Hideki Nakayama
Post Persona Alignment for Multi-Session Dialogue Generation
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Multi-session persona-based dialogue generation presents challenges in maintaining long-term consistency and generating diverse, personalized responses. While large language models (LLMs) excel in single-session dialogues, they struggle to preserve persona fidelity and conversational coherence across extended interactions. Existing methods typically retrieve persona information before response generation, which can constrain diversity and result in generic outputs. We propose Post Persona Alignment (PPA), a novel two-stage framework that reverses this process. PPA first generates a general response based solely on dialogue context, then retrieves relevant persona memories using the response as a query, and finally refines the response to align with the speaker's persona. This post-hoc alignment strategy promotes naturalness and diversity while preserving consistency and personalization. Experiments on multi-session LLM-generated dialogue data demonstrate that PPA significantly outperforms prior approaches in consistency, diversity, and persona relevance, offering a more flexible and effective paradigm for long-term personalized dialogue generation.
Exploring and Controlling Diversity in LLM-Agent Conversation
Dec 30, 2024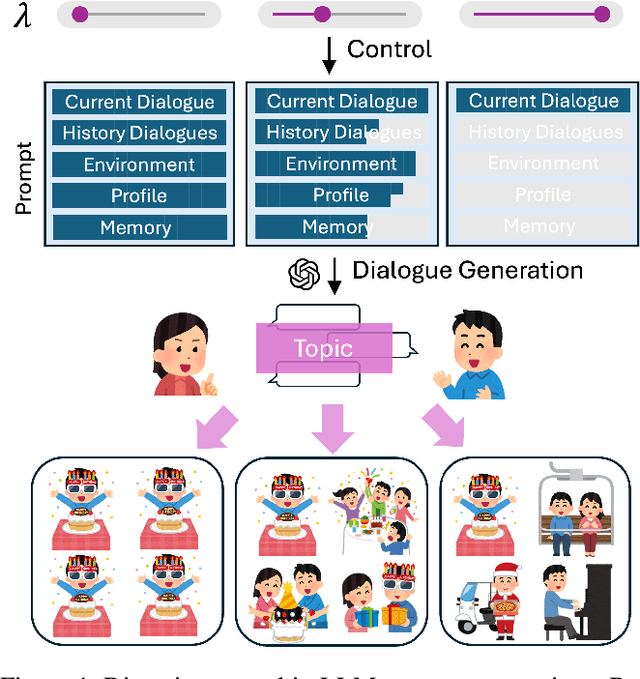
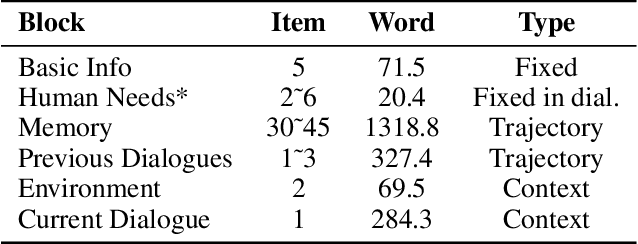
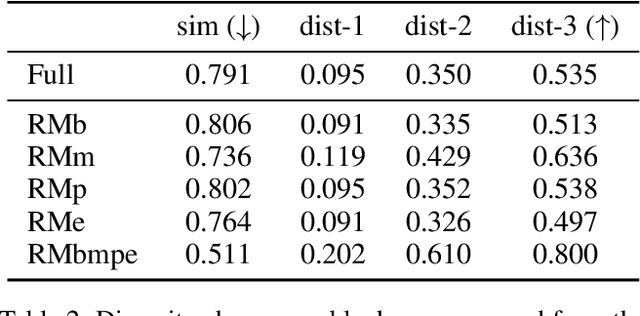
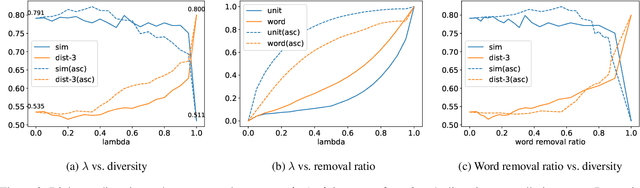
Abstract:Diversity is a critical aspect of multi-agent communication. In this paper, we focus on controlling and exploring diversity in the context of open-domain multi-agent conversations, particularly for world simulation applications. We propose Adaptive Prompt Pruning (APP), a novel method that dynamically adjusts the content of the utterance generation prompt to control diversity using a single parameter, lambda. Through extensive experiments, we show that APP effectively controls the output diversity across models and datasets, with pruning more information leading to more diverse output. We comprehensively analyze the relationship between prompt content and conversational diversity. Our findings reveal that information from all components of the prompt generally constrains the diversity of the output, with the Memory block exerting the most significant influence. APP is compatible with established techniques like temperature sampling and top-p sampling, providing a versatile tool for diversity management. To address the trade-offs of increased diversity, such as inconsistencies with omitted information, we incorporate a post-generation correction step, which effectively balances diversity enhancement with output consistency. Additionally, we examine how prompt structure, including component order and length, impacts diversity. This study addresses key questions surrounding diversity in multi-agent world simulation, offering insights into its control, influencing factors, and associated trade-offs. Our contributions lay the foundation for systematically engineering diversity in LLM-based multi-agent collaborations, advancing their effectiveness in real-world applications.
NEMO: Can Multimodal LLMs Identify Attribute-Modified Objects?
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have made notable advances in visual understanding, yet their abilities to recognize objects modified by specific attributes remain an open question. To address this, we explore MLLMs' reasoning capabilities in object recognition, ranging from commonsense to beyond-commonsense scenarios. We introduce a novel benchmark, NEMO, which comprises 900 images of origiNal fruits and their corresponding attributE-MOdified ones; along with a set of 2,700 questions including open-, multiple-choice-, unsolvable types. We assess 26 recent open-sourced and commercial models using our benchmark. The findings highlight pronounced performance gaps in recognizing objects in NEMO and reveal distinct answer preferences across different models. Although stronger vision encoders improve performance, MLLMs still lag behind standalone vision encoders. Interestingly, scaling up the model size does not consistently yield better outcomes, as deeper analysis reveals that larger LLMs can weaken vision encoders during fine-tuning. These insights shed light on critical limitations in current MLLMs and suggest potential pathways toward developing more versatile and resilient multimodal models.
HALL-E: Hierarchical Neural Codec Language Model for Minute-Long Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Oct 06, 2024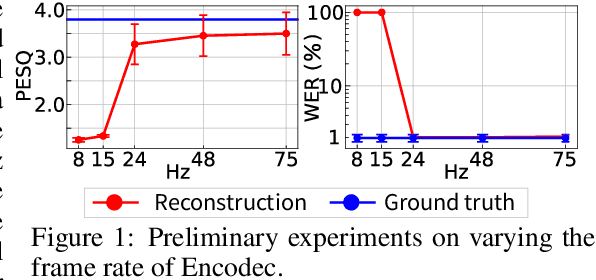
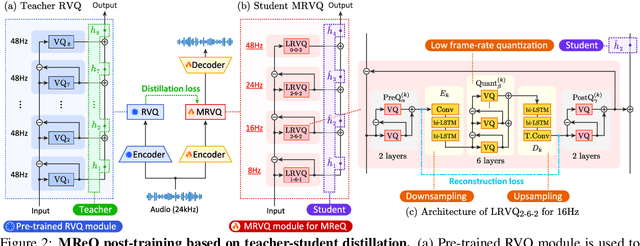
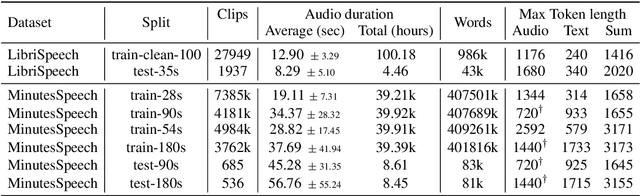
Abstract:Recently, Text-to-speech (TTS) models based on large language models (LLMs) that translate natural language text into sequences of discrete audio tokens have gained great research attention, with advances in neural audio codec (NAC) models using residual vector quantization (RVQ). However, long-form speech synthesis remains a significant challenge due to the high frame rate, which increases the length of audio tokens and makes it difficult for autoregressive language models to generate audio tokens for even a minute of speech. To address this challenge, this paper introduces two novel post-training approaches: 1) Multi-Resolution Requantization (MReQ) and 2) HALL-E. MReQ is a framework to reduce the frame rate of pre-trained NAC models. Specifically, it incorporates multi-resolution residual vector quantization (MRVQ) module that hierarchically reorganizes discrete audio tokens through teacher-student distillation. HALL-E is an LLM-based TTS model designed to predict hierarchical tokens of MReQ. Specifically, it incorporates the technique of using MRVQ sub-modules and continues training from a pre-trained LLM-based TTS model. Furthermore, to promote TTS research, we create MinutesSpeech, a new benchmark dataset consisting of 40k hours of filtered speech data for training and evaluating speech synthesis ranging from 3s up to 180s. In experiments, we demonstrated the effectiveness of our approaches by applying our post-training framework to VALL-E. We achieved the frame rate down to as low as 8 Hz, enabling the stable minitue-long speech synthesis in a single inference step. Audio samples, dataset, codes and pre-trained models are available at https://yutonishimura-v2.github.io/HALL-E_DEMO/.
BrainCodec: Neural fMRI codec for the decoding of cognitive brain states
Oct 06, 2024Abstract:Recently, leveraging big data in deep learning has led to significant performance improvements, as confirmed in applications like mental state decoding using fMRI data. However, fMRI datasets remain relatively small in scale, and the inherent issue of low signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) in fMRI data further exacerbates these challenges. To address this, we apply compression techniques as a preprocessing step for fMRI data. We propose BrainCodec, a novel fMRI codec inspired by the neural audio codec. We evaluated BrainCodec's compression capability in mental state decoding, demonstrating further improvements over previous methods. Furthermore, we analyzed the latent representations obtained through BrainCodec, elucidating the similarities and differences between task and resting state fMRI, highlighting the interpretability of BrainCodec. Additionally, we demonstrated that fMRI reconstructions using BrainCodec can enhance the visibility of brain activity by achieving higher SNR, suggesting its potential as a novel denoising method. Our study shows that BrainCodec not only enhances performance over previous methods but also offers new analytical possibilities for neuroscience. Our codes, dataset, and model weights are available at https://github.com/amano-k-lab/BrainCodec.
Harnessing the Latent Diffusion Model for Training-Free Image Style Transfer
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models have recently shown the ability to generate high-quality images. However, controlling its generation process still poses challenges. The image style transfer task is one of those challenges that transfers the visual attributes of a style image to another content image. Typical obstacle of this task is the requirement of additional training of a pre-trained model. We propose a training-free style transfer algorithm, Style Tracking Reverse Diffusion Process (STRDP) for a pretrained Latent Diffusion Model (LDM). Our algorithm employs Adaptive Instance Normalization (AdaIN) function in a distinct manner during the reverse diffusion process of an LDM while tracking the encoding history of the style image. This algorithm enables style transfer in the latent space of LDM for reduced computational cost, and provides compatibility for various LDM models. Through a series of experiments and a user study, we show that our method can quickly transfer the style of an image without additional training. The speed, compatibility, and training-free aspect of our algorithm facilitates agile experiments with combinations of styles and LDMs for extensive application.
Cohesive Conversations: Enhancing Authenticity in Multi-Agent Simulated Dialogues
Jul 13, 2024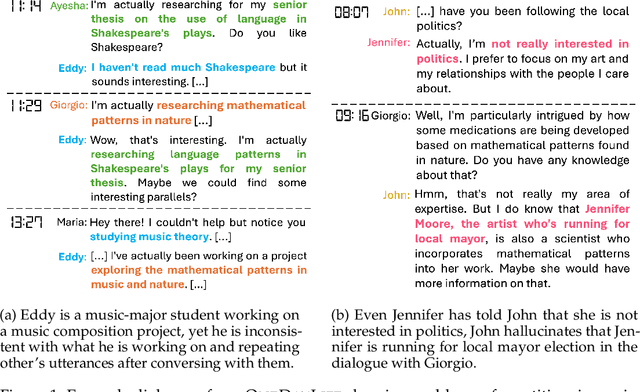
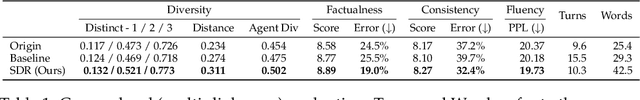
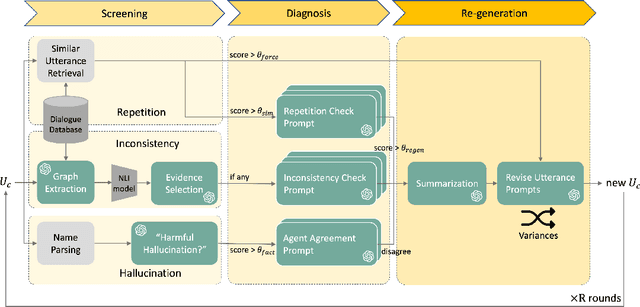
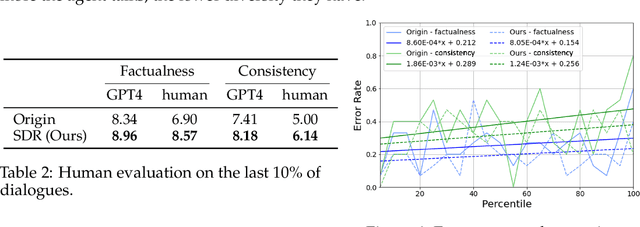
Abstract:This paper investigates the quality of multi-agent dialogues in simulations powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), focusing on a case study from Park et al. (2023), where 25 agents engage in day-long simulations of life, showcasing complex behaviors and interactions. Analyzing dialogues and memory over multiple sessions revealed significant issues such as repetition, inconsistency, and hallucination, exacerbated by the propagation of erroneous information. To combat these challenges, we propose a novel Screening, Diagnosis, and Regeneration (SDR) framework that detects and corrects utterance errors through a comprehensive process involving immediate issue identification, evidence gathering from past dialogues, and LLM analysis for utterance revision. The effectiveness of the SDR framework is validated through GPT-4 assessments and human evaluations, demonstrating marked improvements in dialogue consistency, diversity, and the reduction of false information. This work presents a pioneering approach to enhancing dialogue quality in multi-agent simulations, establishing a new standard for future research in the field.
Enhanced Data Transfer Cooperating with Artificial Triplets for Scene Graph Generation
Jun 27, 2024Abstract:This work focuses on training dataset enhancement of informative relational triplets for Scene Graph Generation (SGG). Due to the lack of effective supervision, the current SGG model predictions perform poorly for informative relational triplets with inadequate training samples. Therefore, we propose two novel training dataset enhancement modules: Feature Space Triplet Augmentation (FSTA) and Soft Transfer. FSTA leverages a feature generator trained to generate representations of an object in relational triplets. The biased prediction based sampling in FSTA efficiently augments artificial triplets focusing on the challenging ones. In addition, we introduce Soft Transfer, which assigns soft predicate labels to general relational triplets to make more supervisions for informative predicate classes effectively. Experimental results show that integrating FSTA and Soft Transfer achieve high levels of both Recall and mean Recall in Visual Genome dataset. The mean of Recall and mean Recall is the highest among all the existing model-agnostic methods.
A Better LLM Evaluator for Text Generation: The Impact of Prompt Output Sequencing and Optimization
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:This research investigates prompt designs of evaluating generated texts using large language models (LLMs). While LLMs are increasingly used for scoring various inputs, creating effective prompts for open-ended text evaluation remains challenging due to model sensitivity and subjectivity in evaluation of text generation. Our study experimented with different prompt structures, altering the sequence of output instructions and including explanatory reasons. We found that the order of presenting reasons and scores significantly influences LLMs' scoring, with a different level of rule understanding in the prompt. An additional optimization may enhance scoring alignment if sufficient data is available. This insight is crucial for improving the accuracy and consistency of LLM-based evaluations.
LLM as a Scorer: The Impact of Output Order on Dialogue Evaluation
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:This research investigates the effect of prompt design on dialogue evaluation using large language models (LLMs). While LLMs are increasingly used for scoring various inputs, creating effective prompts for dialogue evaluation remains challenging due to model sensitivity and subjectivity in dialogue assessments. Our study experimented with different prompt structures, altering the sequence of output instructions and including explanatory reasons. We found that the order of presenting reasons and scores significantly influences LLMs' scoring, with a "reason-first" approach yielding more comprehensive evaluations. This insight is crucial for enhancing the accuracy and consistency of LLM-based evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge