Chia-Yu Li
Improving noisy student training for low-resource languages in End-to-End ASR using CycleGAN and inter-domain losses
Jul 26, 2024



Abstract:Training a semi-supervised end-to-end speech recognition system using noisy student training has significantly improved performance. However, this approach requires a substantial amount of paired speech-text and unlabeled speech, which is costly for low-resource languages. Therefore, this paper considers a more extreme case of semi-supervised end-to-end automatic speech recognition where there are limited paired speech-text, unlabeled speech (less than five hours), and abundant external text. Firstly, we observe improved performance by training the model using our previous work on semi-supervised learning "CycleGAN and inter-domain losses" solely with external text. Secondly, we enhance "CycleGAN and inter-domain losses" by incorporating automatic hyperparameter tuning, calling it "enhanced CycleGAN inter-domain losses." Thirdly, we integrate it into the noisy student training approach pipeline for low-resource scenarios. Our experimental results, conducted on six non-English languages from Voxforge and Common Voice, show a 20% word error rate reduction compared to the baseline teacher model and a 10% word error rate reduction compared to the baseline best student model, highlighting the significant improvements achieved through our proposed method.
Oh, Jeez! or Uh-huh? A Listener-aware Backchannel Predictor on ASR Transcriptions
Apr 10, 2023Abstract:This paper presents our latest investigation on modeling backchannel in conversations. Motivated by a proactive backchanneling theory, we aim at developing a system which acts as a proactive listener by inserting backchannels, such as continuers and assessment, to influence speakers. Our model takes into account not only lexical and acoustic cues, but also introduces the simple and novel idea of using listener embeddings to mimic different backchanneling behaviours. Our experimental results on the Switchboard benchmark dataset reveal that acoustic cues are more important than lexical cues in this task and their combination with listener embeddings works best on both, manual transcriptions and automatically generated transcriptions.
Integrating Knowledge in End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition for Mandarin-English Code-Switching
Dec 19, 2021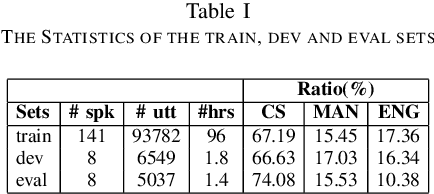
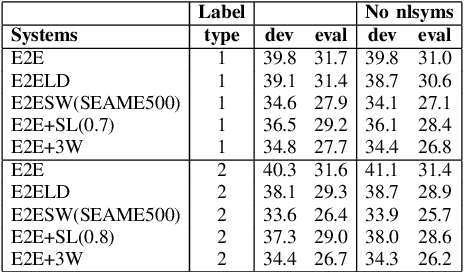

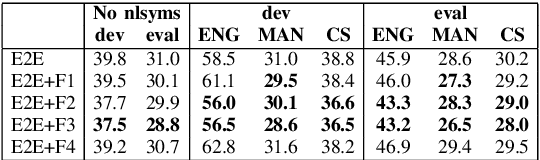
Abstract:Code-Switching (CS) is a common linguistic phenomenon in multilingual communities that consists of switching between languages while speaking. This paper presents our investigations on end-to-end speech recognition for Mandarin-English CS speech. We analyse different CS specific issues such as the properties mismatches between languages in a CS language pair, the unpredictable nature of switching points, and the data scarcity problem. We exploit and improve the state-of-the-art end-to-end system by merging nonlinguistic symbols, by integrating language identification using hierarchical softmax, by modeling sub-word units, by artificially lowering the speaking rate, and by augmenting data using speed perturbed technique and several monolingual datasets to improve the final performance not only on CS speech but also on monolingual benchmarks in order to make the system more applicable on real life settings. Finally, we explore the effect of different language model integration methods on the performance of the proposed model. Our experimental results reveal that all the proposed techniques improve the recognition performance. The best combined system improves the baseline system by up to 35% relatively in terms of mixed error rate and delivers acceptable performance on monolingual benchmarks.
Improving Code-switching Language Modeling with Artificially Generated Texts using Cycle-consistent Adversarial Networks
Dec 12, 2021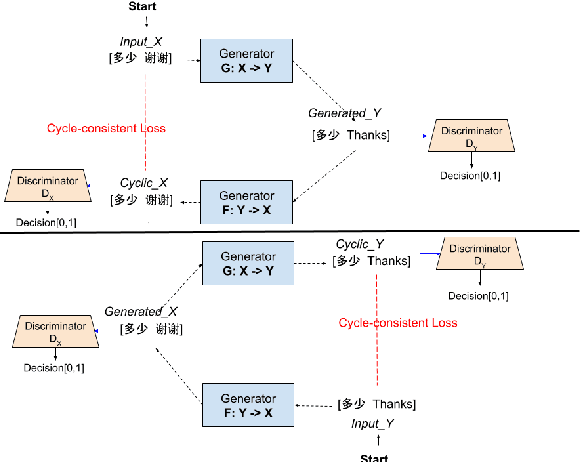
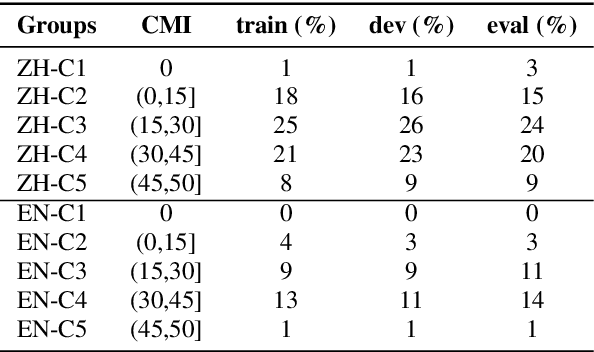
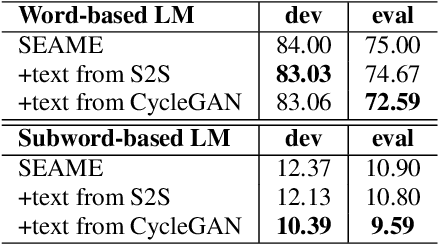
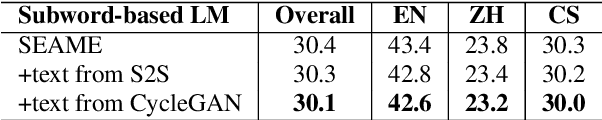
Abstract:This paper presents our latest effort on improving Code-switching language models that suffer from data scarcity. We investigate methods to augment Code-switching training text data by artificially generating them. Concretely, we propose a cycle-consistent adversarial networks based framework to transfer monolingual text into Code-switching text, considering Code-switching as a speaking style. Our experimental results on the SEAME corpus show that utilising artificially generated Code-switching text data improves consistently the language model as well as the automatic speech recognition performance.
Improving Speech Recognition on Noisy Speech via Speech Enhancement with Multi-Discriminators CycleGAN
Dec 12, 2021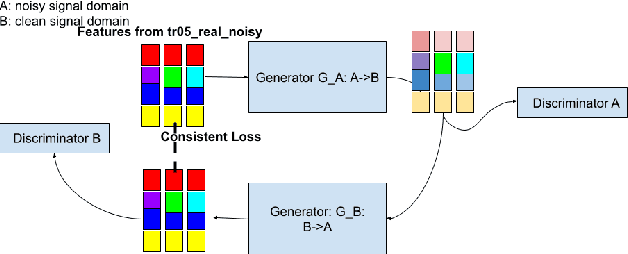
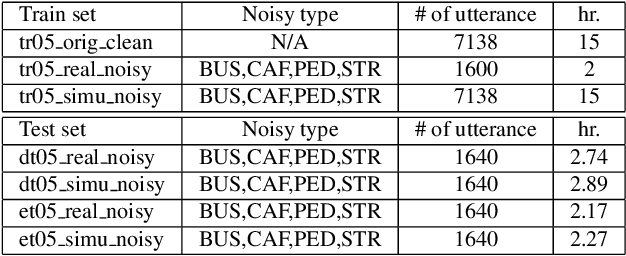
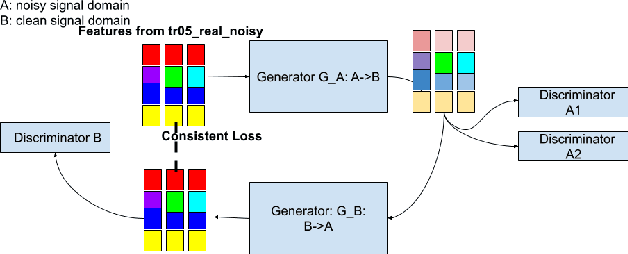
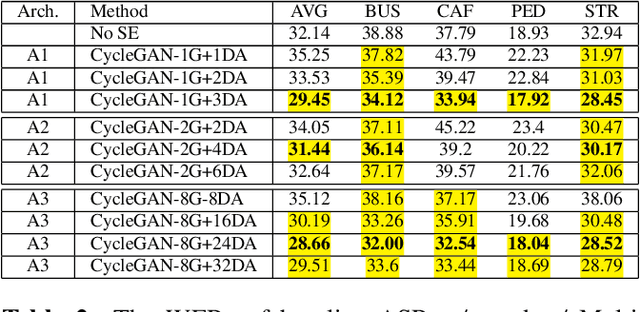
Abstract:This paper presents our latest investigations on improving automatic speech recognition for noisy speech via speech enhancement. We propose a novel method named Multi-discriminators CycleGAN to reduce noise of input speech and therefore improve the automatic speech recognition performance. Our proposed method leverages the CycleGAN framework for speech enhancement without any parallel data and improve it by introducing multiple discriminators that check different frequency areas. Furthermore, we show that training multiple generators on homogeneous subset of the training data is better than training one generator on all the training data. We evaluate our method on CHiME-3 data set and observe up to 10.03% relatively WER improvement on the development set and up to 14.09% on the evaluation set.
Investigations on Speech Recognition Systems for Low-Resource Dialectal Arabic-English Code-Switching Speech
Aug 29, 2021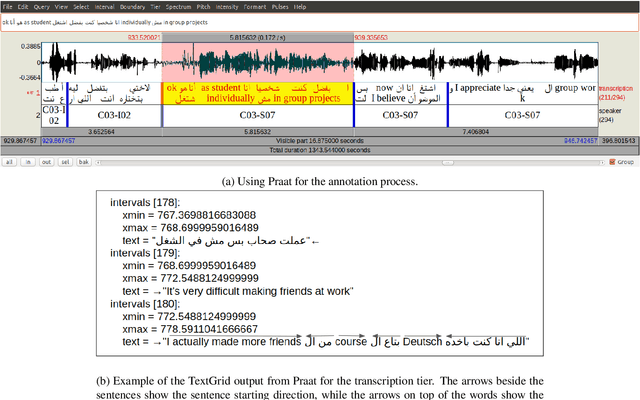
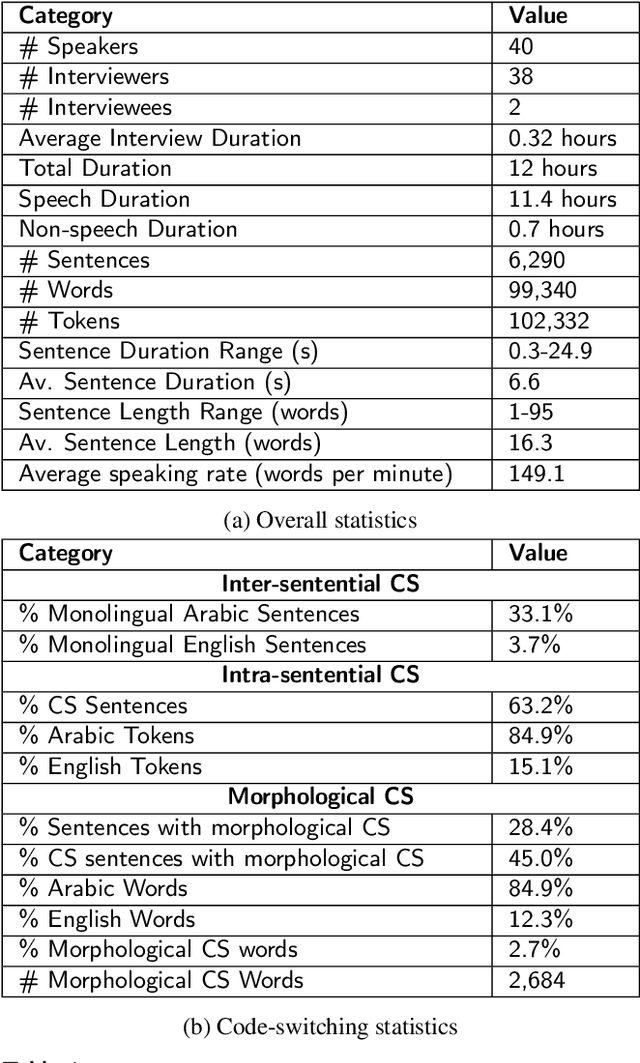
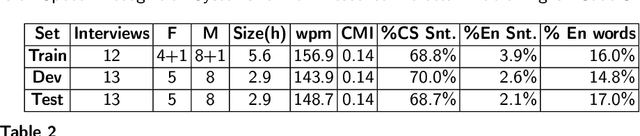
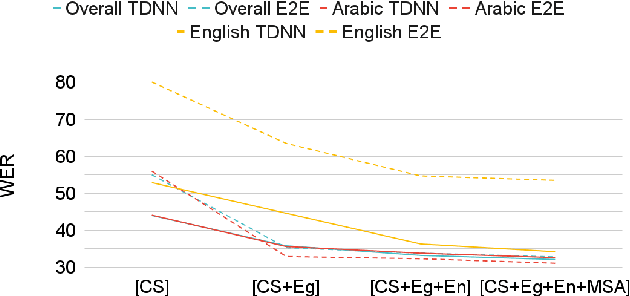
Abstract:Code-switching (CS), defined as the mixing of languages in conversations, has become a worldwide phenomenon. The prevalence of CS has been recently met with a growing demand and interest to build CS ASR systems. In this paper, we present our work on code-switched Egyptian Arabic-English automatic speech recognition (ASR). We first contribute in filling the huge gap in resources by collecting, analyzing and publishing our spontaneous CS Egyptian Arabic-English speech corpus. We build our ASR systems using DNN-based hybrid and Transformer-based end-to-end models. In this paper, we present a thorough comparison between both approaches under the setting of a low-resource, orthographically unstandardized, and morphologically rich language pair. We show that while both systems give comparable overall recognition results, each system provides complementary sets of strength points. We show that recognition can be improved by combining the outputs of both systems. We propose several effective system combination approaches, where hypotheses of both systems are merged on sentence- and word-levels. Our approaches result in overall WER relative improvement of 4.7%, over a baseline performance of 32.1% WER. In the case of intra-sentential CS sentences, we achieve WER relative improvement of 4.8%. Our best performing system achieves 30.6% WER on ArzEn test set.
ADVISER: A Toolkit for Developing Multi-modal, Multi-domain and Socially-engaged Conversational Agents
May 04, 2020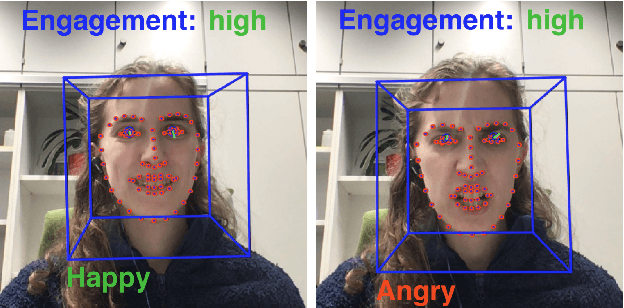
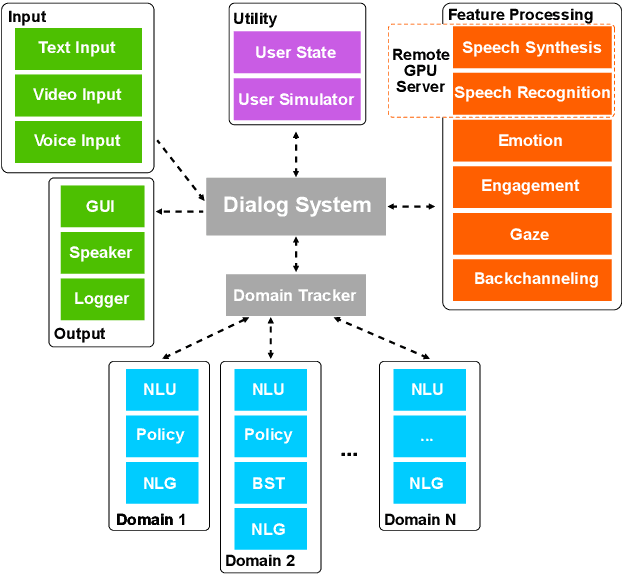
Abstract:We present ADVISER - an open-source, multi-domain dialog system toolkit that enables the development of multi-modal (incorporating speech, text and vision), socially-engaged (e.g. emotion recognition, engagement level prediction and backchanneling) conversational agents. The final Python-based implementation of our toolkit is flexible, easy to use, and easy to extend not only for technically experienced users, such as machine learning researchers, but also for less technically experienced users, such as linguists or cognitive scientists, thereby providing a flexible platform for collaborative research. Link to open-source code: https://github.com/DigitalPhonetics/adviser
Context-aware Neural-based Dialog Act Classification on Automatically Generated Transcriptions
Feb 28, 2019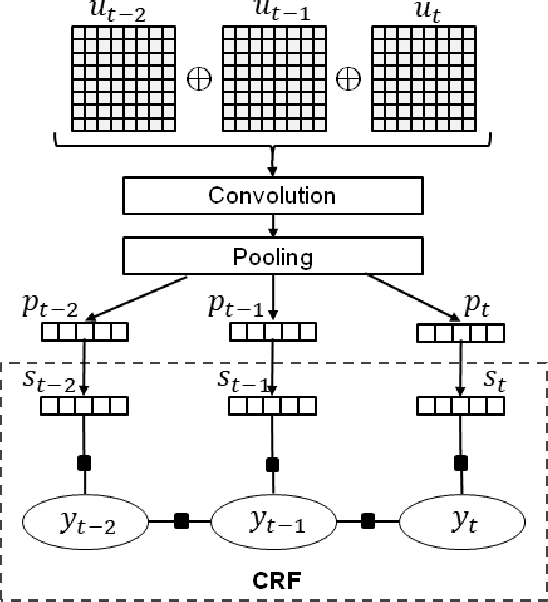
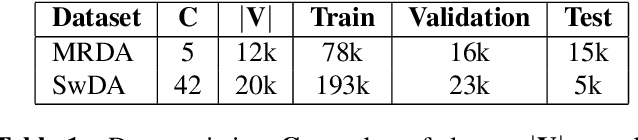
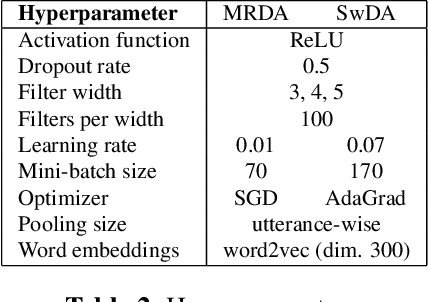
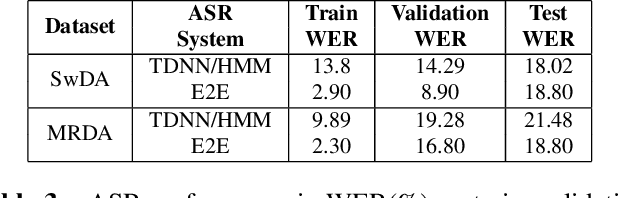
Abstract:This paper presents our latest investigations on dialog act (DA) classification on automatically generated transcriptions. We propose a novel approach that combines convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and conditional random fields (CRFs) for context modeling in DA classification. We explore the impact of transcriptions generated from different automatic speech recognition systems such as hybrid TDNN/HMM and End-to-End systems on the final performance. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets (MRDA and SwDA) show that the combination CNN and CRF improves consistently the accuracy. Furthermore, they show that although the word error rates are comparable, End-to-End ASR system seems to be more suitable for DA classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge