Hongzhan Yu
Learning to Nudge: A Scalable Barrier Function Framework for Safe Robot Interaction in Dense Clutter
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Robots operating in everyday environments must navigate and manipulate within densely cluttered spaces, where physical contact with surrounding objects is unavoidable. Traditional safety frameworks treat contact as unsafe, restricting robots to collision avoidance and limiting their ability to function in dense, everyday settings. As the number of objects grows, model-based approaches for safe manipulation become computationally intractable; meanwhile, learned methods typically tie safety to the task at hand, making them hard to transfer to new tasks without retraining. In this work we introduce Dense Contact Barrier Functions(DCBF). Our approach bypasses the computational complexity of explicitly modeling multi-object dynamics by instead learning a composable, object-centric function that implicitly captures the safety constraints arising from physical interactions. Trained offline on interactions with a few objects, the learned DCBFcomposes across arbitrary object sets at runtime, producing a single global safety filter that scales linearly and transfers across tasks without retraining. We validate our approach through simulated experiments in dense clutter, demonstrating its ability to enable collision-free navigation and safe, contact-rich interaction in suitable settings.
GLIDE: A Coordinated Aerial-Ground Framework for Search and Rescue in Unknown Environments
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:We present a cooperative aerial-ground search-and-rescue (SAR) framework that pairs two unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with an unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) to achieve rapid victim localization and obstacle-aware navigation in unknown environments. We dub this framework Guided Long-horizon Integrated Drone Escort (GLIDE), highlighting the UGV's reliance on UAV guidance for long-horizon planning. In our framework, a goal-searching UAV executes real-time onboard victim detection and georeferencing to nominate goals for the ground platform, while a terrain-scouting UAV flies ahead of the UGV's planned route to provide mid-level traversability updates. The UGV fuses aerial cues with local sensing to perform time-efficient A* planning and continuous replanning as information arrives. Additionally, we present a hardware demonstration (using a GEM e6 golf cart as the UGV and two X500 UAVs) to evaluate end-to-end SAR mission performance and include simulation ablations to assess the planning stack in isolation from detection. Empirical results demonstrate that explicit role separation across UAVs, coupled with terrain scouting and guided planning, improves reach time and navigation safety in time-critical SAR missions.
Safe Human Robot Navigation in Warehouse Scenario
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:The integration of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) in industrial environments, particularly warehouses, has revolutionized logistics and operational efficiency. However, ensuring the safety of human workers in dynamic, shared spaces remains a critical challenge. This work proposes a novel methodology that leverages control barrier functions (CBFs) to enhance safety in warehouse navigation. By integrating learning-based CBFs with the Open Robotics Middleware Framework (OpenRMF), the system achieves adaptive and safety-enhanced controls in multi-robot, multi-agent scenarios. Experiments conducted using various robot platforms demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed approach in avoiding static and dynamic obstacles, including human pedestrians. Our experiments evaluate different scenarios in which the number of robots, robot platforms, speed, and number of obstacles are varied, from which we achieve promising performance.
Controllable Motion Generation via Diffusion Modal Coupling
Mar 04, 2025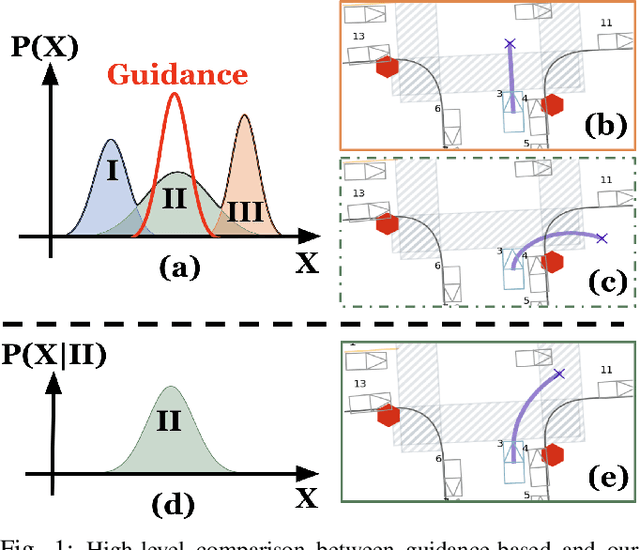
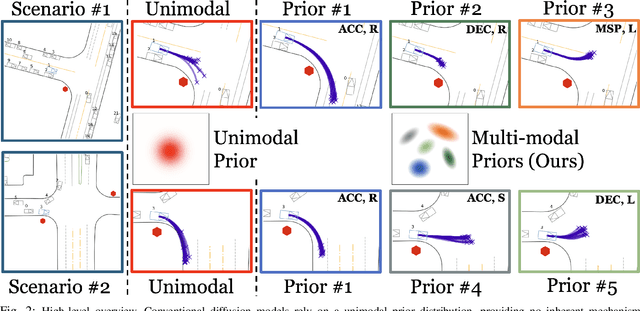
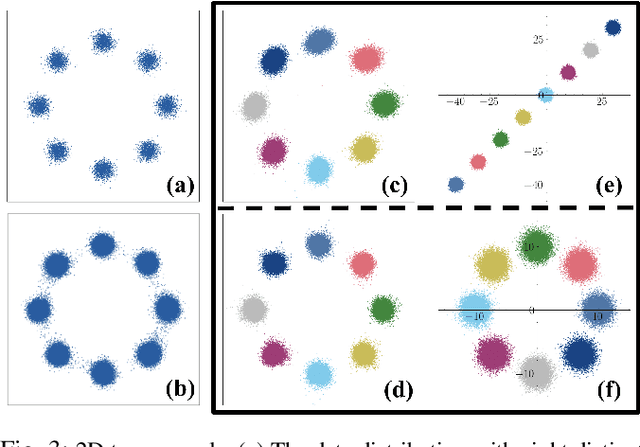
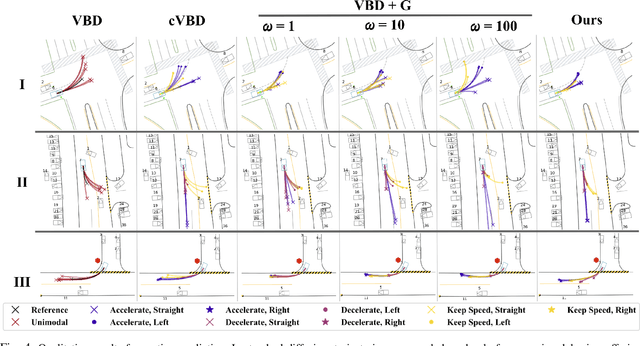
Abstract:Diffusion models have recently gained significant attention in robotics due to their ability to generate multi-modal distributions of system states and behaviors. However, a key challenge remains: ensuring precise control over the generated outcomes without compromising realism. This is crucial for applications such as motion planning or trajectory forecasting, where adherence to physical constraints and task-specific objectives is essential. We propose a novel framework that enhances controllability in diffusion models by leveraging multi-modal prior distributions and enforcing strong modal coupling. This allows us to initiate the denoising process directly from distinct prior modes that correspond to different possible system behaviors, ensuring sampling to align with the training distribution. We evaluate our approach on motion prediction using the Waymo dataset and multi-task control in Maze2D environments. Experimental results show that our framework outperforms both guidance-based techniques and conditioned models with unimodal priors, achieving superior fidelity, diversity, and controllability, even in the absence of explicit conditioning. Overall, our approach provides a more reliable and scalable solution for controllable motion generation in robotics.
ROS-LLM: A ROS framework for embodied AI with task feedback and structured reasoning
Jun 28, 2024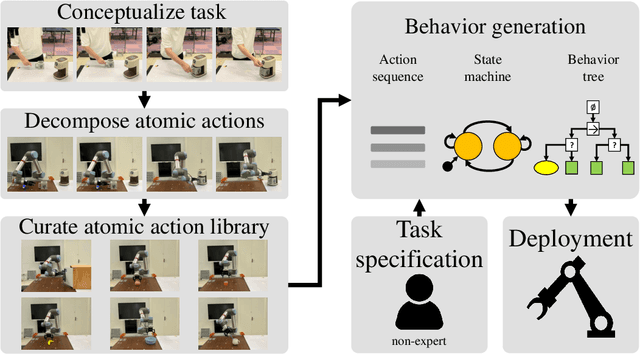
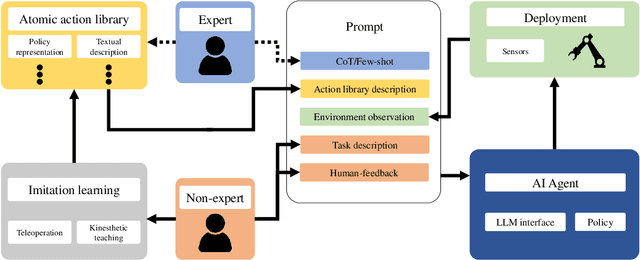
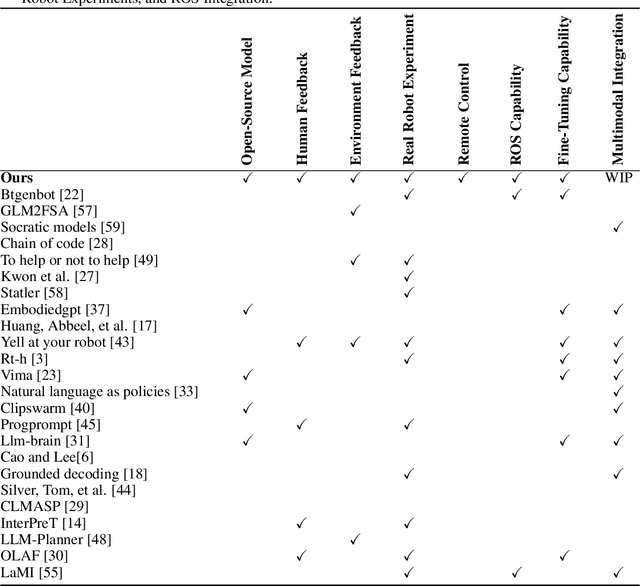
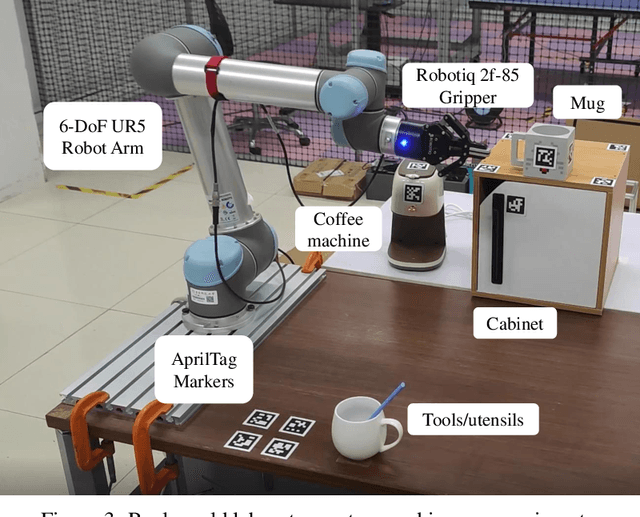
Abstract:We present a framework for intuitive robot programming by non-experts, leveraging natural language prompts and contextual information from the Robot Operating System (ROS). Our system integrates large language models (LLMs), enabling non-experts to articulate task requirements to the system through a chat interface. Key features of the framework include: integration of ROS with an AI agent connected to a plethora of open-source and commercial LLMs, automatic extraction of a behavior from the LLM output and execution of ROS actions/services, support for three behavior modes (sequence, behavior tree, state machine), imitation learning for adding new robot actions to the library of possible actions, and LLM reflection via human and environment feedback. Extensive experiments validate the framework, showcasing robustness, scalability, and versatility in diverse scenarios, including long-horizon tasks, tabletop rearrangements, and remote supervisory control. To facilitate the adoption of our framework and support the reproduction of our results, we have made our code open-source. You can access it at: https://github.com/huawei-noah/HEBO/tree/master/ROSLLM.
Activation-Descent Regularization for Input Optimization of ReLU Networks
Jun 01, 2024



Abstract:We present a new approach for input optimization of ReLU networks that explicitly takes into account the effect of changes in activation patterns. We analyze local optimization steps in both the input space and the space of activation patterns to propose methods with superior local descent properties. To accomplish this, we convert the discrete space of activation patterns into differentiable representations and propose regularization terms that improve each descent step. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed input-optimization methods for improving the state-of-the-art in various areas, such as adversarial learning, generative modeling, and reinforcement learning.
Sequential Neural Barriers for Scalable Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance
Jul 06, 2023



Abstract:There are two major challenges for scaling up robot navigation around dynamic obstacles: the complex interaction dynamics of the obstacles can be hard to model analytically, and the complexity of planning and control grows exponentially in the number of obstacles. Data-driven and learning-based methods are thus particularly valuable in this context. However, data-driven methods are sensitive to distribution drift, making it hard to train and generalize learned models across different obstacle densities. We propose a novel method for compositional learning of Sequential Neural Control Barrier models (SNCBFs) to achieve scalability. Our approach exploits an important observation: the spatial interaction patterns of multiple dynamic obstacles can be decomposed and predicted through temporal sequences of states for each obstacle. Through decomposition, we can generalize control policies trained only with a small number of obstacles, to environments where the obstacle density can be 100x higher. We demonstrate the benefits of the proposed methods in improving dynamic collision avoidance in comparison with existing methods including potential fields, end-to-end reinforcement learning, and model-predictive control. We also perform hardware experiments and show the practical effectiveness of the approach in the supplementary video.
Learning Control Admissibility Models with Graph Neural Networks for Multi-Agent Navigation
Oct 17, 2022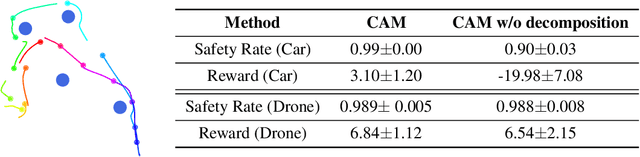
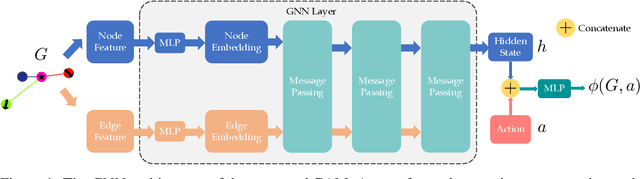
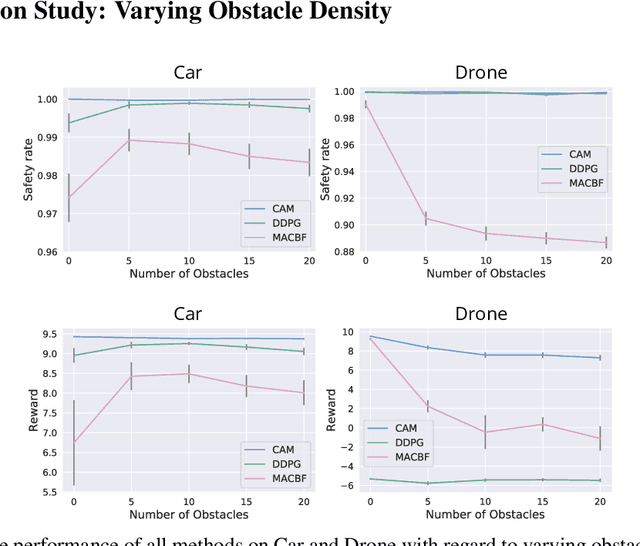
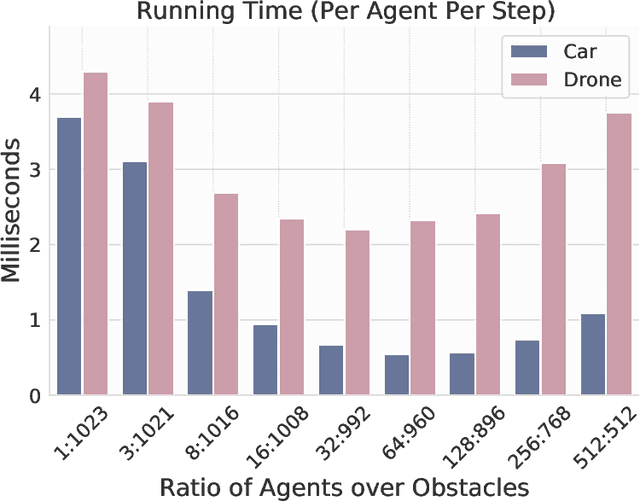
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning in continuous domains focuses on learning control policies that map states to distributions over actions that ideally concentrate on the optimal choices in each step. In multi-agent navigation problems, the optimal actions depend heavily on the agents' density. Their interaction patterns grow exponentially with respect to such density, making it hard for learning-based methods to generalize. We propose to switch the learning objectives from predicting the optimal actions to predicting sets of admissible actions, which we call control admissibility models (CAMs), such that they can be easily composed and used for online inference for an arbitrary number of agents. We design CAMs using graph neural networks and develop training methods that optimize the CAMs in the standard model-free setting, with the additional benefit of eliminating the need for reward engineering typically required to balance collision avoidance and goal-reaching requirements. We evaluate the proposed approach in multi-agent navigation environments. We show that the CAM models can be trained in environments with only a few agents and be easily composed for deployment in dense environments with hundreds of agents, achieving better performance than state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge