Gisela Vallejo
CVQA: Culturally-diverse Multilingual Visual Question Answering Benchmark
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:Visual Question Answering (VQA) is an important task in multimodal AI, and it is often used to test the ability of vision-language models to understand and reason on knowledge present in both visual and textual data. However, most of the current VQA models use datasets that are primarily focused on English and a few major world languages, with images that are typically Western-centric. While recent efforts have tried to increase the number of languages covered on VQA datasets, they still lack diversity in low-resource languages. More importantly, although these datasets often extend their linguistic range via translation or some other approaches, they usually keep images the same, resulting in narrow cultural representation. To address these limitations, we construct CVQA, a new Culturally-diverse multilingual Visual Question Answering benchmark, designed to cover a rich set of languages and cultures, where we engage native speakers and cultural experts in the data collection process. As a result, CVQA includes culturally-driven images and questions from across 28 countries on four continents, covering 26 languages with 11 scripts, providing a total of 9k questions. We then benchmark several Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) on CVQA, and show that the dataset is challenging for the current state-of-the-art models. This benchmark can serve as a probing evaluation suite for assessing the cultural capability and bias of multimodal models and hopefully encourage more research efforts toward increasing cultural awareness and linguistic diversity in this field.
Connecting the Dots in News Analysis: A Cross-Disciplinary Survey of Media Bias and Framing
Sep 14, 2023Abstract:The manifestation and effect of bias in news reporting have been central topics in the social sciences for decades, and have received increasing attention in the NLP community recently. While NLP can help to scale up analyses or contribute automatic procedures to investigate the impact of biased news in society, we argue that methodologies that are currently dominant fall short of addressing the complex questions and effects addressed in theoretical media studies. In this survey paper, we review social science approaches and draw a comparison with typical task formulations, methods, and evaluation metrics used in the analysis of media bias in NLP. We discuss open questions and suggest possible directions to close identified gaps between theory and predictive models, and their evaluation. These include model transparency, considering document-external information, and cross-document reasoning rather than single-label assignment.
Evidence-based Verification for Real World Information Needs
Apr 01, 2021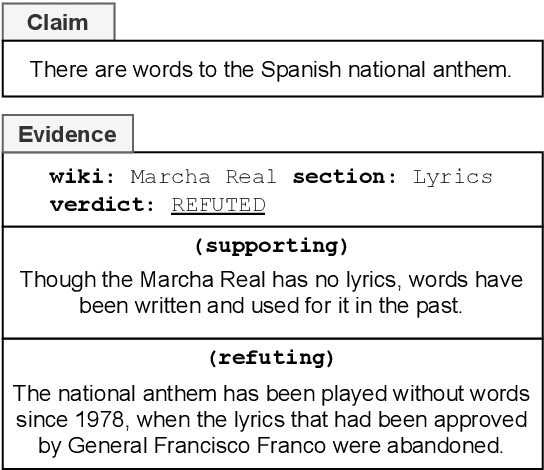
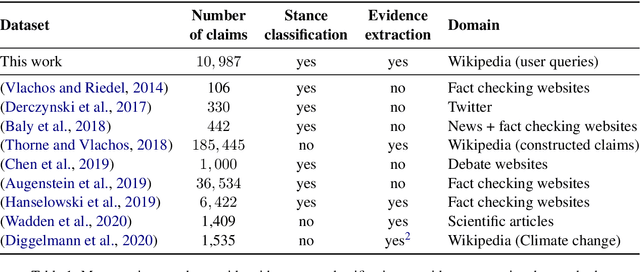

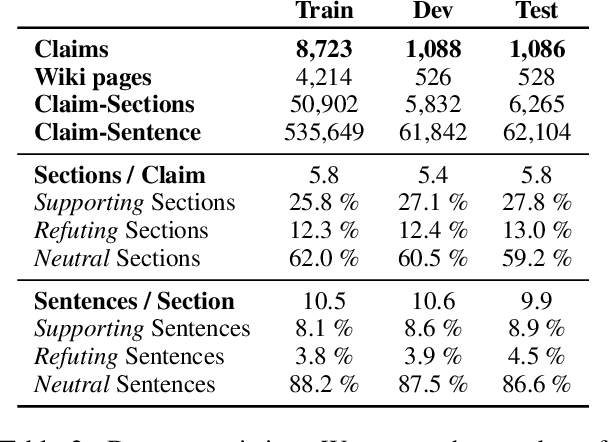
Abstract:Claim verification is the task of predicting the veracity of written statements against evidence. Previous large-scale datasets model the task as classification, ignoring the need to retrieve evidence, or are constructed for research purposes, and may not be representative of real-world needs. In this paper, we introduce a novel claim verification dataset with instances derived from search-engine queries, yielding 10,987 claims annotated with evidence that represent real-world information needs. For each claim, we annotate evidence from full Wikipedia articles with both section and sentence-level granularity. Our annotation allows comparison between two complementary approaches to verification: stance classification, and evidence extraction followed by entailment recognition. In our comprehensive evaluation, we find no significant difference in accuracy between these two approaches. This enables systems to use evidence extraction to summarize a rationale for an end-user while maintaining the accuracy when predicting a claim's veracity. With challenging claims and evidence documents containing hundreds of sentences, our dataset presents interesting challenges that are not captured in previous work -- evidenced through transfer learning experiments. We release code and data to support further research on this task.
Context-aware Neural-based Dialog Act Classification on Automatically Generated Transcriptions
Feb 28, 2019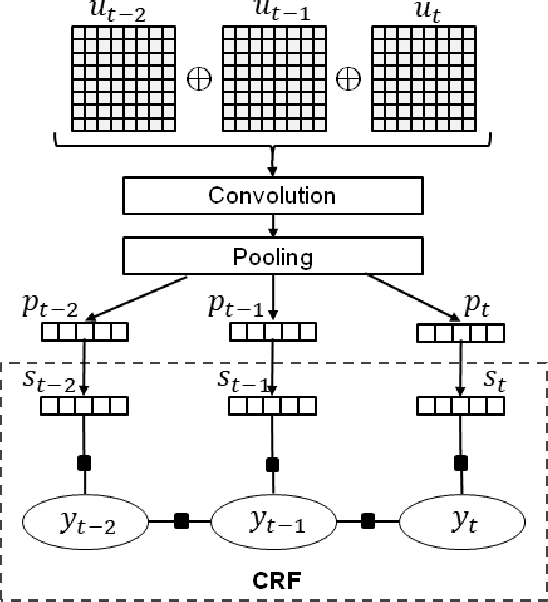
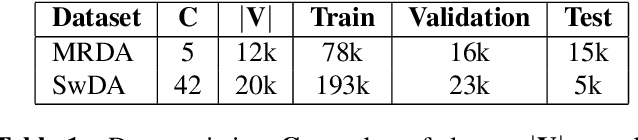
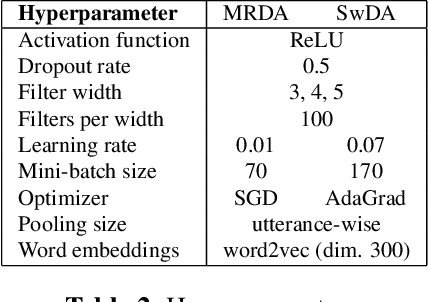
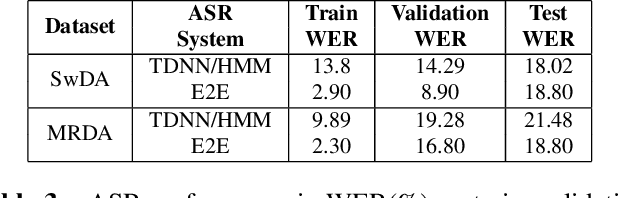
Abstract:This paper presents our latest investigations on dialog act (DA) classification on automatically generated transcriptions. We propose a novel approach that combines convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and conditional random fields (CRFs) for context modeling in DA classification. We explore the impact of transcriptions generated from different automatic speech recognition systems such as hybrid TDNN/HMM and End-to-End systems on the final performance. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets (MRDA and SwDA) show that the combination CNN and CRF improves consistently the accuracy. Furthermore, they show that although the word error rates are comparable, End-to-End ASR system seems to be more suitable for DA classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge