Guangyu Gao
CoMBO: Conflict Mitigation via Branched Optimization for Class Incremental Segmentation
Apr 05, 2025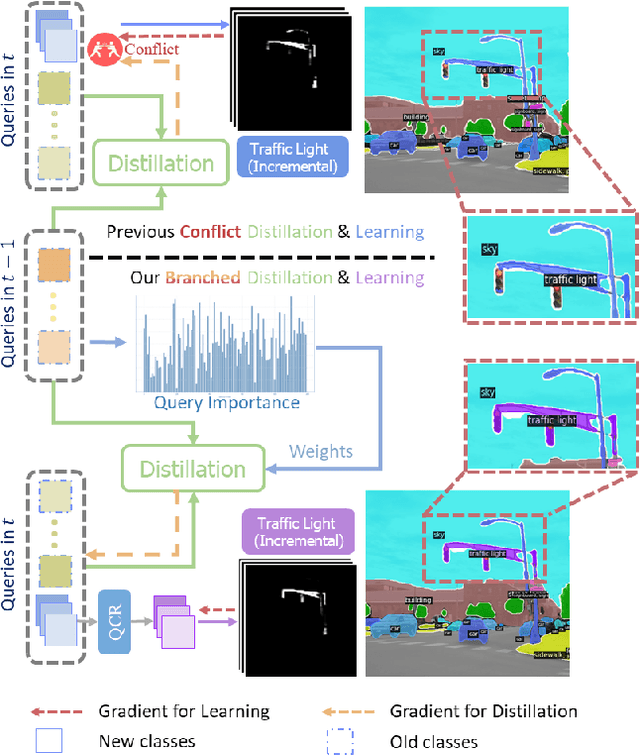
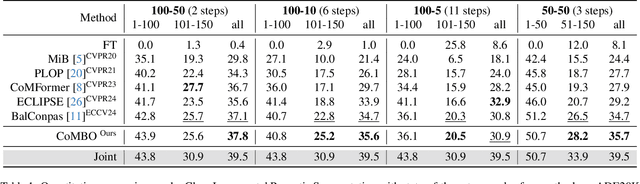
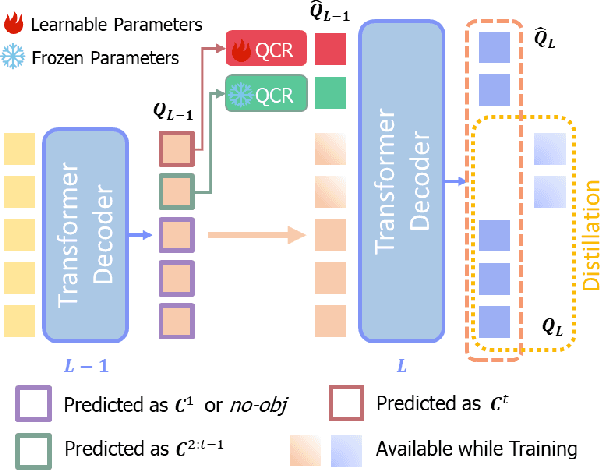
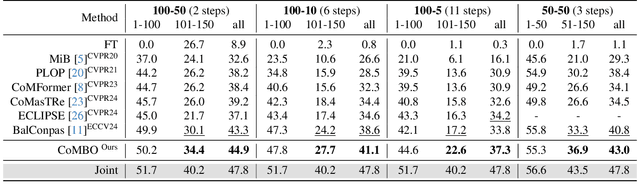
Abstract:Effective Class Incremental Segmentation (CIS) requires simultaneously mitigating catastrophic forgetting and ensuring sufficient plasticity to integrate new classes. The inherent conflict above often leads to a back-and-forth, which turns the objective into finding the balance between the performance of previous~(old) and incremental~(new) classes. To address this conflict, we introduce a novel approach, Conflict Mitigation via Branched Optimization~(CoMBO). Within this approach, we present the Query Conflict Reduction module, designed to explicitly refine queries for new classes through lightweight, class-specific adapters. This module provides an additional branch for the acquisition of new classes while preserving the original queries for distillation. Moreover, we develop two strategies to further mitigate the conflict following the branched structure, \textit{i.e.}, the Half-Learning Half-Distillation~(HDHL) over classification probabilities, and the Importance-Based Knowledge Distillation~(IKD) over query features. HDHL selectively engages in learning for classification probabilities of queries that match the ground truth of new classes, while aligning unmatched ones to the corresponding old probabilities, thus ensuring retention of old knowledge while absorbing new classes via learning negative samples. Meanwhile, IKD assesses the importance of queries based on their matching degree to old classes, prioritizing the distillation of important features and allowing less critical features to evolve. Extensive experiments in Class Incremental Panoptic and Semantic Segmentation settings have demonstrated the superior performance of CoMBO. Project page: https://guangyu-ryan.github.io/CoMBO.
Control Map Distribution using Map Query Bank for Online Map Generation
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Reliable autonomous driving systems require high-definition (HD) map that contains detailed map information for planning and navigation. However, pre-build HD map requires a large cost. Visual-based Online Map Generation (OMG) has become an alternative low-cost solution to build a local HD map. Query-based BEV Transformer has been a base model for this task. This model learns HD map predictions from an initial map queries distribution which is obtained by offline optimization on training set. Besides the quality of BEV feature, the performance of this model also highly relies on the capacity of initial map query distribution. However, this distribution is limited because the limited query number. To make map predictions optimal on each test sample, it is essential to generate a suitable initial distribution for each specific scenario. This paper proposes to decompose the whole HD map distribution into a set of point representations, namely map query bank (MQBank). To build specific map query initial distributions of different scenarios, low-cost standard definition map (SD map) data is introduced as a kind of prior knowledge. Moreover, each layer of map decoder network learns instance-level map query features, which will lose detailed information of each point. However, BEV feature map is a point-level dense feature. It is important to keep point-level information in map queries when interacting with BEV feature map. This can also be solved with map query bank method. Final experiments show a new insight on SD map prior and a new record on OpenLaneV2 benchmark with 40.5%, 45.7% mAP on vehicle lane and pedestrian area.
Bridge the Points: Graph-based Few-shot Segment Anything Semantically
Oct 09, 2024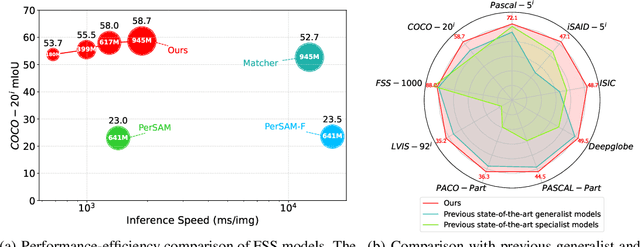
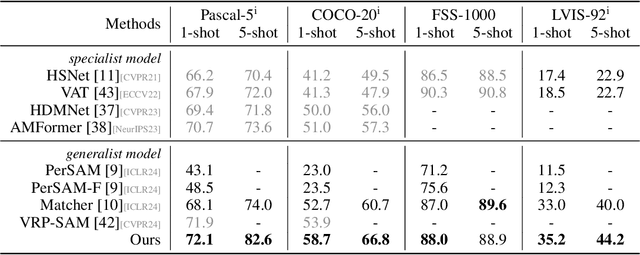
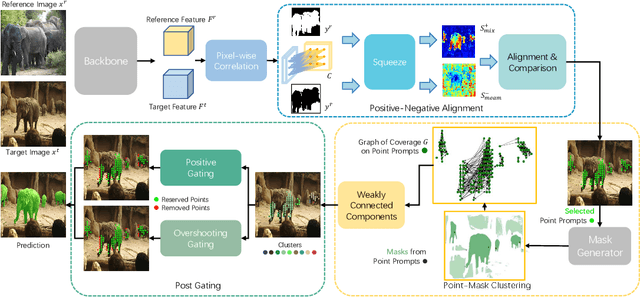
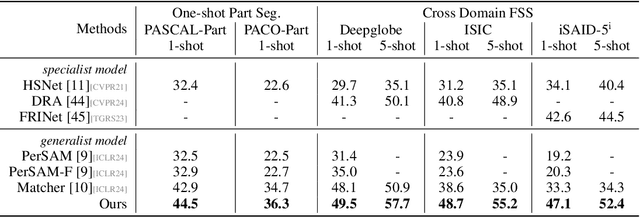
Abstract:The recent advancements in large-scale pre-training techniques have significantly enhanced the capabilities of vision foundation models, notably the Segment Anything Model (SAM), which can generate precise masks based on point and box prompts. Recent studies extend SAM to Few-shot Semantic Segmentation (FSS), focusing on prompt generation for SAM-based automatic semantic segmentation. However, these methods struggle with selecting suitable prompts, require specific hyperparameter settings for different scenarios, and experience prolonged one-shot inference times due to the overuse of SAM, resulting in low efficiency and limited automation ability. To address these issues, we propose a simple yet effective approach based on graph analysis. In particular, a Positive-Negative Alignment module dynamically selects the point prompts for generating masks, especially uncovering the potential of the background context as the negative reference. Another subsequent Point-Mask Clustering module aligns the granularity of masks and selected points as a directed graph, based on mask coverage over points. These points are then aggregated by decomposing the weakly connected components of the directed graph in an efficient manner, constructing distinct natural clusters. Finally, the positive and overshooting gating, benefiting from graph-based granularity alignment, aggregate high-confident masks and filter out the false-positive masks for final prediction, reducing the usage of additional hyperparameters and redundant mask generation. Extensive experimental analysis across standard FSS, One-shot Part Segmentation, and Cross Domain FSS datasets validate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed approach, surpassing state-of-the-art generalist models with a mIoU of 58.7% on COCO-20i and 35.2% on LVIS-92i. The code is available in https://andyzaq.github.io/GF-SAM/.
Background Adaptation with Residual Modeling for Exemplar-Free Class-Incremental Semantic Segmentation
Jul 13, 2024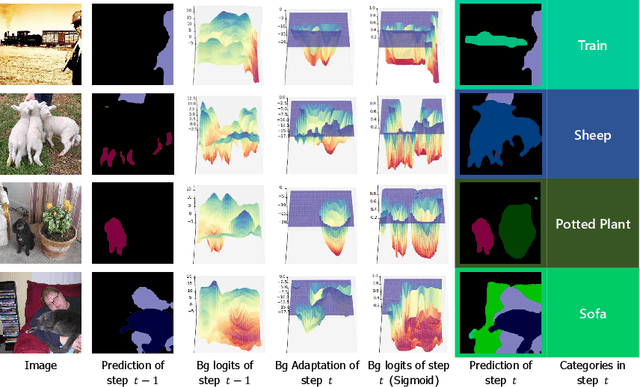
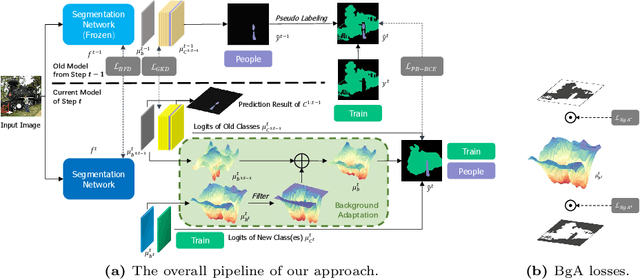
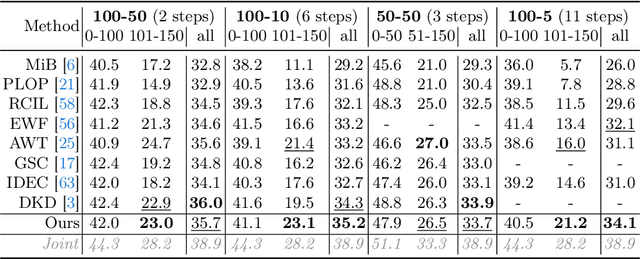
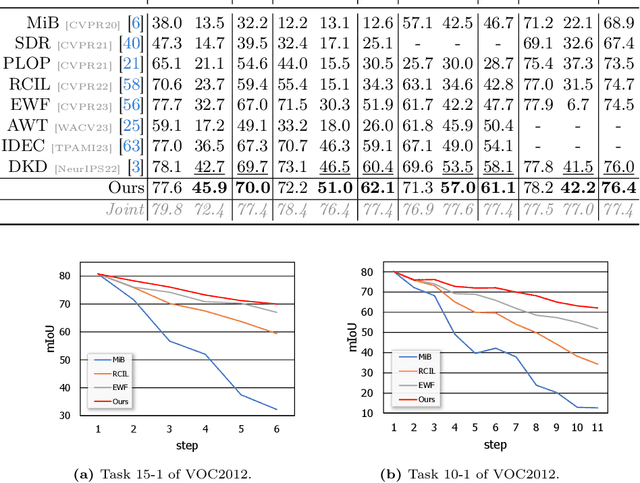
Abstract:Class Incremental Semantic Segmentation~(CISS), within Incremental Learning for semantic segmentation, targets segmenting new categories while reducing the catastrophic forgetting on the old categories.Besides, background shifting, where the background category changes constantly in each step, is a special challenge for CISS. Current methods with a shared background classifier struggle to keep up with these changes, leading to decreased stability in background predictions and reduced accuracy of segmentation. For this special challenge, we designed a novel background adaptation mechanism, which explicitly models the background residual rather than the background itself in each step, and aggregates these residuals to represent the evolving background. Therefore, the background adaptation mechanism ensures the stability of previous background classifiers, while enabling the model to concentrate on the easy-learned residuals from the additional channel, which enhances background discernment for better prediction of novel categories. To precisely optimize the background adaptation mechanism, we propose Pseudo Background Binary Cross-Entropy loss and Background Adaptation losses, which amplify the adaptation effect. Group Knowledge Distillation and Background Feature Distillation strategies are designed to prevent forgetting old categories. Our approach, evaluated across various incremental scenarios on Pascal VOC 2012 and ADE20K datasets, outperforms prior exemplar-free state-of-the-art methods with mIoU of 3.0% in VOC 10-1 and 2.0% in ADE 100-5, notably enhancing the accuracy of new classes while mitigating catastrophic forgetting. Code is available in https://andyzaq.github.io/barmsite/.
CoinSeg: Contrast Inter- and Intra- Class Representations for Incremental Segmentation
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:Class incremental semantic segmentation aims to strike a balance between the model's stability and plasticity by maintaining old knowledge while adapting to new concepts. However, most state-of-the-art methods use the freeze strategy for stability, which compromises the model's plasticity.In contrast, releasing parameter training for plasticity could lead to the best performance for all categories, but this requires discriminative feature representation.Therefore, we prioritize the model's plasticity and propose the Contrast inter- and intra-class representations for Incremental Segmentation (CoinSeg), which pursues discriminative representations for flexible parameter tuning. Inspired by the Gaussian mixture model that samples from a mixture of Gaussian distributions, CoinSeg emphasizes intra-class diversity with multiple contrastive representation centroids. Specifically, we use mask proposals to identify regions with strong objectness that are likely to be diverse instances/centroids of a category. These mask proposals are then used for contrastive representations to reinforce intra-class diversity. Meanwhile, to avoid bias from intra-class diversity, we also apply category-level pseudo-labels to enhance category-level consistency and inter-category diversity. Additionally, CoinSeg ensures the model's stability and alleviates forgetting through a specific flexible tuning strategy. We validate CoinSeg on Pascal VOC 2012 and ADE20K datasets with multiple incremental scenarios and achieve superior results compared to previous state-of-the-art methods, especially in more challenging and realistic long-term scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/zkzhang98/CoinSeg.
Mining Unseen Classes via Regional Objectness: A Simple Baseline for Incremental Segmentation
Nov 15, 2022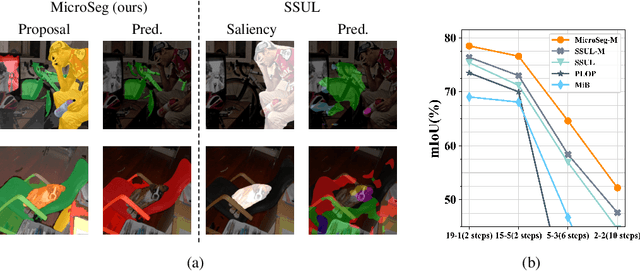
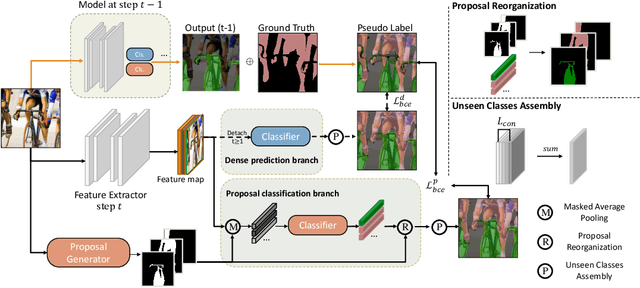
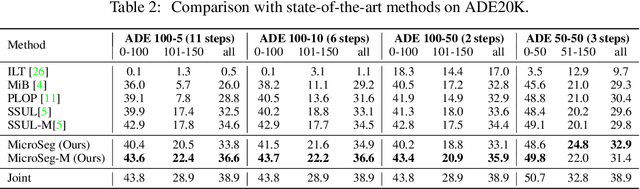
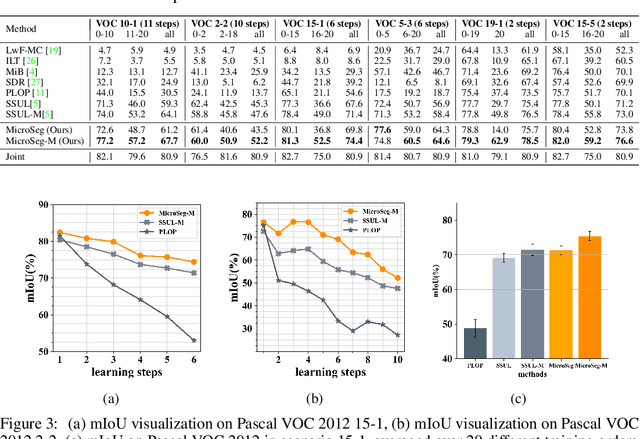
Abstract:Incremental or continual learning has been extensively studied for image classification tasks to alleviate catastrophic forgetting, a phenomenon that earlier learned knowledge is forgotten when learning new concepts. For class incremental semantic segmentation, such a phenomenon often becomes much worse due to the background shift, i.e., some concepts learned at previous stages are assigned to the background class at the current training stage, therefore, significantly reducing the performance of these old concepts. To address this issue, we propose a simple yet effective method in this paper, named Mining unseen Classes via Regional Objectness for Segmentation (MicroSeg). Our MicroSeg is based on the assumption that background regions with strong objectness possibly belong to those concepts in the historical or future stages. Therefore, to avoid forgetting old knowledge at the current training stage, our MicroSeg first splits the given image into hundreds of segment proposals with a proposal generator. Those segment proposals with strong objectness from the background are then clustered and assigned newly-defined labels during the optimization. In this way, the distribution characterizes of old concepts in the feature space could be better perceived, relieving the catastrophic forgetting caused by the background shift accordingly. Extensive experiments on Pascal VOC and ADE20K datasets show competitive results with state-of-the-art, well validating the effectiveness of the proposed MicroSeg.
DTG-Net: Differentiated Teachers Guided Self-Supervised Video Action Recognition
Jun 13, 2020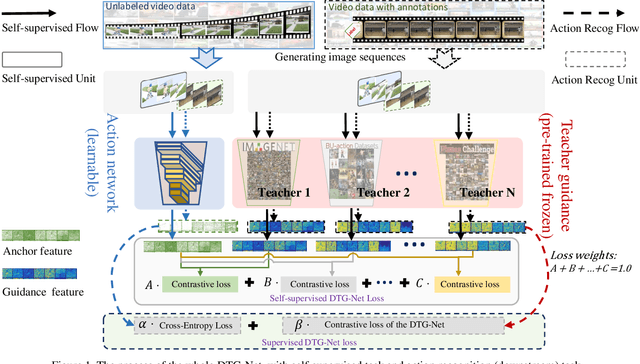
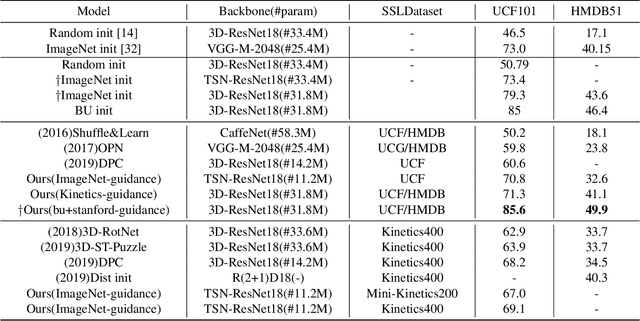
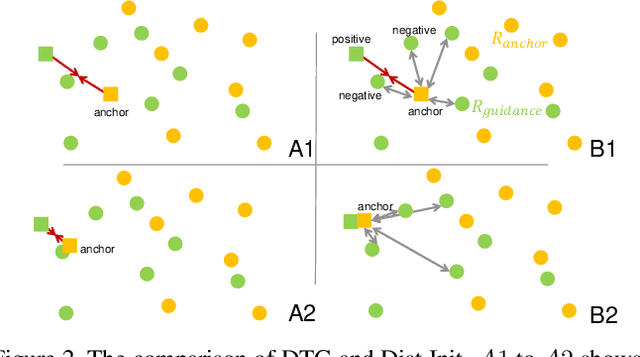
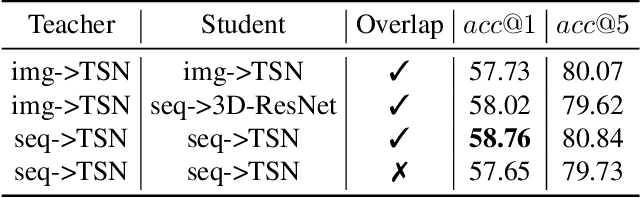
Abstract:State-of-the-art video action recognition models with complex network architecture have archived significant improvements, but these models heavily depend on large-scale well-labeled datasets. To reduce such dependency, we propose a self-supervised teacher-student architecture, i.e., the Differentiated Teachers Guided self-supervised Network (DTG-Net). In DTG-Net, except for reducing labeled data dependency by self-supervised learning (SSL), pre-trained action related models are used as teacher guidance providing prior knowledge to alleviate the demand for a large number of unlabeled videos in SSL. Specifically, leveraging the years of effort in action-related tasks, e.g., image classification, image-based action recognition, the DTG-Net learns the self-supervised video representation under various teacher guidance, i.e., those well-trained models of action-related tasks. Meanwhile, the DTG-Net is optimized in the way of contrastive self-supervised learning. When two image sequences are randomly sampled from the same video or different videos as the positive or negative pairs, respectively, they are then sent to the teacher and student networks for feature embedding. After that, the contrastive feature consistency is defined between features embedding of each pair, i.e., consistent for positive pair and inconsistent for negative pairs. Meanwhile, to reflect various teacher tasks' different guidance, we also explore different weighted guidance on teacher tasks. Finally, the DTG-Net is evaluated in two ways: (i) the self-supervised DTG-Net to pre-train the supervised action recognition models with only unlabeled videos; (ii) the supervised DTG-Net to be jointly trained with the supervised action networks in an end-to-end way. Its performance is better than most pre-training methods but also has excellent competitiveness compared to supervised action recognition methods.
HRDNet: High-resolution Detection Network for Small Objects
Jun 13, 2020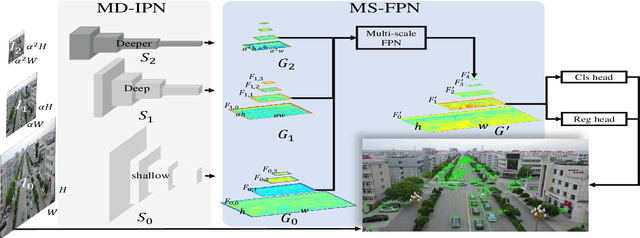
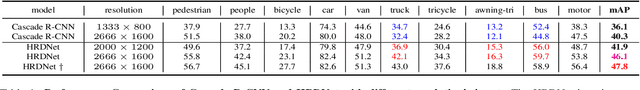
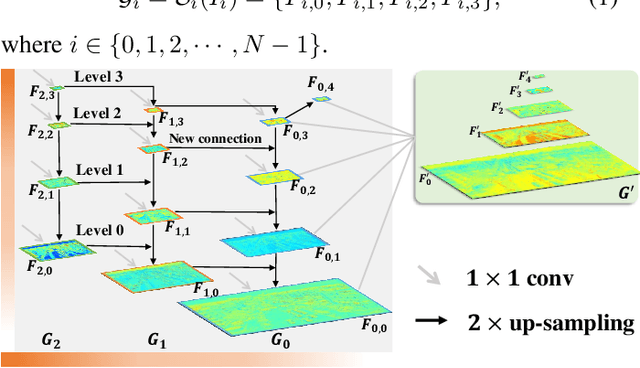
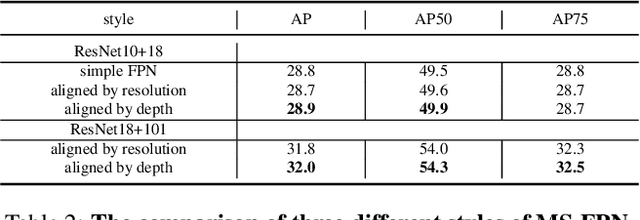
Abstract:Small object detection is challenging because small objects do not contain detailed information and may even disappear in the deep network. Usually, feeding high-resolution images into a network can alleviate this issue. However, simply enlarging the resolution will cause more problems, such as that, it aggravates the large variant of object scale and introduces unbearable computation cost. To keep the benefits of high-resolution images without bringing up new problems, we proposed the High-Resolution Detection Network (HRDNet). HRDNet takes multiple resolution inputs using multi-depth backbones. To fully take advantage of multiple features, we proposed Multi-Depth Image Pyramid Network (MD-IPN) and Multi-Scale Feature Pyramid Network (MS-FPN) in HRDNet. MD-IPN maintains multiple position information using multiple depth backbones. Specifically, high-resolution input will be fed into a shallow network to reserve more positional information and reducing the computational cost while low-resolution input will be fed into a deep network to extract more semantics. By extracting various features from high to low resolutions, the MD-IPN is able to improve the performance of small object detection as well as maintaining the performance of middle and large objects. MS-FPN is proposed to align and fuse multi-scale feature groups generated by MD-IPN to reduce the information imbalance between these multi-scale multi-level features. Extensive experiments and ablation studies are conducted on the standard benchmark dataset MS COCO2017, Pascal VOC2007/2012 and a typical small object dataset, VisDrone 2019. Notably, our proposed HRDNet achieves the state-of-the-art on these datasets and it performs better on small objects.
Visual-Textual Association with Hardest and Semi-Hard Negative Pairs Mining for Person Search
Dec 06, 2019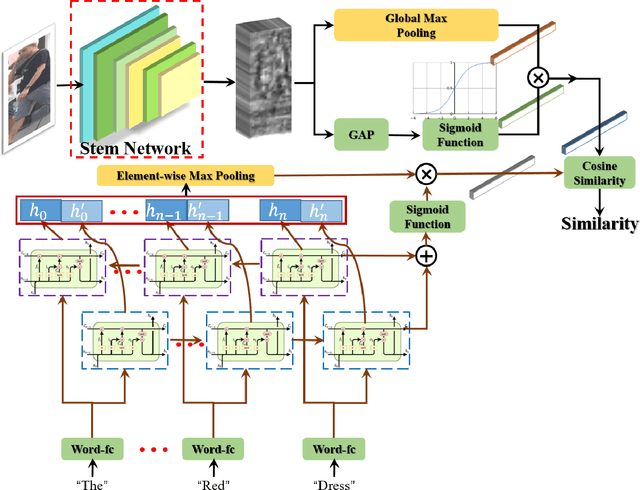
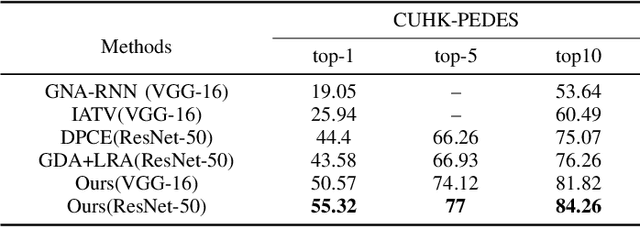
Abstract:Searching persons in large-scale image databases with the query of natural language description is a more practical important applications in video surveillance. Intuitively, for person search, the core issue should be visual-textual association, which is still an extremely challenging task, due to the contradiction between the high abstraction of textual description and the intuitive expression of visual images. However, for this task, while positive image-text pairs are always well provided, most existing methods doesn't tackle this problem effectively by mining more reasonable negative pairs. In this paper, we proposed a novel visual-textual association approach with visual and textual attention, and cross-modality hardest and semi-hard negative pair mining. In order to evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed approach, we conduct extensive experiments on typical person search datasdet: CUHK-PEDES, in which our approach achieves the top1 score of 55.32% as a new state-of-the-art. Besides, we also evaluate the semi-hard pair mining approach in COCO caption dataset, and validate the effectiveness and complementarity of the methods.
IPG-Net: Image Pyramid Guidance Network for Object Detection
Dec 05, 2019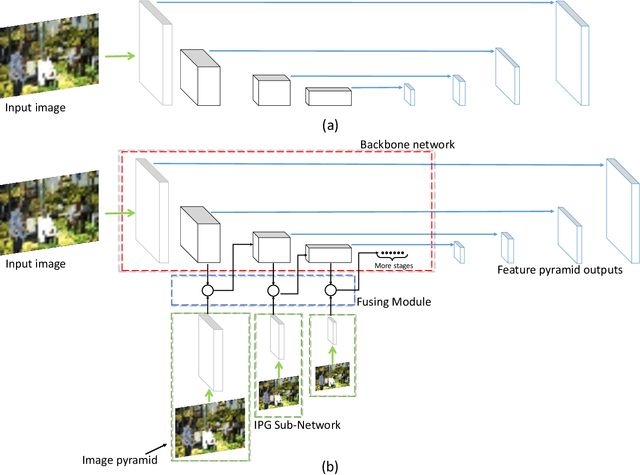
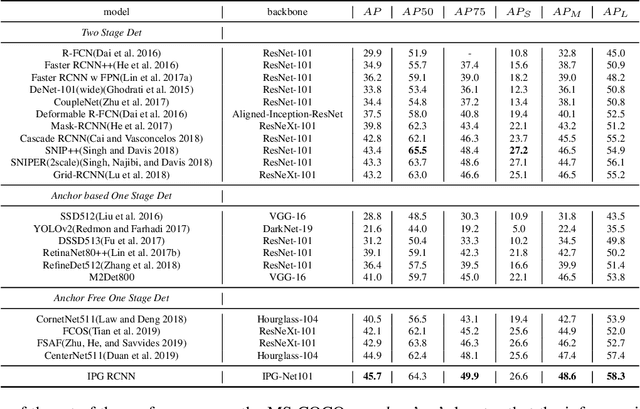
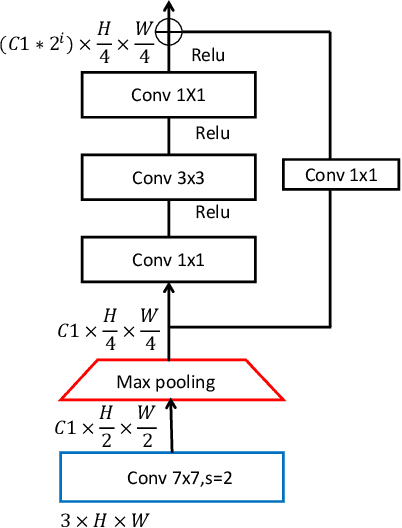
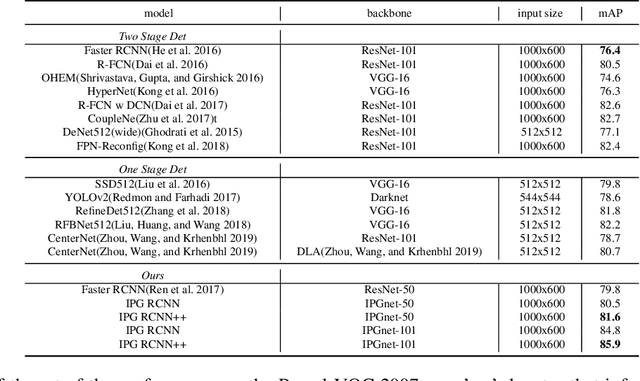
Abstract:For Convolutional Neural Network based object detection, there is a typical dilemma: the spatial information is well kept in the shallow layers which unfortunately do not have enough semantic information, while the deep layers have high semantic concept but lost a lot of spatial information, resulting in serious information imbalance. To acquire enough semantic information for shallow layers, Feature Pyramid Networks (FPN) is used to build a top-down propagated path. In this paper, except for top-down combining of information for shallow layers, we propose a novel network called Image Pyramid Guidance Network(IPG-Net) to make sure both the spatial information and semantic information are abundant for each layer. Our IPG-Net has three main parts: the image pyramid guidance sub-network, the ResNet based backbone network and the fusing module. The image pyramid guidance sub-network supplies spatial information to each scale's feature to solve the information imbalance problem. This sub-network promise even in the deepest stage of the ResNet, there is enough spatial information for bounding box regression and classification. Furthermore, we designed an effective fusing module to fuse the features from the image pyramid and features from the feature pyramid. We have tried to apply this novel network to both one stage and two stage models, state of the art results are obtained on the most popular benchmark data sets, i.e. MS COCO and Pascal VOC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge