Feng Pan
Microsoft
Pose-Free 3D Quantitative Phase Imaging of Flowing Cellular Populations
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:High-throughput 3D quantitative phase imaging (QPI) in flow cytometry enables label-free, volumetric characterization of individual cells by reconstructing their refractive index (RI) distributions from multiple viewing angles during flow through microfluidic channels. However, current imaging methods assume that cells undergo uniform, single-axis rotation, which require their poses to be known at each frame. This assumption restricts applicability to near-spherical cells and prevents accurate imaging of irregularly shaped cells with complex rotations. As a result, only a subset of the cellular population can be analyzed, limiting the ability of flow-based assays to perform robust statistical analysis. We introduce OmniFHT, a pose-free 3D RI reconstruction framework that leverages the Fourier diffraction theorem and implicit neural representations (INRs) for high-throughput flow cytometry tomographic imaging. By jointly optimizing each cell's unknown rotational trajectory and volumetric structure under weak scattering assumptions, OmniFHT supports arbitrary cell geometries and multi-axis rotations. Its continuous representation also allows accurate reconstruction from sparsely sampled projections and restricted angular coverage, producing high-fidelity results with as few as 10 views or only 120 degrees of angular range. OmniFHT enables, for the first time, in situ, high-throughput tomographic imaging of entire flowing cell populations, providing a scalable and unbiased solution for label-free morphometric analysis in flow cytometry platforms.
Cognition-Mode Aware Variational Representation Learning Framework for Knowledge Tracing
Sep 03, 2023Abstract:The Knowledge Tracing (KT) task plays a crucial role in personalized learning, and its purpose is to predict student responses based on their historical practice behavior sequence. However, the KT task suffers from data sparsity, which makes it challenging to learn robust representations for students with few practice records and increases the risk of model overfitting. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a Cognition-Mode Aware Variational Representation Learning Framework (CMVF) that can be directly applied to existing KT methods. Our framework uses a probabilistic model to generate a distribution for each student, accounting for uncertainty in those with limited practice records, and estimate the student's distribution via variational inference (VI). In addition, we also introduce a cognition-mode aware multinomial distribution as prior knowledge that constrains the posterior student distributions learning, so as to ensure that students with similar cognition modes have similar distributions, avoiding overwhelming personalization for students with few practice records. At last, extensive experimental results confirm that CMVF can effectively aid existing KT methods in learning more robust student representations. Our code is available at https://github.com/zmy-9/CMVF.
* Accepted by ICDM 2023, 10 pages, 5 figures, 4 tables
Focused Specific Objects NeRF
Aug 11, 2023

Abstract:Most NeRF-based models are designed for learning the entire scene, and complex scenes can lead to longer learning times and poorer rendering effects. This paper utilizes scene semantic priors to make improvements in fast training, allowing the network to focus on the specific targets and not be affected by complex backgrounds. The training speed can be increased by 7.78 times with better rendering effect, and small to medium sized targets can be rendered faster. In addition, this improvement applies to all NeRF-based models. Considering the inherent multi-view consistency and smoothness of NeRF, this paper also studies weak supervision by sparsely sampling negative ray samples. With this method, training can be further accelerated and rendering quality can be maintained. Finally, this paper extends pixel semantic and color rendering formulas and proposes a new scene editing technique that can achieve unique displays of the specific semantic targets or masking them in rendering. To address the problem of unsupervised regions incorrect inferences in the scene, we also designed a self-supervised loop that combines morphological operations and clustering.
No Length Left Behind: Enhancing Knowledge Tracing for Modeling Sequences of Excessive or Insufficient Lengths
Aug 07, 2023Abstract:Knowledge tracing (KT) aims to predict students' responses to practices based on their historical question-answering behaviors. However, most current KT methods focus on improving overall AUC, leaving ample room for optimization in modeling sequences of excessive or insufficient lengths. As sequences get longer, computational costs will increase exponentially. Therefore, KT methods usually truncate sequences to an acceptable length, which makes it difficult for models on online service systems to capture complete historical practice behaviors of students with too long sequences. Conversely, modeling students with short practice sequences using most KT methods may result in overfitting due to limited observation samples. To address the above limitations, we propose a model called Sequence-Flexible Knowledge Tracing (SFKT).
Counterfactual Monotonic Knowledge Tracing for Assessing Students' Dynamic Mastery of Knowledge Concepts
Aug 07, 2023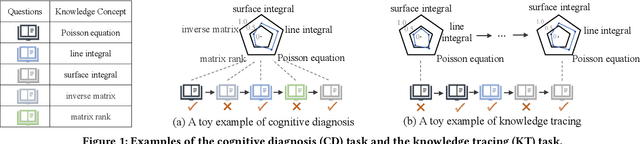
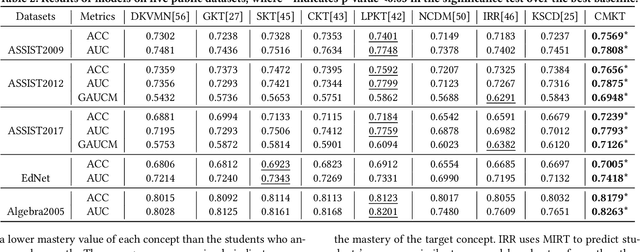
Abstract:As the core of the Knowledge Tracking (KT) task, assessing students' dynamic mastery of knowledge concepts is crucial for both offline teaching and online educational applications. Since students' mastery of knowledge concepts is often unlabeled, existing KT methods rely on the implicit paradigm of historical practice to mastery of knowledge concepts to students' responses to practices to address the challenge of unlabeled concept mastery. However, purely predicting student responses without imposing specific constraints on hidden concept mastery values does not guarantee the accuracy of these intermediate values as concept mastery values. To address this issue, we propose a principled approach called Counterfactual Monotonic Knowledge Tracing (CMKT), which builds on the implicit paradigm described above by using a counterfactual assumption to constrain the evolution of students' mastery of knowledge concepts.
qecGPT: decoding Quantum Error-correcting Codes with Generative Pre-trained Transformers
Jul 18, 2023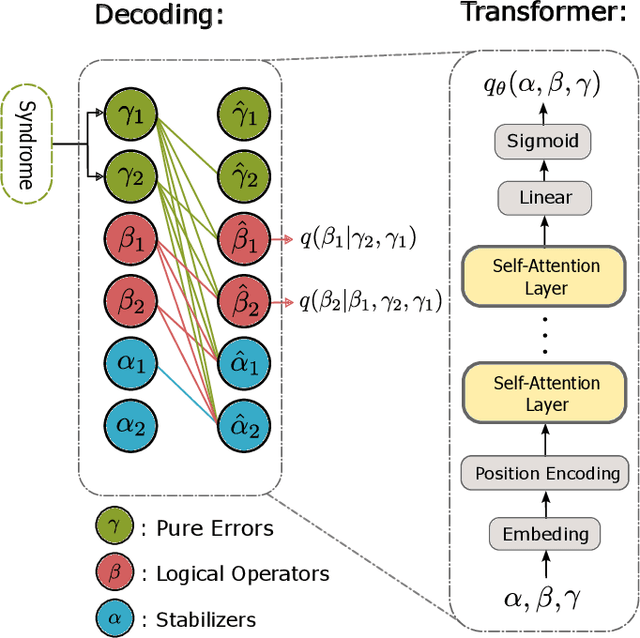
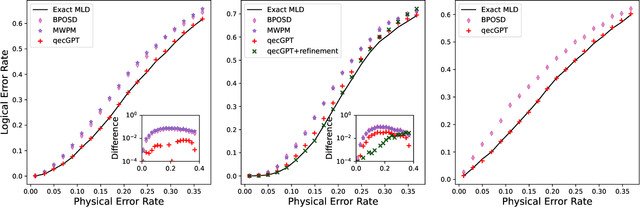
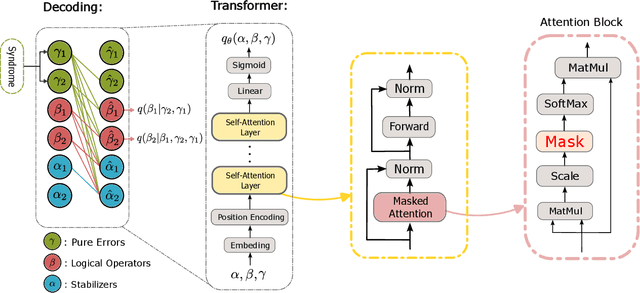
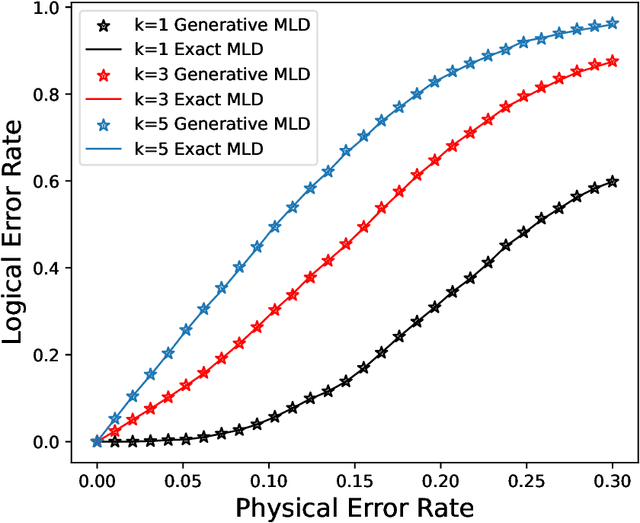
Abstract:We propose a general framework for decoding quantum error-correcting codes with generative modeling. The model utilizes autoregressive neural networks, specifically Transformers, to learn the joint probability of logical operators and syndromes. This training is in an unsupervised way, without the need for labeled training data, and is thus referred to as pre-training. After the pre-training, the model can efficiently compute the likelihood of logical operators for any given syndrome, using maximum likelihood decoding. It can directly generate the most-likely logical operators with computational complexity $\mathcal O(2k)$ in the number of logical qubits $k$, which is significantly better than the conventional maximum likelihood decoding algorithms that require $\mathcal O(4^k)$ computation. Based on the pre-trained model, we further propose refinement to achieve more accurately the likelihood of logical operators for a given syndrome by directly sampling the stabilizer operators. We perform numerical experiments on stabilizer codes with small code distances, using both depolarizing error models and error models with correlated noise. The results show that our approach provides significantly better decoding accuracy than the minimum weight perfect matching and belief-propagation-based algorithms. Our framework is general and can be applied to any error model and quantum codes with different topologies such as surface codes and quantum LDPC codes. Furthermore, it leverages the parallelization capabilities of GPUs, enabling simultaneous decoding of a large number of syndromes. Our approach sheds light on the efficient and accurate decoding of quantum error-correcting codes using generative artificial intelligence and modern computational power.
Managed Geo-Distributed Feature Store: Architecture and System Design
May 31, 2023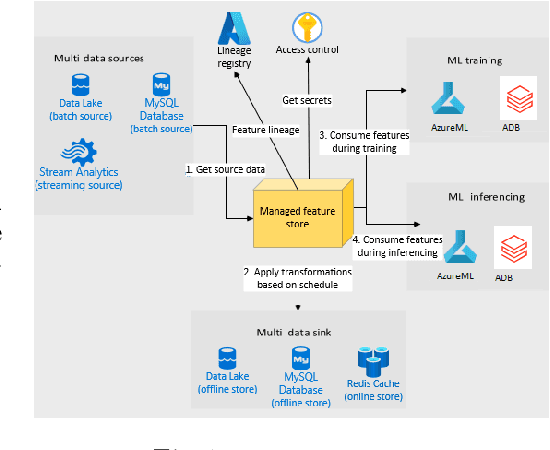

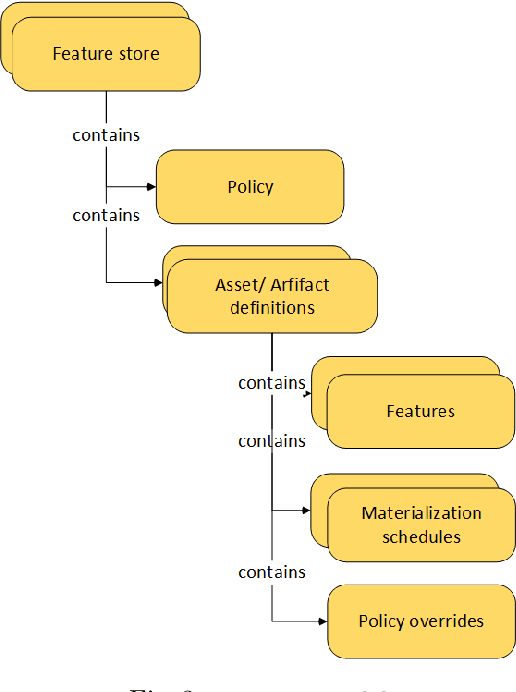
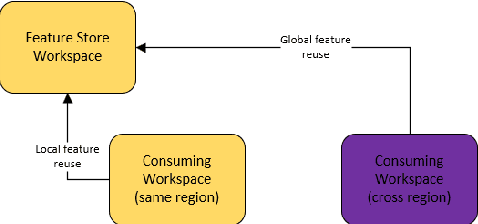
Abstract:Companies are using machine learning to solve real-world problems and are developing hundreds to thousands of features in the process. They are building feature engineering pipelines as part of MLOps life cycle to transform data from various data sources and materialize the same for future consumption. Without feature stores, different teams across various business groups would maintain the above process independently, which can lead to conflicting and duplicated features in the system. Data scientists find it hard to search for and reuse existing features and it is painful to maintain version control. Furthermore, feature correctness violations related to online (inferencing) - offline (training) skews and data leakage are common. Although the machine learning community has extensively discussed the need for feature stores and their purpose, this paper aims to capture the core architectural components that make up a managed feature store and to share the design learning in building such a system.
Affinity Feature Strengthening for Accurate, Complete and Robust Vessel Segmentation
Nov 12, 2022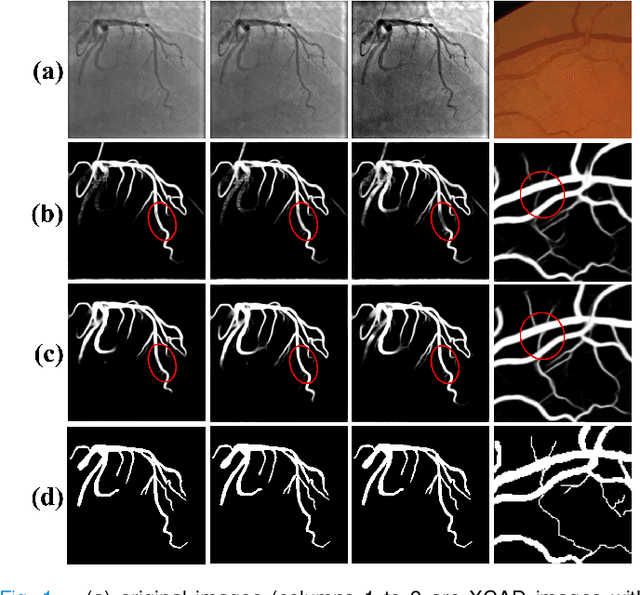
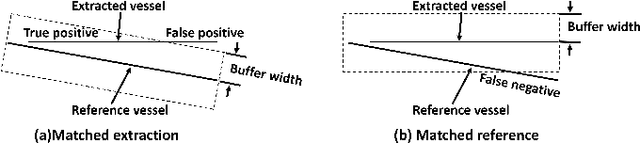

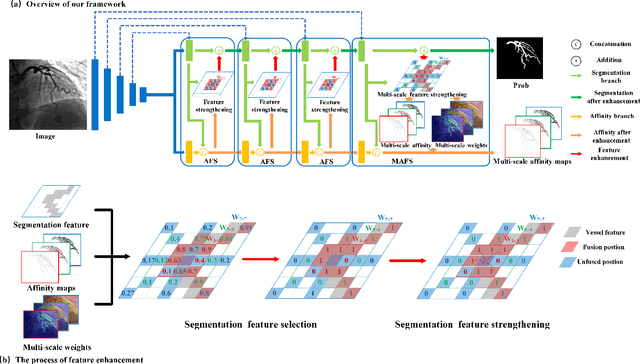
Abstract:Vessel segmentation is essential in many medical image applications, such as the detection of coronary stenoses, retinal vessel diseases and brain aneurysms. A high pixel-wise accuracy, complete topology structure and robustness to various contrast variations are three critical aspects of vessel segmentation. However, most existing methods only focus on achieving part of them via dedicated designs while few of them can concurrently achieve the three goals. In this paper, we present a novel affinity feature strengthening network (AFN) which adopts a contrast-insensitive approach based on multiscale affinity to jointly model topology and refine pixel-wise segmentation features. Specifically, for each pixel we derive a multiscale affinity field which captures the semantic relationships of the pixel with its neighbors on the predicted mask image. Such a multiscale affinity field can effectively represent the local topology of a vessel segment of different sizes. Meanwhile, it does not depend on image intensities and hence is robust to various illumination and contrast changes. We further learn spatial- and scale-aware adaptive weights for the corresponding affinity fields to strengthen vessel features. We evaluate our AFN on four different types of vascular datasets: X-ray angiography coronary vessel dataset (XCAD), portal vein dataset (PV), digital subtraction angiography cerebrovascular vessel dataset (DSA) and retinal vessel dataset (DRIVE). Extensive experimental results on the four datasets demonstrate that our AFN outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of both higher accuracy and topological metrics, and meanwhile is more robust to various contrast changes than existing methods. Codes will be made public.
Multi-Factors Aware Dual-Attentional Knowledge Tracing
Aug 10, 2021Abstract:With the increasing demands of personalized learning, knowledge tracing has become important which traces students' knowledge states based on their historical practices. Factor analysis methods mainly use two kinds of factors which are separately related to students and questions to model students' knowledge states. These methods use the total number of attempts of students to model students' learning progress and hardly highlight the impact of the most recent relevant practices. Besides, current factor analysis methods ignore rich information contained in questions. In this paper, we propose Multi-Factors Aware Dual-Attentional model (MF-DAKT) which enriches question representations and utilizes multiple factors to model students' learning progress based on a dual-attentional mechanism. More specifically, we propose a novel student-related factor which records the most recent attempts on relevant concepts of students to highlight the impact of recent exercises. To enrich questions representations, we use a pre-training method to incorporate two kinds of question information including questions' relation and difficulty level. We also add a regularization term about questions' difficulty level to restrict pre-trained question representations to fine-tuning during the process of predicting students' performance. Moreover, we apply a dual-attentional mechanism to differentiate contributions of factors and factor interactions to final prediction in different practice records. At last, we conduct experiments on several real-world datasets and results show that MF-DAKT can outperform existing knowledge tracing methods. We also conduct several studies to validate the effects of each component of MF-DAKT.
* 10 pages, 10 figures, 6 tables
TS4Net: Two-Stage Sample Selective Strategy for Rotating Object Detection
Aug 06, 2021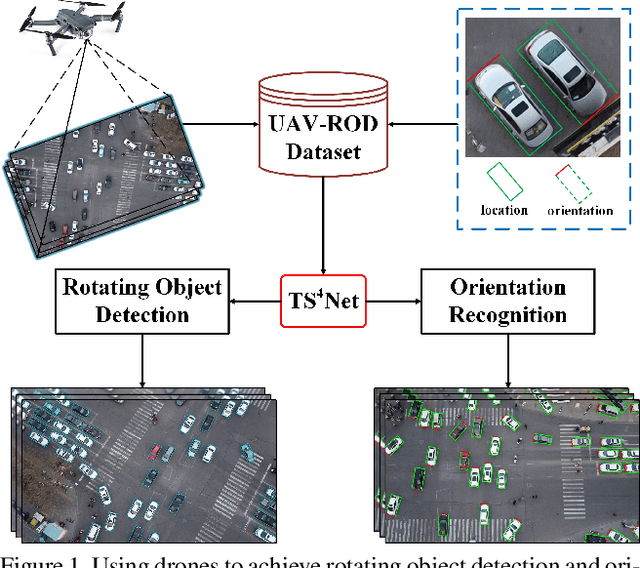
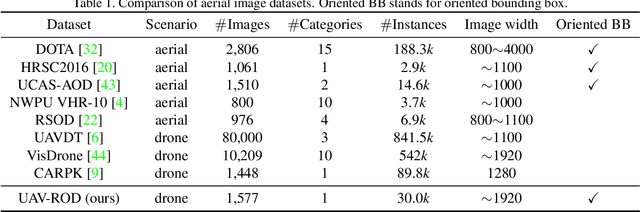
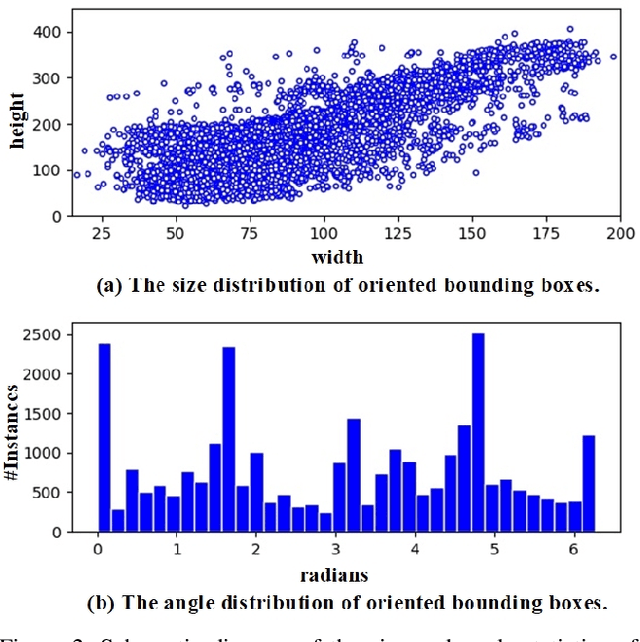
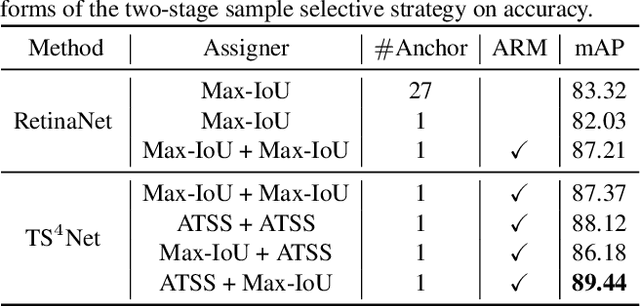
Abstract:Rotating object detection has wide applications in aerial photographs, remote sensing images, UAVs, etc. At present, most of the rotating object detection datasets focus on the field of remote sensing, and these images are usually shot in high-altitude scenes. However, image datasets captured at low-altitude areas also should be concerned, such as drone-based datasets. So we present a low-altitude dronebased dataset, named UAV-ROD, aiming to promote the research and development in rotating object detection and UAV applications. The UAV-ROD consists of 1577 images and 30,090 instances of car category annotated by oriented bounding boxes. In particular, The UAV-ROD can be utilized for the rotating object detection, vehicle orientation recognition and object counting tasks. Compared with horizontal object detection, the regression stage of the rotation detection is a tricky problem. In this paper, we propose a rotating object detector TS4Net, which contains anchor refinement module (ARM) and two-stage sample selective strategy (TS4). The ARM can convert preseted horizontal anchors into high-quality rotated anchors through twostage anchor refinement. The TS4 module utilizes different constrained sample selective strategies to allocate positive and negative samples, which is adaptive to the regression task in different stages. Benefiting from the ARM and TS4, the TS4Net can achieve superior performance for rotating object detection solely with one preseted horizontal anchor. Extensive experimental results on UAV-ROD dataset and three remote sensing datasets DOTA, HRSC2016 and UCAS-AOD demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance against most state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge