Haiming Gang
UniGen-1.5: Enhancing Image Generation and Editing through Reward Unification in Reinforcement Learning
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:We present UniGen-1.5, a unified multimodal large language model (MLLM) for advanced image understanding, generation and editing. Building upon UniGen, we comprehensively enhance the model architecture and training pipeline to strengthen the image understanding and generation capabilities while unlocking strong image editing ability. Especially, we propose a unified Reinforcement Learning (RL) strategy that improves both image generation and image editing jointly via shared reward models. To further enhance image editing performance, we propose a light Edit Instruction Alignment stage that significantly improves the editing instruction comprehension that is essential for the success of the RL training. Experimental results show that UniGen-1.5 demonstrates competitive understanding and generation performance. Specifically, UniGen-1.5 achieves 0.89 and 4.31 overall scores on GenEval and ImgEdit that surpass the state-of-the-art models such as BAGEL and reaching performance comparable to proprietary models such as GPT-Image-1.
MM-Spatial: Exploring 3D Spatial Understanding in Multimodal LLMs
Mar 17, 2025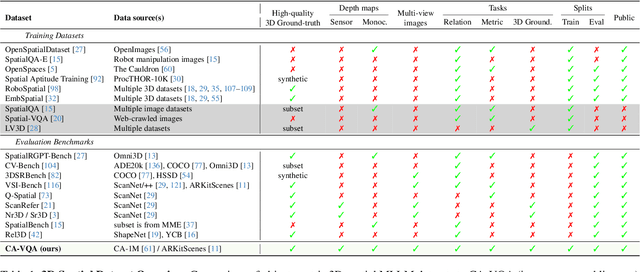

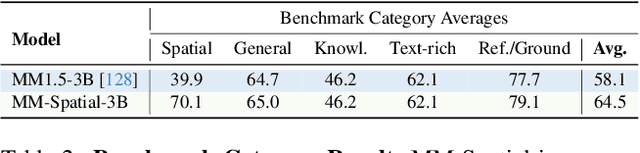

Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) excel at 2D visual understanding but remain limited in their ability to reason about 3D space. In this work, we leverage large-scale high-quality 3D scene data with open-set annotations to introduce 1) a novel supervised fine-tuning dataset and 2) a new evaluation benchmark, focused on indoor scenes. Our Cubify Anything VQA (CA-VQA) data covers diverse spatial tasks including spatial relationship prediction, metric size and distance estimation, and 3D grounding. We show that CA-VQA enables us to train MM-Spatial, a strong generalist MLLM that also achieves state-of-the-art performance on 3D spatial understanding benchmarks, including our own. We show how incorporating metric depth and multi-view inputs (provided in CA-VQA) can further improve 3D understanding, and demonstrate that data alone allows our model to achieve depth perception capabilities comparable to dedicated monocular depth estimation models. We will publish our SFT dataset and benchmark.
SlowFast-LLaVA: A Strong Training-Free Baseline for Video Large Language Models
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:We propose SlowFast-LLaVA (or SF-LLaVA for short), a training-free video large language model (LLM) that can jointly capture the detailed spatial semantics and long-range temporal context without exceeding the token budget of commonly used LLMs. This is realized by using a two-stream SlowFast design of inputs for Video LLMs to aggregate features from sampled video frames in an effective way. Specifically, the Slow pathway extracts features at a low frame rate while keeping as many spatial details as possible (e.g., with 24x24 tokens), and the Fast pathway operates on a high frame rate but uses a larger spatial pooling stride (e.g., downsampling 6x) to focus on the motion cues. As a result, this design allows us to adequately capture both spatial and temporal features that are beneficial for understanding details along the video. Experimental results show that SF-LLaVA outperforms existing training-free methods on a wide range of video tasks. On some benchmarks, it achieves comparable or even better performance compared to state-of-the-art Video LLMs that are fine-tuned on video datasets.
Important Object Identification with Semi-Supervised Learning for Autonomous Driving
Mar 05, 2022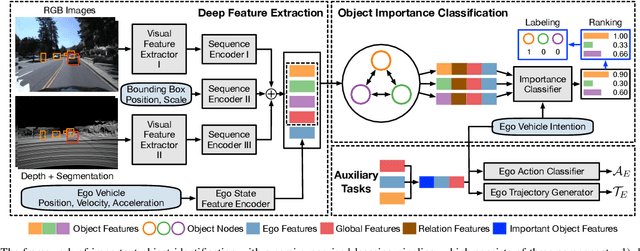
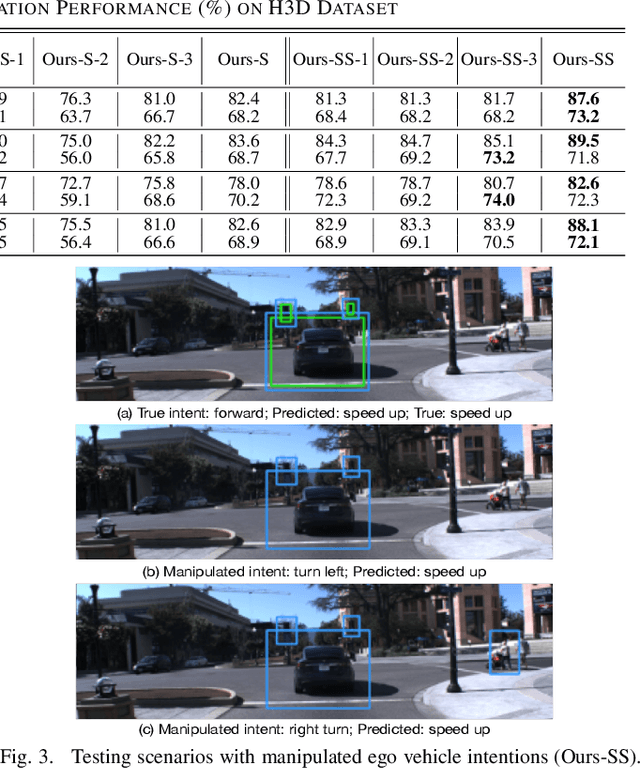
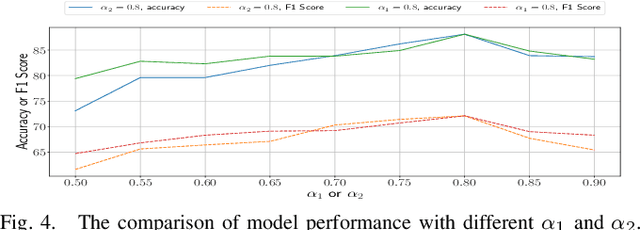
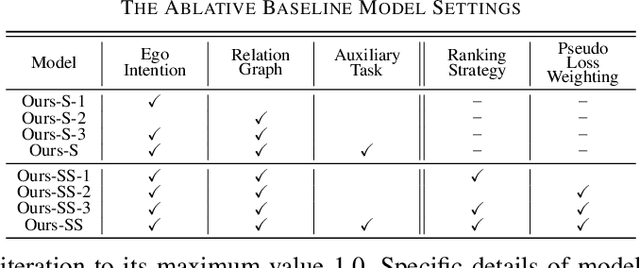
Abstract:Accurate identification of important objects in the scene is a prerequisite for safe and high-quality decision making and motion planning of intelligent agents (e.g., autonomous vehicles) that navigate in complex and dynamic environments. Most existing approaches attempt to employ attention mechanisms to learn importance weights associated with each object indirectly via various tasks (e.g., trajectory prediction), which do not enforce direct supervision on the importance estimation. In contrast, we tackle this task in an explicit way and formulate it as a binary classification ("important" or "unimportant") problem. We propose a novel approach for important object identification in egocentric driving scenarios with relational reasoning on the objects in the scene. Besides, since human annotations are limited and expensive to obtain, we present a semi-supervised learning pipeline to enable the model to learn from unlimited unlabeled data. Moreover, we propose to leverage the auxiliary tasks of ego vehicle behavior prediction to further improve the accuracy of importance estimation. The proposed approach is evaluated on a public egocentric driving dataset (H3D) collected in complex traffic scenarios. A detailed ablative study is conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of each model component and the training strategy. Our approach also outperforms rule-based baselines by a large margin.
Semi-supervised 3D Object Detection via Temporal Graph Neural Networks
Feb 01, 2022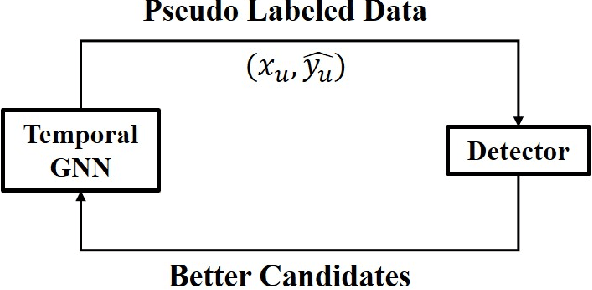

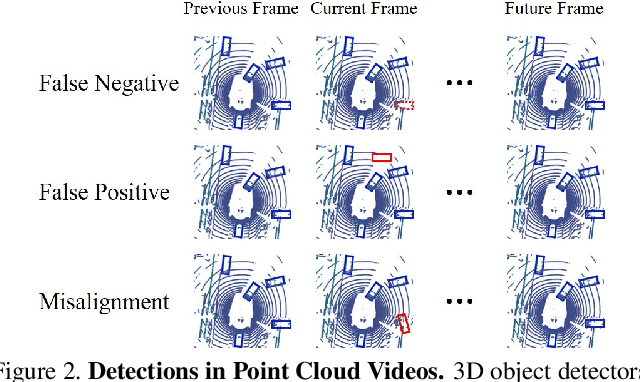
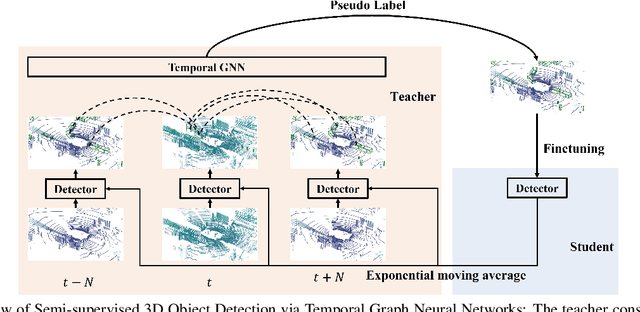
Abstract:3D object detection plays an important role in autonomous driving and other robotics applications. However, these detectors usually require training on large amounts of annotated data that is expensive and time-consuming to collect. Instead, we propose leveraging large amounts of unlabeled point cloud videos by semi-supervised learning of 3D object detectors via temporal graph neural networks. Our insight is that temporal smoothing can create more accurate detection results on unlabeled data, and these smoothed detections can then be used to retrain the detector. We learn to perform this temporal reasoning with a graph neural network, where edges represent the relationship between candidate detections in different time frames. After semi-supervised learning, our method achieves state-of-the-art detection performance on the challenging nuScenes and H3D benchmarks, compared to baselines trained on the same amount of labeled data. Project and code are released at https://www.jianrenw.com/SOD-TGNN/.
LOKI: Long Term and Key Intentions for Trajectory Prediction
Aug 18, 2021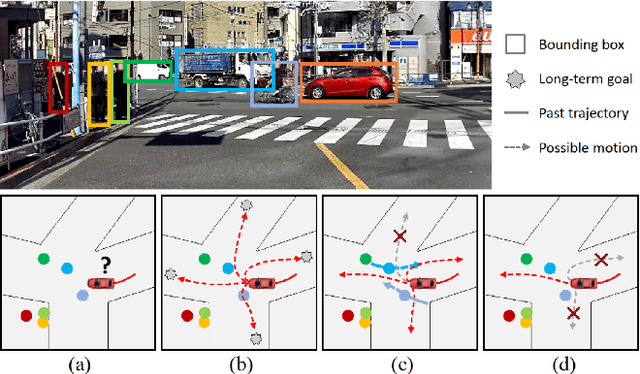
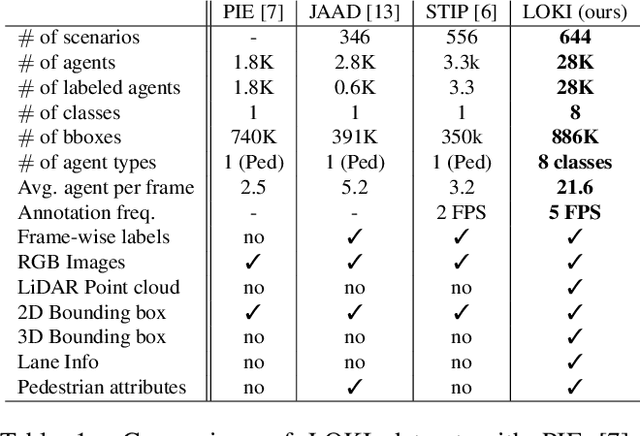
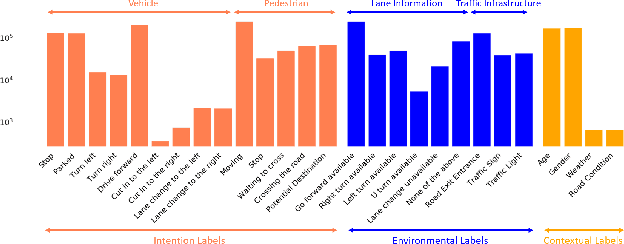
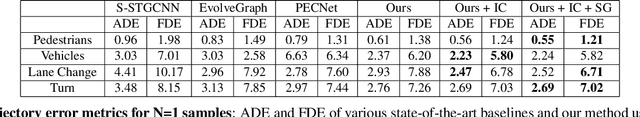
Abstract:Recent advances in trajectory prediction have shown that explicit reasoning about agents' intent is important to accurately forecast their motion. However, the current research activities are not directly applicable to intelligent and safety critical systems. This is mainly because very few public datasets are available, and they only consider pedestrian-specific intents for a short temporal horizon from a restricted egocentric view. To this end, we propose LOKI (LOng term and Key Intentions), a novel large-scale dataset that is designed to tackle joint trajectory and intention prediction for heterogeneous traffic agents (pedestrians and vehicles) in an autonomous driving setting. The LOKI dataset is created to discover several factors that may affect intention, including i) agent's own will, ii) social interactions, iii) environmental constraints, and iv) contextual information. We also propose a model that jointly performs trajectory and intention prediction, showing that recurrently reasoning about intention can assist with trajectory prediction. We show our method outperforms state-of-the-art trajectory prediction methods by upto $27\%$ and also provide a baseline for frame-wise intention estimation.
The H3D Dataset for Full-Surround 3D Multi-Object Detection and Tracking in Crowded Urban Scenes
Mar 04, 2019
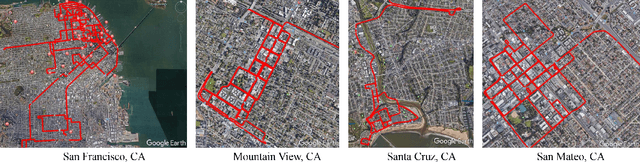
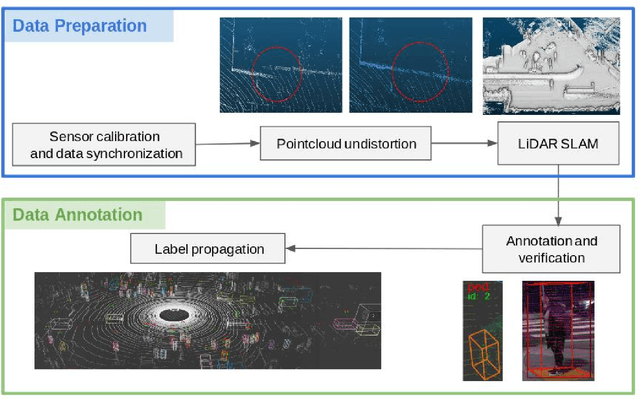
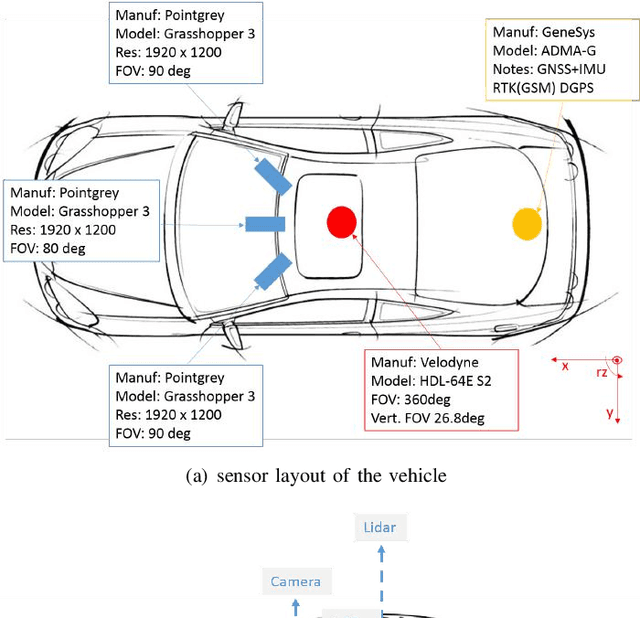
Abstract:3D multi-object detection and tracking are crucial for traffic scene understanding. However, the community pays less attention to these areas due to the lack of a standardized benchmark dataset to advance the field. Moreover, existing datasets (e.g., KITTI) do not provide sufficient data and labels to tackle challenging scenes where highly interactive and occluded traffic participants are present. To address the issues, we present the Honda Research Institute 3D Dataset (H3D), a large-scale full-surround 3D multi-object detection and tracking dataset collected using a 3D LiDAR scanner. H3D comprises of 160 crowded and highly interactive traffic scenes with a total of 1 million labeled instances in 27,721 frames. With unique dataset size, rich annotations, and complex scenes, H3D is gathered to stimulate research on full-surround 3D multi-object detection and tracking. To effectively and efficiently annotate a large-scale 3D point cloud dataset, we propose a labeling methodology to speed up the overall annotation cycle. A standardized benchmark is created to evaluate full-surround 3D multi-object detection and tracking algorithms. 3D object detection and tracking algorithms are trained and tested on H3D. Finally, sources of errors are discussed for the development of future algorithms.
* The dataset is available at https://usa.honda-ri.com/H3D
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge