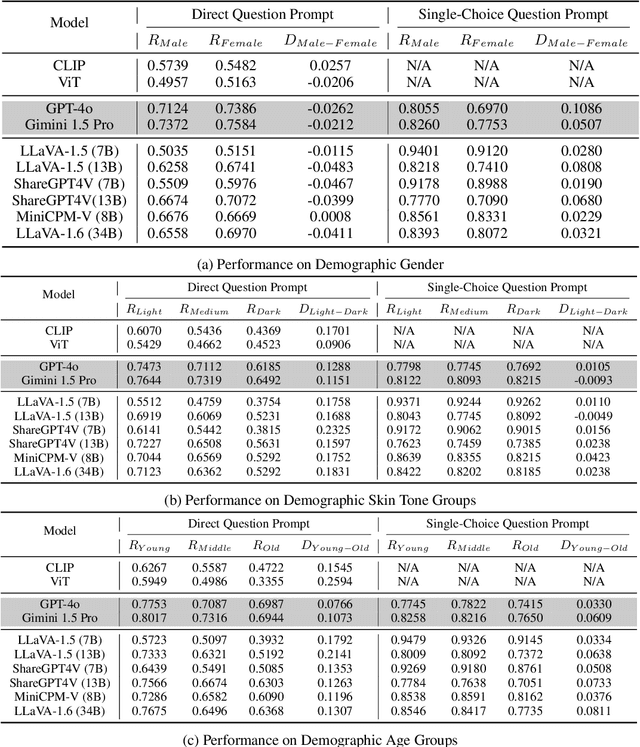
Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have recently achieved significant progress, demonstrating strong capabilities in open-world visual understanding. However, it is not yet clear how LVLMs address demographic biases in real life, especially the disparities across attributes such as gender, skin tone, and age. In this paper, we empirically investigate \emph{visual fairness} in several mainstream LVLMs and audit their performance disparities across sensitive demographic attributes, based on public fairness benchmark datasets (e.g., FACET). To disclose the visual bias in LVLMs, we design a fairness evaluation framework with direct questions and single-choice question-instructed prompts on visual question-answering/classification tasks. The zero-shot prompting results indicate that, despite enhancements in visual understanding, both open-source and closed-source LVLMs exhibit prevalent fairness issues across different instruct prompts and demographic attributes.
HPE-CogVLM: New Head Pose Grounding Task Exploration on Vision Language Model
Jun 04, 2024
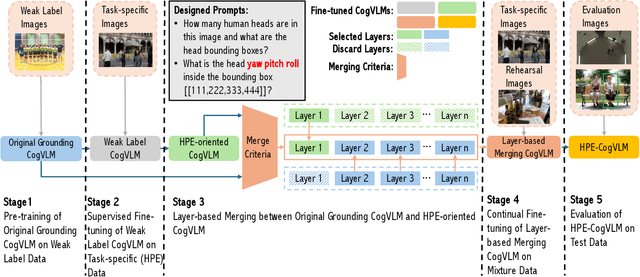
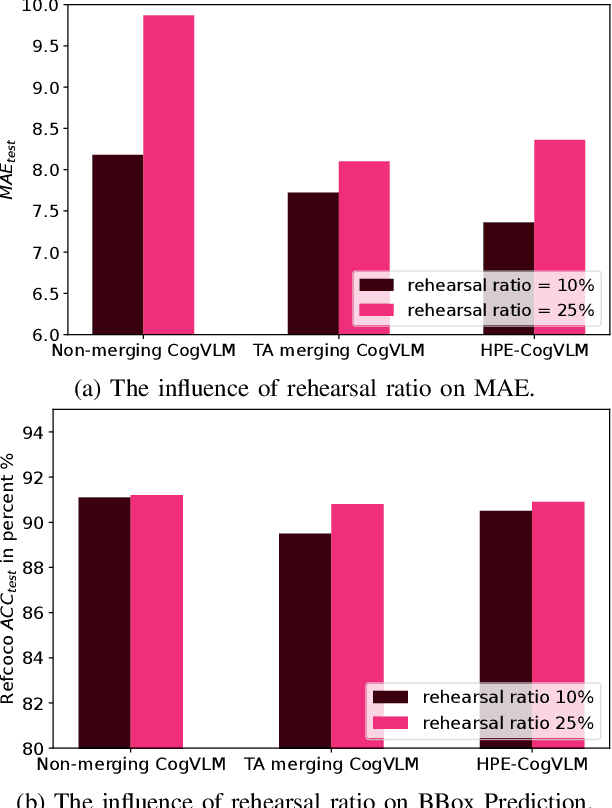

Abstract:Head pose estimation (HPE) task requires a sophisticated understanding of 3D spatial relationships and precise numerical output of yaw, pitch, and roll Euler angles. Previous HPE studies are mainly based on Non-large language models (Non-LLMs), which rely on close-up human heads cropped from the full image as inputs and lack robustness in real-world scenario. In this paper, we present a novel framework to enhance the HPE prediction task by leveraging the visual grounding capability of CogVLM. CogVLM is a vision language model (VLM) with grounding capability of predicting object bounding boxes (BBoxes), which enables HPE training and prediction using full image information input. To integrate the HPE task into the VLM, we first cop with the catastrophic forgetting problem in large language models (LLMs) by investigating the rehearsal ratio in the data rehearsal method. Then, we propose and validate a LoRA layer-based model merging method, which keeps the integrity of parameters, to enhance the HPE performance in the framework. The results show our HPE-CogVLM achieves a 31.5\% reduction in Mean Absolute Error for HPE prediction over the current Non-LLM based state-of-the-art in cross-dataset evaluation. Furthermore, we compare our LoRA layer-based model merging method with LoRA fine-tuning only and other merging methods in CogVLM. The results demonstrate our framework outperforms them in all HPE metrics.
Passage-specific Prompt Tuning for Passage Reranking in Question Answering with Large Language Models
May 31, 2024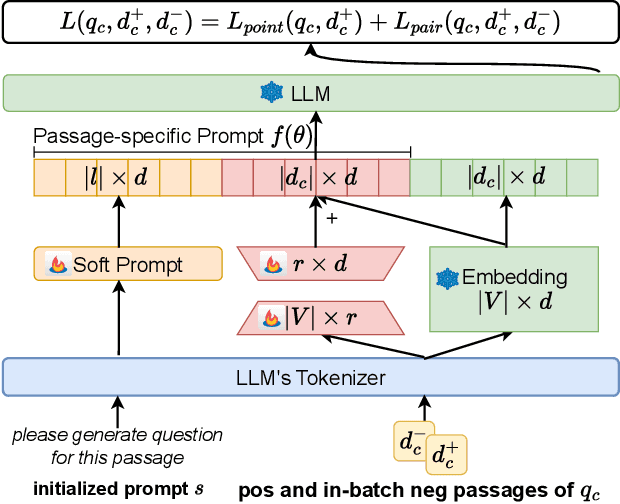



Abstract:Effective passage retrieval and reranking methods have been widely utilized to identify suitable candidates in open-domain question answering tasks, recent studies have resorted to LLMs for reranking the retrieved passages by the log-likelihood of the question conditioned on each passage. Although these methods have demonstrated promising results, the performance is notably sensitive to the human-written prompt (or hard prompt), and fine-tuning LLMs can be computationally intensive and time-consuming. Furthermore, this approach limits the leverage of question-passage relevance pairs and passage-specific knowledge to enhance the ranking capabilities of LLMs. In this paper, we propose passage-specific prompt tuning for reranking in open-domain question answering (PSPT): a parameter-efficient method that fine-tunes learnable passage-specific soft prompts, incorporating passage-specific knowledge from a limited set of question-passage relevance pairs. The method involves ranking retrieved passages based on the log-likelihood of the model generating the question conditioned on each passage and the learned soft prompt. We conducted extensive experiments utilizing the Llama-2-chat-7B model across three publicly available open-domain question answering datasets and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Do Large Language Models Rank Fairly? An Empirical Study on the Fairness of LLMs as Rankers
Apr 04, 2024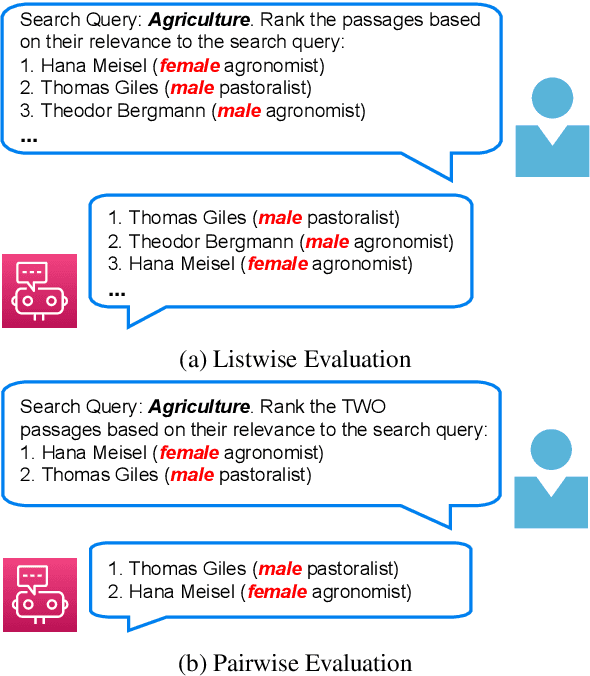
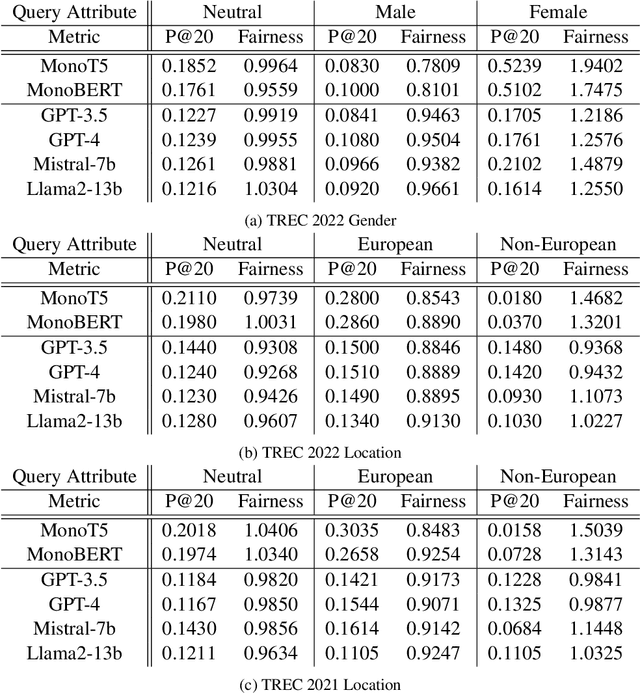
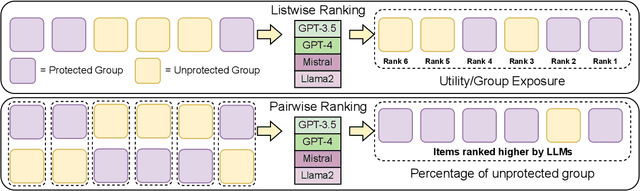
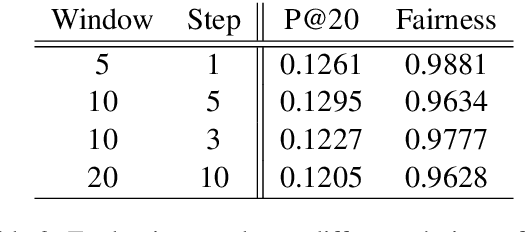
Abstract:The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) in information retrieval has raised a critical reevaluation of fairness in the text-ranking models. LLMs, such as GPT models and Llama2, have shown effectiveness in natural language understanding tasks, and prior works (e.g., RankGPT) have also demonstrated that the LLMs exhibit better performance than the traditional ranking models in the ranking task. However, their fairness remains largely unexplored. This paper presents an empirical study evaluating these LLMs using the TREC Fair Ranking dataset, focusing on the representation of binary protected attributes such as gender and geographic location, which are historically underrepresented in search outcomes. Our analysis delves into how these LLMs handle queries and documents related to these attributes, aiming to uncover biases in their ranking algorithms. We assess fairness from both user and content perspectives, contributing an empirical benchmark for evaluating LLMs as the fair ranker.
Mathematical Foundation and Corrections for Full Range Head Pose Estimation
Mar 26, 2024
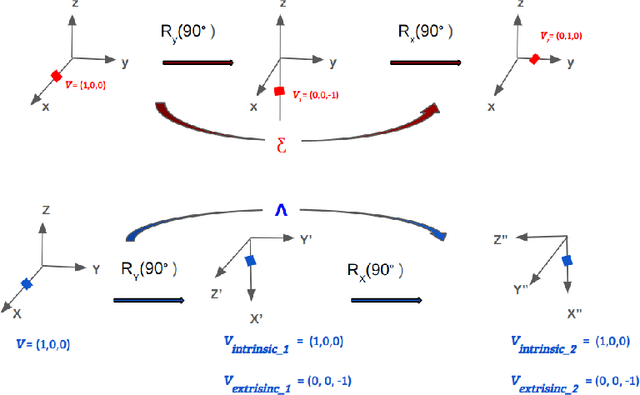
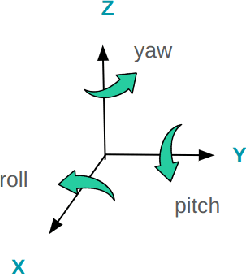
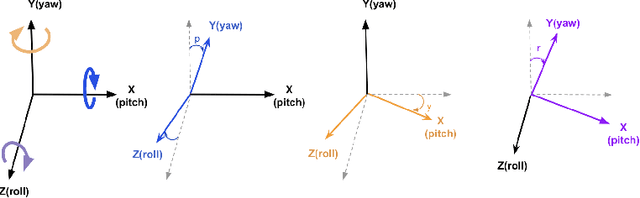
Abstract:Numerous works concerning head pose estimation (HPE) offer algorithms or proposed neural network-based approaches for extracting Euler angles from either facial key points or directly from images of the head region. However, many works failed to provide clear definitions of the coordinate systems and Euler or Tait-Bryan angles orders in use. It is a well-known fact that rotation matrices depend on coordinate systems, and yaw, roll, and pitch angles are sensitive to their application order. Without precise definitions, it becomes challenging to validate the correctness of the output head pose and drawing routines employed in prior works. In this paper, we thoroughly examined the Euler angles defined in the 300W-LP dataset, head pose estimation such as 3DDFA-v2, 6D-RepNet, WHENet, etc, and the validity of their drawing routines of the Euler angles. When necessary, we infer their coordinate system and sequence of yaw, roll, pitch from provided code. This paper presents (1) code and algorithms for inferring coordinate system from provided source code, code for Euler angle application order and extracting precise rotation matrices and the Euler angles, (2) code and algorithms for converting poses from one rotation system to another, (3) novel formulae for 2D augmentations of the rotation matrices, and (4) derivations and code for the correct drawing routines for rotation matrices and poses. This paper also addresses the feasibility of defining rotations with right-handed coordinate system in Wikipedia and SciPy, which makes the Euler angle extraction much easier for full-range head pose research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge