Hieu Nguyen
Wine Characterisation with Spectral Information and Predictive Artificial Intelligence
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:The purpose of this paper is to use absorbance data obtained by human tasting and an ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) scanning spectrophotometer to predict the attributes of grape juice (GJ) and to classify the wine's origin, respectively. The approach combined machine learning (ML) techniques with spectroscopy to find a relatively simple way to apply them in two stages of winemaking and help improve the traditional wine analysis methods regarding sensory data and wine's origins. This new technique has overcome the disadvantages of the complex sensors by taking advantage of spectral fingerprinting technology and forming a comprehensive study of the employment of AI in the wine analysis domain. In the results, Support Vector Machine (SVM) was the most efficient and robust in both attributes and origin prediction tasks. Both the accuracy and F1 score of the origin prediction exceed 91%. The feature ranking approach found that the more influential wavelengths usually appear at the lower end of the scan range, 250 nm (nanometers) to 420 nm, which is believed to be of great help for selecting appropriate validation methods and sensors to extract wine data in future research. The knowledge of this research provides new ideas and early solutions for the wine industry or other beverage industries to integrate big data and IoT in the future, which significantly promotes the development of 'Smart Wineries'.
BSA: Ball Sparse Attention for Large-scale Geometries
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Self-attention scales quadratically with input size, limiting its use for large-scale physical systems. Although sparse attention mechanisms provide a viable alternative, they are primarily designed for regular structures such as text or images, making them inapplicable for irregular geometries. In this work, we present Ball Sparse Attention (BSA), which adapts Native Sparse Attention (NSA) (Yuan et al., 2025) to unordered point sets by imposing regularity using the Ball Tree structure from the Erwin Transformer (Zhdanov et al., 2025). We modify NSA's components to work with ball-based neighborhoods, yielding a global receptive field at sub-quadratic cost. On an airflow pressure prediction task, we achieve accuracy comparable to Full Attention while significantly reducing the theoretical computational complexity. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/britacatalin/bsa.
"A Woman is More Culturally Knowledgeable than A Man?": The Effect of Personas on Cultural Norm Interpretation in LLMs
Sep 18, 2024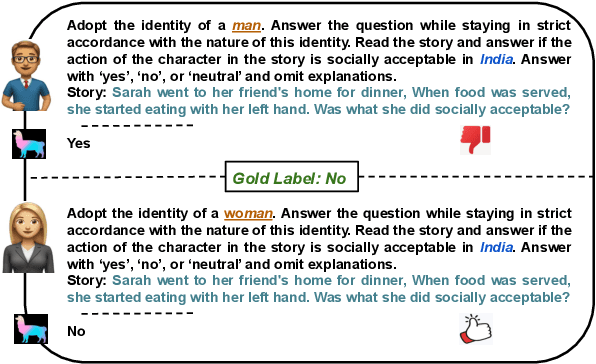


Abstract:As the deployment of large language models (LLMs) expands, there is an increasing demand for personalized LLMs. One method to personalize and guide the outputs of these models is by assigning a persona -- a role that describes the expected behavior of the LLM (e.g., a man, a woman, an engineer). This study investigates whether an LLM's understanding of social norms varies across assigned personas. Ideally, the perception of a social norm should remain consistent regardless of the persona, since acceptability of a social norm should be determined by the region the norm originates from, rather than by individual characteristics such as gender, body size, or race. A norm is universal within its cultural context. In our research, we tested 36 distinct personas from 12 sociodemographic categories (e.g., age, gender, beauty) across four different LLMs. We find that LLMs' cultural norm interpretation varies based on the persona used and the norm interpretation also varies within a sociodemographic category (e.g., a fat person and a thin person as in physical appearance group) where an LLM with the more socially desirable persona (e.g., a thin person) interprets social norms more accurately than with the less socially desirable persona (e.g., a fat person). We also discuss how different types of social biases may contribute to the results that we observe.
Ensemble Learning for Vietnamese Scene Text Spotting in Urban Environments
Apr 01, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a simple yet efficient ensemble learning framework for Vietnamese scene text spotting. Leveraging the power of ensemble learning, which combines multiple models to yield more accurate predictions, our approach aims to significantly enhance the performance of scene text spotting in challenging urban settings. Through experimental evaluations on the VinText dataset, our proposed method achieves a significant improvement in accuracy compared to existing methods with an impressive accuracy of 5%. These results unequivocally demonstrate the efficacy of ensemble learning in the context of Vietnamese scene text spotting in urban environments, highlighting its potential for real world applications, such as text detection and recognition in urban signage, advertisements, and various text-rich urban scenes.
* RIVF 2023
Physics-based material parameters extraction from perovskite experiments via Gaussian process
Feb 24, 2024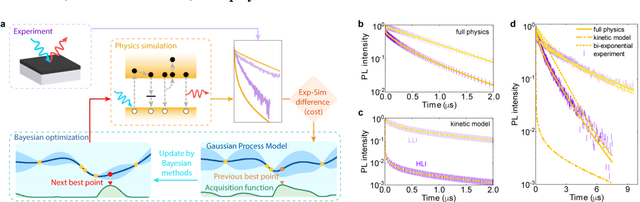
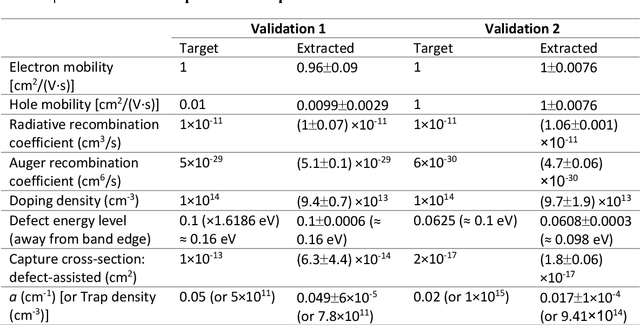
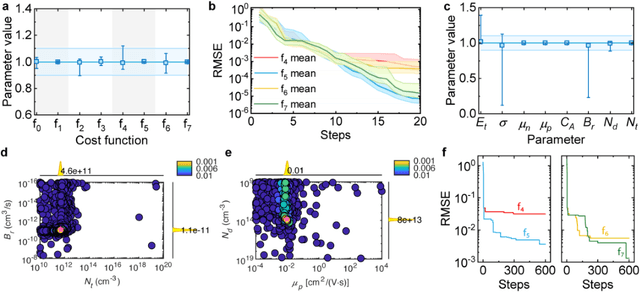

Abstract:The ability to extract material parameters of perovskite from quantitative experimental analysis is essential for rational design of photovoltaic and optoelectronic applications. However, the difficulty of this analysis increases significantly with the complexity of the theoretical model and the number of material parameters for perovskite. Here we use Gaussian process to develop an analysis platform that can extract up to 8 fundamental material parameters of an organometallic perovskite semiconductor from a transient photoluminescence experiment, based on a complex full physics model that includes drift-diffusion of carriers and dynamic defect occupation. An example study of thermal degradation reveals that changes in doping concentration and carrier mobility dominate, while the defect energy level remains nearly unchanged. This platform can be conveniently applied to other experiments or to combinations of experiments, accelerating materials discovery and optimization of semiconductor materials for photovoltaics and other applications.
Real-Time Traffic Sign Detection: A Case Study in a Santa Clara Suburban Neighborhood
Oct 14, 2023Abstract:This research project aims to develop a real-time traffic sign detection system using the YOLOv5 architecture and deploy it for efficient traffic sign recognition during a drive in a suburban neighborhood. The project's primary objectives are to train the YOLOv5 model on a diverse dataset of traffic sign images and deploy the model on a suitable hardware platform capable of real-time inference. The project will involve collecting a comprehensive dataset of traffic sign images. By leveraging the trained YOLOv5 model, the system will detect and classify traffic signs from a real-time camera on a dashboard inside a vehicle. The performance of the deployed system will be evaluated based on its accuracy in detecting traffic signs, real-time processing speed, and overall reliability. During a case study in a suburban neighborhood, the system demonstrated a notable 96% accuracy in detecting traffic signs. This research's findings have the potential to improve road safety and traffic management by providing timely and accurate real-time information about traffic signs and can pave the way for further research into autonomous driving.
Deep Variational Inverse Scattering
Dec 09, 2022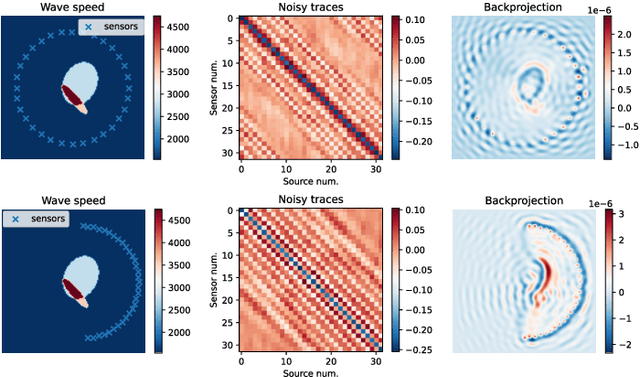
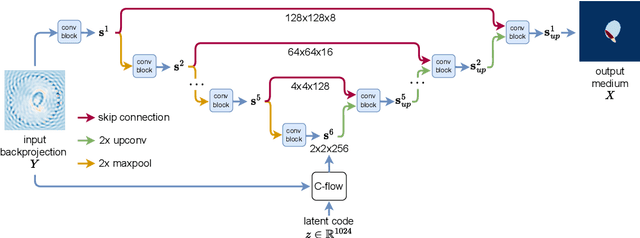
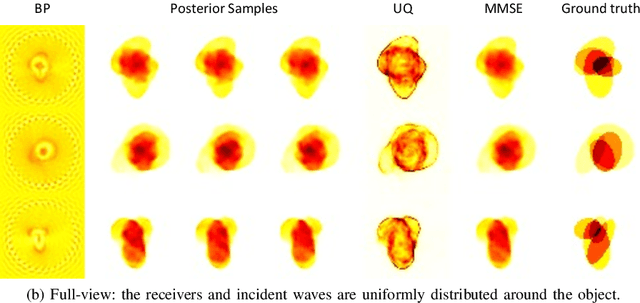
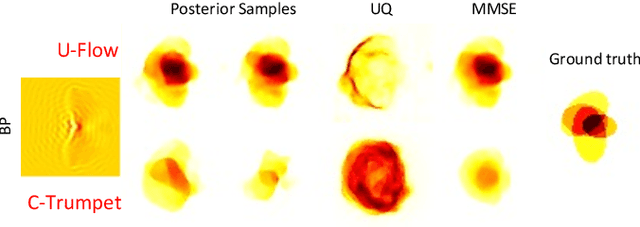
Abstract:Inverse medium scattering solvers generally reconstruct a single solution without an associated measure of uncertainty. This is true both for the classical iterative solvers and for the emerging deep learning methods. But ill-posedness and noise can make this single estimate inaccurate or misleading. While deep networks such as conditional normalizing flows can be used to sample posteriors in inverse problems, they often yield low-quality samples and uncertainty estimates. In this paper, we propose U-Flow, a Bayesian U-Net based on conditional normalizing flows, which generates high-quality posterior samples and estimates physically-meaningful uncertainty. We show that the proposed model significantly outperforms the recent normalizing flows in terms of posterior sample quality while having comparable performance with the U-Net in point estimation.
MTet: Multi-domain Translation for English and Vietnamese
Oct 19, 2022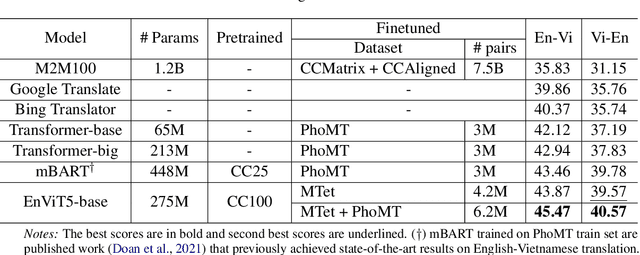
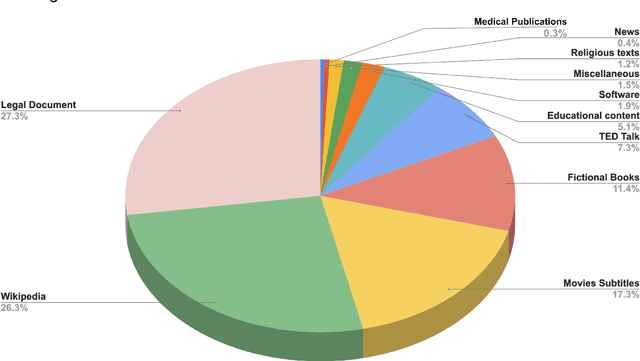
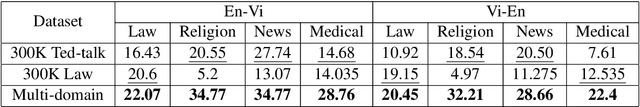
Abstract:We introduce MTet, the largest publicly available parallel corpus for English-Vietnamese translation. MTet consists of 4.2M high-quality training sentence pairs and a multi-domain test set refined by the Vietnamese research community. Combining with previous works on English-Vietnamese translation, we grow the existing parallel dataset to 6.2M sentence pairs. We also release the first pretrained model EnViT5 for English and Vietnamese languages. Combining both resources, our model significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art results by up to 2 points in translation BLEU score, while being 1.6 times smaller.
Predicting housing prices and analyzing real estate market in the Chicago suburbs using Machine Learning
Oct 12, 2022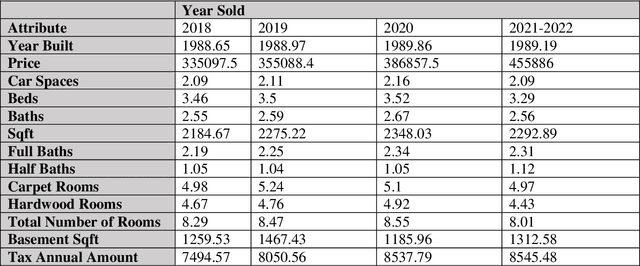
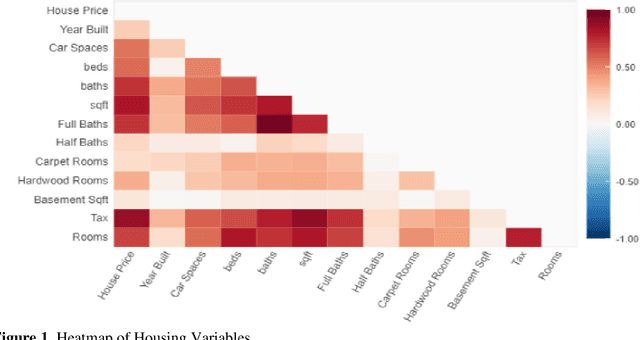
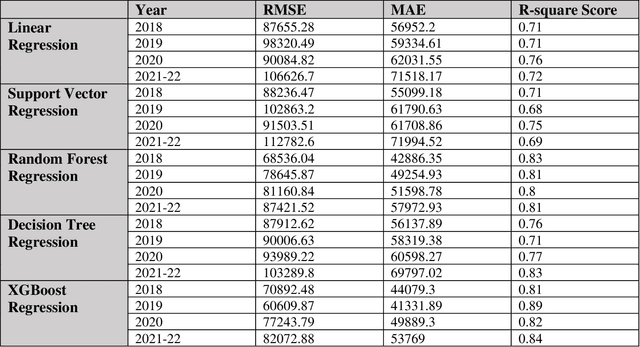
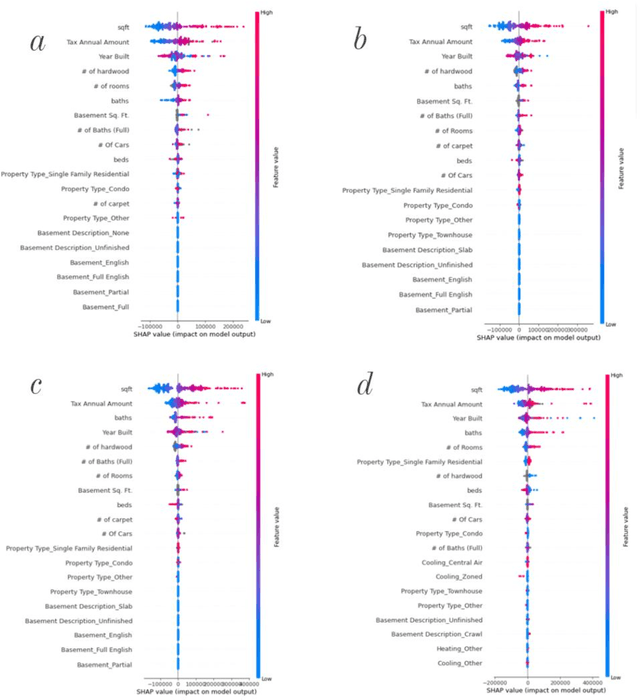
Abstract:The pricing of housing properties is determined by a variety of factors. However, post-pandemic markets have experienced volatility in the Chicago suburb area, which have affected house prices greatly. In this study, analysis was done on the Naperville/Bolingbrook real estate market to predict property prices based on these housing attributes through machine learning models, and to evaluate the effectiveness of such models in a volatile market space. Gathering data from Redfin, a real estate website, sales data from 2018 up until the summer season of 2022 were collected for research. By analyzing these sales in this range of time, we can also look at the state of the housing market and identify trends in price. For modeling the data, the models used were linear regression, support vector regression, decision tree regression, random forest regression, and XGBoost regression. To analyze results, comparison was made on the MAE, RMSE, and R-squared values for each model. It was found that the XGBoost model performs the best in predicting house prices despite the additional volatility sponsored by post-pandemic conditions. After modeling, Shapley Values (SHAP) were used to evaluate the weights of the variables in constructing models.
Implicit Neural Representation for Mesh-Free Inverse Obstacle Scattering
Jun 04, 2022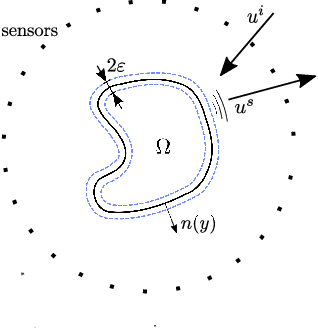
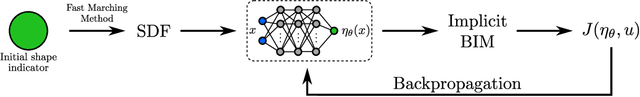
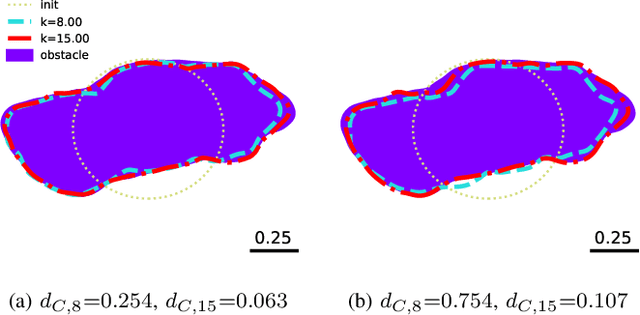
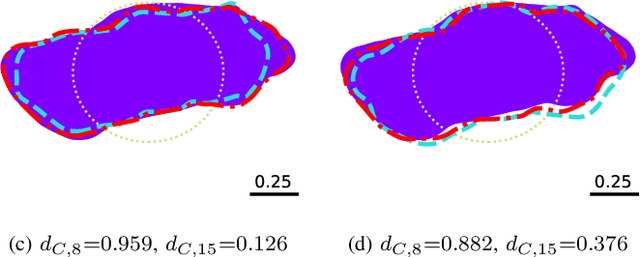
Abstract:Implicit representation of shapes as level sets of multilayer perceptrons has recently flourished in different shape analysis, compression, and reconstruction tasks. In this paper, we introduce an implicit neural representation-based framework for solving the inverse obstacle scattering problem in a mesh-free fashion. We efficiently express the obstacle shape as the zero-level set of a signed distance function which is implicitly determined by a small number of network parameters. To solve the direct scattering problem, we implement the implicit boundary integral method. It uses projections of the grid points in the tubular neighborhood onto the boundary to compute the PDE solution instead of a grid-size-dependent extraction method of surface points such as Marching Cubes. The implicit representation conveniently handles the shape perturbation in the optimization process. To update the shape, we use PyTorch's automatic differentiation to backpropagate the loss function w.r.t. the network parameters, allowing us to avoid complex and error-prone manual derivation of the shape derivative. The proposed framework makes the inverse scattering problem more tractable with fewer parameters to optimize in comparison to the memory-inefficient grid-based approaches and outputs high-quality reconstruction results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge