Futang Peng
MM1: Methods, Analysis & Insights from Multimodal LLM Pre-training
Mar 22, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we discuss building performant Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). In particular, we study the importance of various architecture components and data choices. Through careful and comprehensive ablations of the image encoder, the vision language connector, and various pre-training data choices, we identified several crucial design lessons. For example, we demonstrate that for large-scale multimodal pre-training using a careful mix of image-caption, interleaved image-text, and text-only data is crucial for achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) few-shot results across multiple benchmarks, compared to other published pre-training results. Further, we show that the image encoder together with image resolution and the image token count has substantial impact, while the vision-language connector design is of comparatively negligible importance. By scaling up the presented recipe, we build MM1, a family of multimodal models up to 30B parameters, including both dense models and mixture-of-experts (MoE) variants, that are SOTA in pre-training metrics and achieve competitive performance after supervised fine-tuning on a range of established multimodal benchmarks. Thanks to large-scale pre-training, MM1 enjoys appealing properties such as enhanced in-context learning, and multi-image reasoning, enabling few-shot chain-of-thought prompting.
CARLS: Cross-platform Asynchronous Representation Learning System
May 26, 2021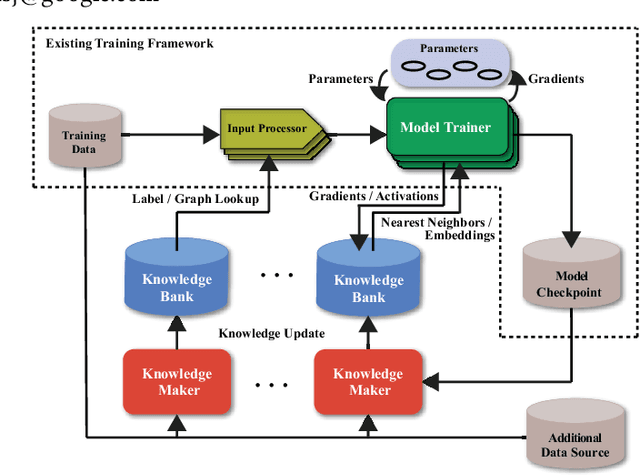

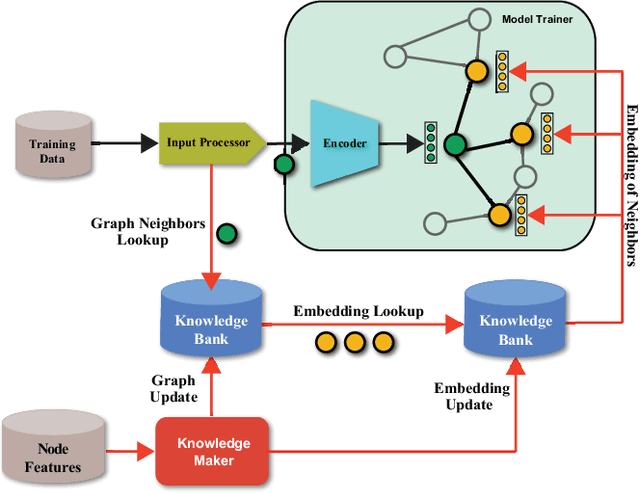
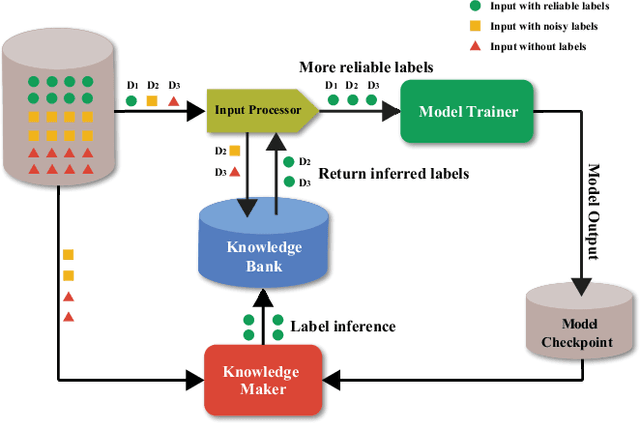
Abstract:In this work, we propose CARLS, a novel framework for augmenting the capacity of existing deep learning frameworks by enabling multiple components -- model trainers, knowledge makers and knowledge banks -- to concertedly work together in an asynchronous fashion across hardware platforms. The proposed CARLS is particularly suitable for learning paradigms where model training benefits from additional knowledge inferred or discovered during training, such as node embeddings for graph neural networks or reliable pseudo labels from model predictions. We also describe three learning paradigms -- semi-supervised learning, curriculum learning and multimodal learning -- as examples that can be scaled up efficiently by CARLS. One version of CARLS has been open-sourced and available for download at: https://github.com/tensorflow/neural-structured-learning/tree/master/research/carls
Unifying Specialist Image Embedding into Universal Image Embedding
Mar 08, 2020



Abstract:Deep image embedding provides a way to measure the semantic similarity of two images. It plays a central role in many applications such as image search, face verification, and zero-shot learning. It is desirable to have a universal deep embedding model applicable to various domains of images. However, existing methods mainly rely on training specialist embedding models each of which is applicable to images from a single domain. In this paper, we study an important but unexplored task: how to train a single universal image embedding model to match the performance of several specialists on each specialist's domain. Simply fusing the training data from multiple domains cannot solve this problem because some domains become overfitted sooner when trained together using existing methods. Therefore, we propose to distill the knowledge in multiple specialists into a universal embedding to solve this problem. In contrast to existing embedding distillation methods that distill the absolute distances between images, we transform the absolute distances between images into a probabilistic distribution and minimize the KL-divergence between the distributions of the specialists and the universal embedding. Using several public datasets, we validate that our proposed method accomplishes the goal of universal image embedding.
Graph-RISE: Graph-Regularized Image Semantic Embedding
Feb 14, 2019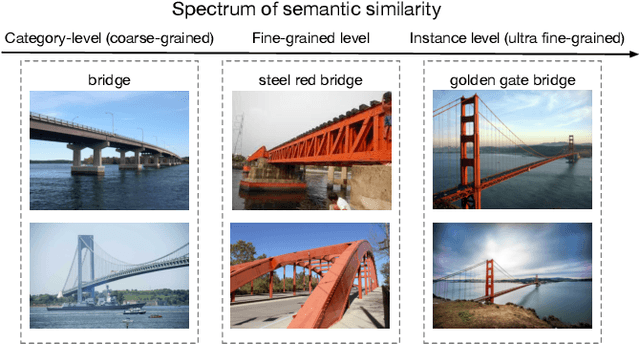
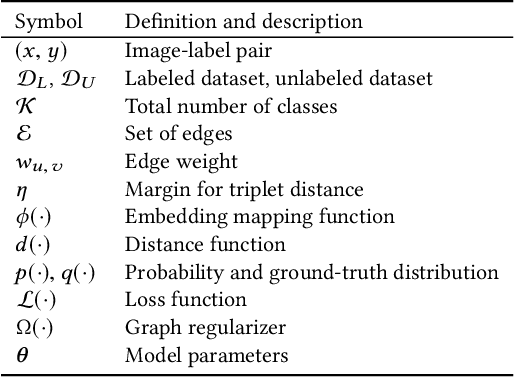

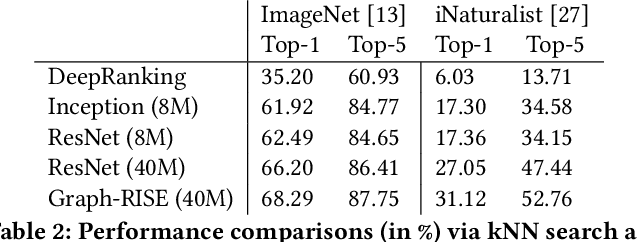
Abstract:Learning image representations to capture fine-grained semantics has been a challenging and important task enabling many applications such as image search and clustering. In this paper, we present Graph-Regularized Image Semantic Embedding (Graph-RISE), a large-scale neural graph learning framework that allows us to train embeddings to discriminate an unprecedented O(40M) ultra-fine-grained semantic labels. Graph-RISE outperforms state-of-the-art image embedding algorithms on several evaluation tasks, including image classification and triplet ranking. We provide case studies to demonstrate that, qualitatively, image retrieval based on Graph-RISE effectively captures semantics and, compared to the state-of-the-art, differentiates nuances at levels that are closer to human-perception.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge