Integrating Knowledge in End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition for Mandarin-English Code-Switching
Paper and Code
Dec 19, 2021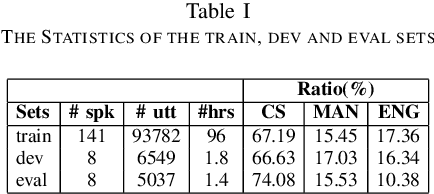
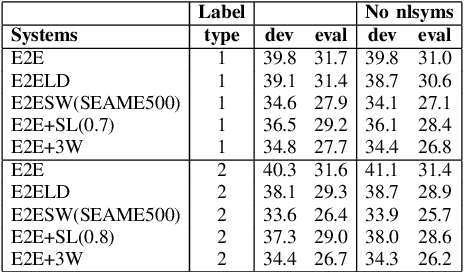

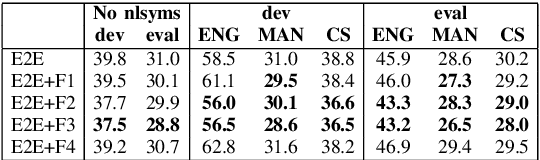
Code-Switching (CS) is a common linguistic phenomenon in multilingual communities that consists of switching between languages while speaking. This paper presents our investigations on end-to-end speech recognition for Mandarin-English CS speech. We analyse different CS specific issues such as the properties mismatches between languages in a CS language pair, the unpredictable nature of switching points, and the data scarcity problem. We exploit and improve the state-of-the-art end-to-end system by merging nonlinguistic symbols, by integrating language identification using hierarchical softmax, by modeling sub-word units, by artificially lowering the speaking rate, and by augmenting data using speed perturbed technique and several monolingual datasets to improve the final performance not only on CS speech but also on monolingual benchmarks in order to make the system more applicable on real life settings. Finally, we explore the effect of different language model integration methods on the performance of the proposed model. Our experimental results reveal that all the proposed techniques improve the recognition performance. The best combined system improves the baseline system by up to 35% relatively in terms of mixed error rate and delivers acceptable performance on monolingual benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge