Yuto Nishimura
HALL-E: Hierarchical Neural Codec Language Model for Minute-Long Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Oct 06, 2024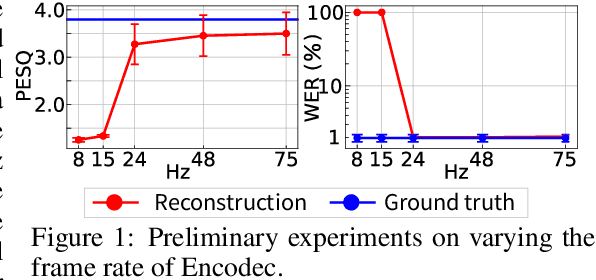
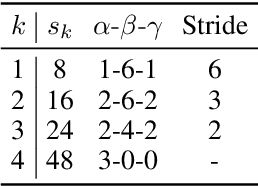
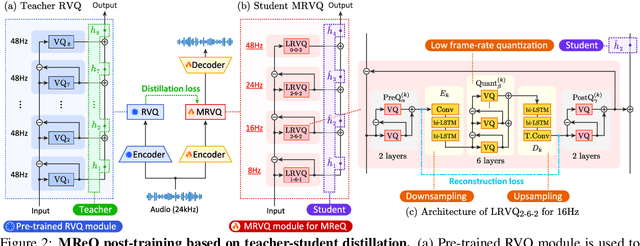
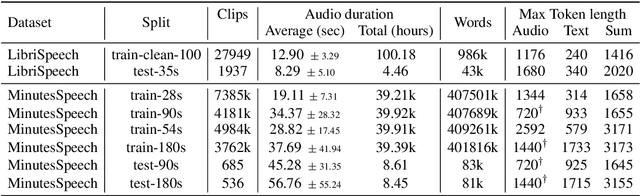
Abstract:Recently, Text-to-speech (TTS) models based on large language models (LLMs) that translate natural language text into sequences of discrete audio tokens have gained great research attention, with advances in neural audio codec (NAC) models using residual vector quantization (RVQ). However, long-form speech synthesis remains a significant challenge due to the high frame rate, which increases the length of audio tokens and makes it difficult for autoregressive language models to generate audio tokens for even a minute of speech. To address this challenge, this paper introduces two novel post-training approaches: 1) Multi-Resolution Requantization (MReQ) and 2) HALL-E. MReQ is a framework to reduce the frame rate of pre-trained NAC models. Specifically, it incorporates multi-resolution residual vector quantization (MRVQ) module that hierarchically reorganizes discrete audio tokens through teacher-student distillation. HALL-E is an LLM-based TTS model designed to predict hierarchical tokens of MReQ. Specifically, it incorporates the technique of using MRVQ sub-modules and continues training from a pre-trained LLM-based TTS model. Furthermore, to promote TTS research, we create MinutesSpeech, a new benchmark dataset consisting of 40k hours of filtered speech data for training and evaluating speech synthesis ranging from 3s up to 180s. In experiments, we demonstrated the effectiveness of our approaches by applying our post-training framework to VALL-E. We achieved the frame rate down to as low as 8 Hz, enabling the stable minitue-long speech synthesis in a single inference step. Audio samples, dataset, codes and pre-trained models are available at https://yutonishimura-v2.github.io/HALL-E_DEMO/.
BrainCodec: Neural fMRI codec for the decoding of cognitive brain states
Oct 06, 2024Abstract:Recently, leveraging big data in deep learning has led to significant performance improvements, as confirmed in applications like mental state decoding using fMRI data. However, fMRI datasets remain relatively small in scale, and the inherent issue of low signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) in fMRI data further exacerbates these challenges. To address this, we apply compression techniques as a preprocessing step for fMRI data. We propose BrainCodec, a novel fMRI codec inspired by the neural audio codec. We evaluated BrainCodec's compression capability in mental state decoding, demonstrating further improvements over previous methods. Furthermore, we analyzed the latent representations obtained through BrainCodec, elucidating the similarities and differences between task and resting state fMRI, highlighting the interpretability of BrainCodec. Additionally, we demonstrated that fMRI reconstructions using BrainCodec can enhance the visibility of brain activity by achieving higher SNR, suggesting its potential as a novel denoising method. Our study shows that BrainCodec not only enhances performance over previous methods but also offers new analytical possibilities for neuroscience. Our codes, dataset, and model weights are available at https://github.com/amano-k-lab/BrainCodec.
Acoustic Modeling for End-to-End Empathetic Dialogue Speech Synthesis Using Linguistic and Prosodic Contexts of Dialogue History
Jun 16, 2022



Abstract:We propose an end-to-end empathetic dialogue speech synthesis (DSS) model that considers both the linguistic and prosodic contexts of dialogue history. Empathy is the active attempt by humans to get inside the interlocutor in dialogue, and empathetic DSS is a technology to implement this act in spoken dialogue systems. Our model is conditioned by the history of linguistic and prosody features for predicting appropriate dialogue context. As such, it can be regarded as an extension of the conventional linguistic-feature-based dialogue history modeling. To train the empathetic DSS model effectively, we investigate 1) a self-supervised learning model pretrained with large speech corpora, 2) a style-guided training using a prosody embedding of the current utterance to be predicted by the dialogue context embedding, 3) a cross-modal attention to combine text and speech modalities, and 4) a sentence-wise embedding to achieve fine-grained prosody modeling rather than utterance-wise modeling. The evaluation results demonstrate that 1) simply considering prosodic contexts of the dialogue history does not improve the quality of speech in empathetic DSS and 2) introducing style-guided training and sentence-wise embedding modeling achieves higher speech quality than that by the conventional method.
STUDIES: Corpus of Japanese Empathetic Dialogue Speech Towards Friendly Voice Agent
Mar 28, 2022



Abstract:We present STUDIES, a new speech corpus for developing a voice agent that can speak in a friendly manner. Humans naturally control their speech prosody to empathize with each other. By incorporating this "empathetic dialogue" behavior into a spoken dialogue system, we can develop a voice agent that can respond to a user more naturally. We designed the STUDIES corpus to include a speaker who speaks with empathy for the interlocutor's emotion explicitly. We describe our methodology to construct an empathetic dialogue speech corpus and report the analysis results of the STUDIES corpus. We conducted a text-to-speech experiment to initially investigate how we can develop more natural voice agent that can tune its speaking style corresponding to the interlocutor's emotion. The results show that the use of interlocutor's emotion label and conversational context embedding can produce speech with the same degree of naturalness as that synthesized by using the agent's emotion label. Our project page of the STUDIES corpus is http://sython.org/Corpus/STUDIES.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge