Hengrong Du
Optimal Stochastic Trace Estimation in Generative Modeling
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Hutchinson estimators are widely employed in training divergence-based likelihoods for diffusion models to ensure optimal transport (OT) properties. However, this estimator often suffers from high variance and scalability concerns. To address these challenges, we investigate Hutch++, an optimal stochastic trace estimator for generative models, designed to minimize training variance while maintaining transport optimality. Hutch++ is particularly effective for handling ill-conditioned matrices with large condition numbers, which commonly arise when high-dimensional data exhibits a low-dimensional structure. To mitigate the need for frequent and costly QR decompositions, we propose practical schemes that balance frequency and accuracy, backed by theoretical guarantees. Our analysis demonstrates that Hutch++ leads to generations of higher quality. Furthermore, this method exhibits effective variance reduction in various applications, including simulations, conditional time series forecasts, and image generation.
Non-Reversible Langevin Algorithms for Constrained Sampling
Jan 20, 2025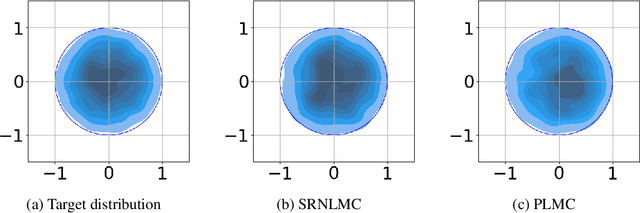
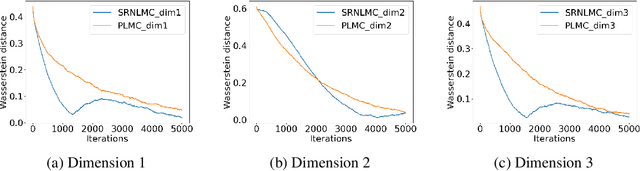
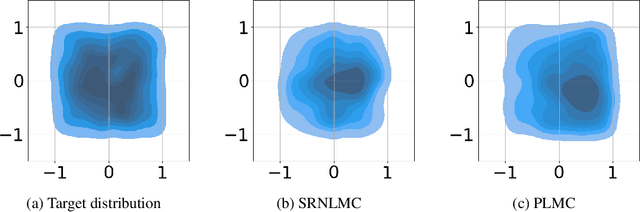
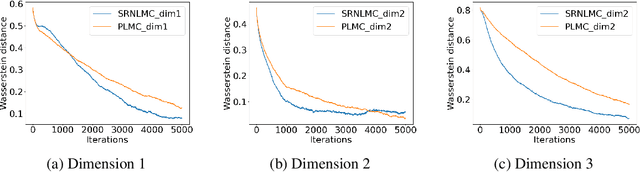
Abstract:We consider the constrained sampling problem where the goal is to sample from a target distribution on a constrained domain. We propose skew-reflected non-reversible Langevin dynamics (SRNLD), a continuous-time stochastic differential equation with skew-reflected boundary. We obtain non-asymptotic convergence rate of SRNLD to the target distribution in both total variation and 1-Wasserstein distances. By breaking reversibility, we show that the convergence is faster than the special case of the reversible dynamics. Based on the discretization of SRNLD, we propose skew-reflected non-reversible Langevin Monte Carlo (SRNLMC), and obtain non-asymptotic discretization error from SRNLD, and convergence guarantees to the target distribution in 1-Wasserstein distance. We show better performance guarantees than the projected Langevin Monte Carlo in the literature that is based on the reversible dynamics. Numerical experiments are provided for both synthetic and real datasets to show efficiency of the proposed algorithms.
Linear Partial Gromov-Wasserstein Embedding
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:The Gromov Wasserstein (GW) problem, a variant of the classical optimal transport (OT) problem, has attracted growing interest in the machine learning and data science communities due to its ability to quantify similarity between measures in different metric spaces. However, like the classical OT problem, GW imposes an equal mass constraint between measures, which restricts its application in many machine learning tasks. To address this limitation, the partial Gromov-Wasserstein (PGW) problem has been introduced, which relaxes the equal mass constraint, enabling the comparison of general positive Radon measures. Despite this, both GW and PGW face significant computational challenges due to their non-convex nature. To overcome these challenges, we propose the linear partial Gromov-Wasserstein (LPGW) embedding, a linearized embedding technique for the PGW problem. For $K$ different metric measure spaces, the pairwise computation of the PGW distance requires solving the PGW problem $\mathcal{O}(K^2)$ times. In contrast, the proposed linearization technique reduces this to $\mathcal{O}(K)$ times. Similar to the linearization technique for the classical OT problem, we prove that LPGW defines a valid metric for metric measure spaces. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of LPGW in practical applications such as shape retrieval and learning with transport-based embeddings, showing that LPGW preserves the advantages of PGW in partial matching while significantly enhancing computational efficiency.
Constrained Exploration via Reflected Replica Exchange Stochastic Gradient Langevin Dynamics
May 13, 2024



Abstract:Replica exchange stochastic gradient Langevin dynamics (reSGLD) is an effective sampler for non-convex learning in large-scale datasets. However, the simulation may encounter stagnation issues when the high-temperature chain delves too deeply into the distribution tails. To tackle this issue, we propose reflected reSGLD (r2SGLD): an algorithm tailored for constrained non-convex exploration by utilizing reflection steps within a bounded domain. Theoretically, we observe that reducing the diameter of the domain enhances mixing rates, exhibiting a \emph{quadratic} behavior. Empirically, we test its performance through extensive experiments, including identifying dynamical systems with physical constraints, simulations of constrained multi-modal distributions, and image classification tasks. The theoretical and empirical findings highlight the crucial role of constrained exploration in improving the simulation efficiency.
Efficient Solvers for Partial Gromov-Wasserstein
Feb 06, 2024



Abstract:The partial Gromov-Wasserstein (PGW) problem facilitates the comparison of measures with unequal masses residing in potentially distinct metric spaces, thereby enabling unbalanced and partial matching across these spaces. In this paper, we demonstrate that the PGW problem can be transformed into a variant of the Gromov-Wasserstein problem, akin to the conversion of the partial optimal transport problem into an optimal transport problem. This transformation leads to two new solvers, mathematically and computationally equivalent, based on the Frank-Wolfe algorithm, that provide efficient solutions to the PGW problem. We further establish that the PGW problem constitutes a metric for metric measure spaces. Finally, we validate the effectiveness of our proposed solvers in terms of computation time and performance on shape-matching and positive-unlabeled learning problems, comparing them against existing baselines.
Reflected Schrödinger Bridge for Constrained Generative Modeling
Jan 06, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have become the go-to method for large-scale generative models in real-world applications. These applications often involve data distributions confined within bounded domains, typically requiring ad-hoc thresholding techniques for boundary enforcement. Reflected diffusion models (Lou23) aim to enhance generalizability by generating the data distribution through a backward process governed by reflected Brownian motion. However, reflected diffusion models may not easily adapt to diverse domains without the derivation of proper diffeomorphic mappings and do not guarantee optimal transport properties. To overcome these limitations, we introduce the Reflected Schrodinger Bridge algorithm: an entropy-regularized optimal transport approach tailored for generating data within diverse bounded domains. We derive elegant reflected forward-backward stochastic differential equations with Neumann and Robin boundary conditions, extend divergence-based likelihood training to bounded domains, and explore natural connections to entropic optimal transport for the study of approximate linear convergence - a valuable insight for practical training. Our algorithm yields robust generative modeling in diverse domains, and its scalability is demonstrated in real-world constrained generative modeling through standard image benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge