Zengqiang Yan
School of Electronic Information and Communications, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
FedPCA: Noise-Robust Fair Federated Learning via Performance-Capacity Analysis
Mar 13, 2025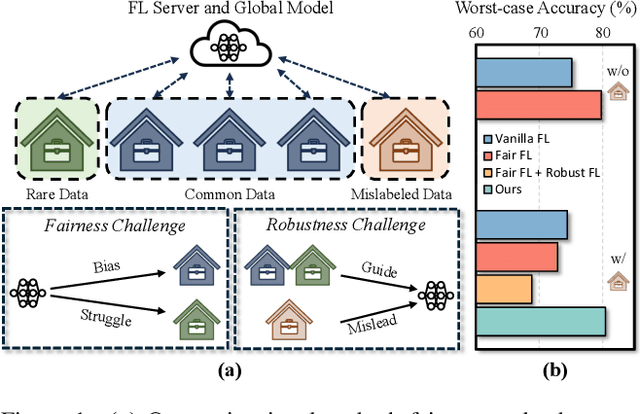
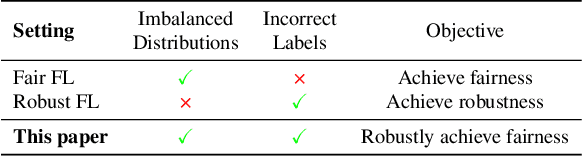
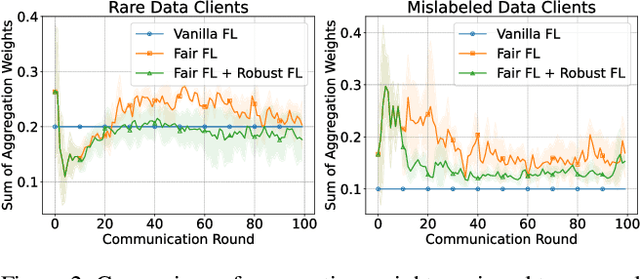
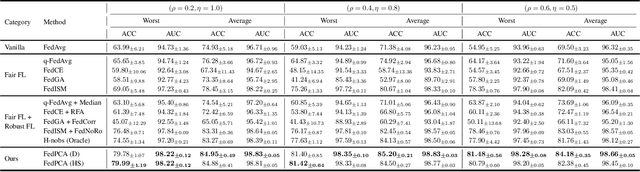
Abstract:Training a model that effectively handles both common and rare data-i.e., achieving performance fairness-is crucial in federated learning (FL). While existing fair FL methods have shown effectiveness, they remain vulnerable to mislabeled data. Ensuring robustness in fair FL is therefore essential. However, fairness and robustness inherently compete, which causes robust strategies to hinder fairness. In this paper, we attribute this competition to the homogeneity in loss patterns exhibited by rare and mislabeled data clients, preventing existing loss-based fair and robust FL methods from effectively distinguishing and handling these two distinct client types. To address this, we propose performance-capacity analysis, which jointly considers model performance on each client and its capacity to handle the dataset, measured by loss and a newly introduced feature dispersion score. This allows mislabeled clients to be identified by their significantly deviated performance relative to capacity while preserving rare data clients. Building on this, we introduce FedPCA, an FL method that robustly achieves fairness. FedPCA first identifies mislabeled clients via a Gaussian Mixture Model on loss-dispersion pairs, then applies fairness and robustness strategies in global aggregation and local training by adjusting client weights and selectively using reliable data. Extensive experiments on three datasets demonstrate FedPCA's effectiveness in tackling this complex challenge. Code will be publicly available upon acceptance.
Fair Federated Medical Image Classification Against Quality Shift via Inter-Client Progressive State Matching
Mar 12, 2025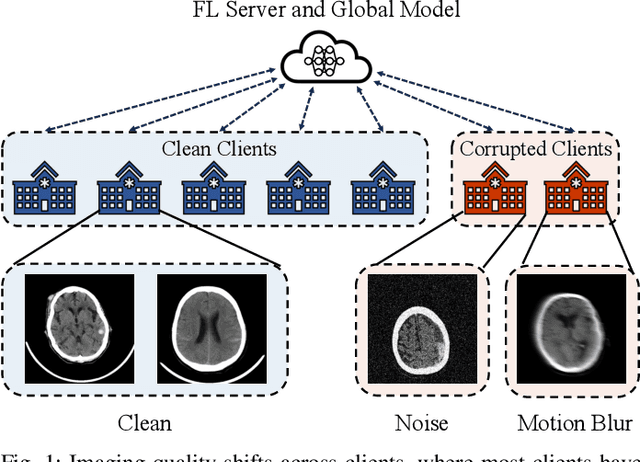
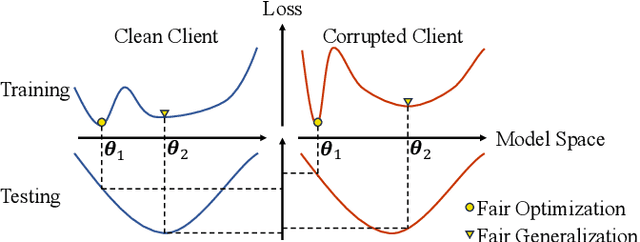
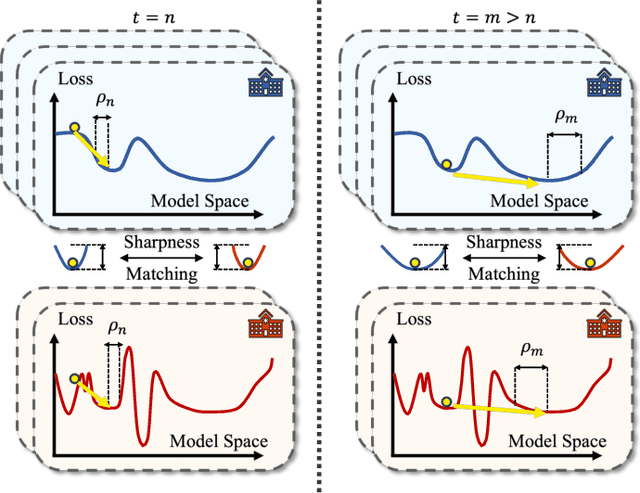
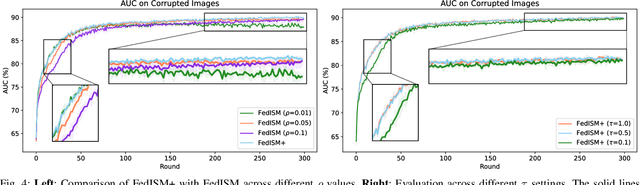
Abstract:Despite the potential of federated learning in medical applications, inconsistent imaging quality across institutions-stemming from lower-quality data from a minority of clients-biases federated models toward more common high-quality images. This raises significant fairness concerns. Existing fair federated learning methods have demonstrated some effectiveness in solving this problem by aligning a single 0th- or 1st-order state of convergence (e.g., training loss or sharpness). However, we argue in this work that fairness based on such a single state is still not an adequate surrogate for fairness during testing, as these single metrics fail to fully capture the convergence characteristics, making them suboptimal for guiding fair learning. To address this limitation, we develop a generalized framework. Specifically, we propose assessing convergence using multiple states, defined as sharpness or perturbed loss computed at varying search distances. Building on this comprehensive assessment, we propose promoting fairness for these states across clients to achieve our ultimate fairness objective. This is accomplished through the proposed method, FedISM+. In FedISM+, the search distance evolves over time, progressively focusing on different states. We then incorporate two components in local training and global aggregation to ensure cross-client fairness for each state. This gradually makes convergence equitable for all states, thereby improving fairness during testing. Our empirical evaluations, performed on the well-known RSNA ICH and ISIC 2019 datasets, demonstrate the superiority of FedISM+ over existing state-of-the-art methods for fair federated learning. The code is available at https://github.com/wnn2000/FFL4MIA.
PASSION: Towards Effective Incomplete Multi-Modal Medical Image Segmentation with Imbalanced Missing Rates
Jul 20, 2024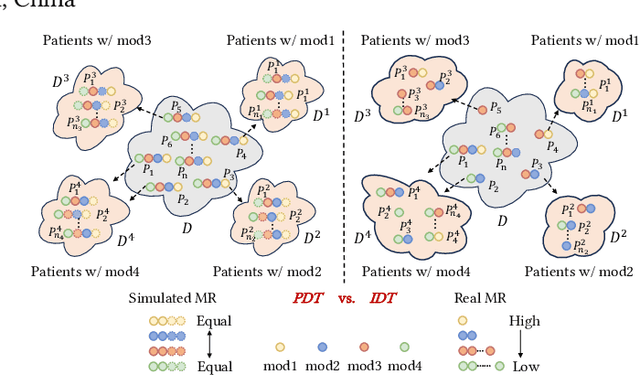
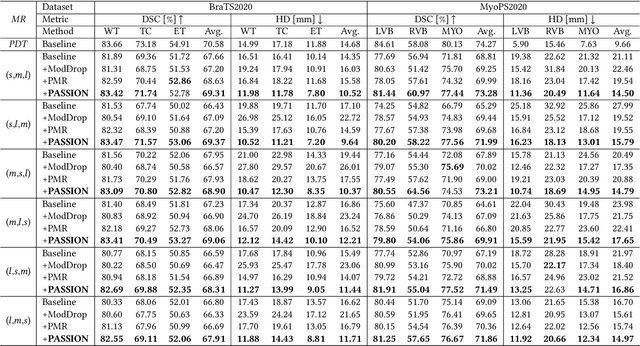
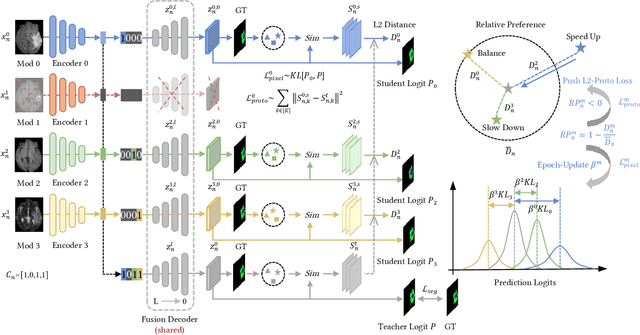
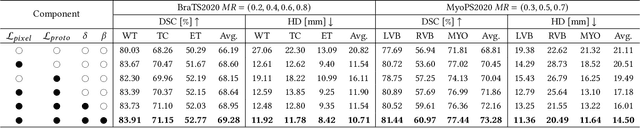
Abstract:Incomplete multi-modal image segmentation is a fundamental task in medical imaging to refine deployment efficiency when only partial modalities are available. However, the common practice that complete-modality data is visible during model training is far from realistic, as modalities can have imbalanced missing rates in clinical scenarios. In this paper, we, for the first time, formulate such a challenging setting and propose Preference-Aware Self-diStillatION (PASSION) for incomplete multi-modal medical image segmentation under imbalanced missing rates. Specifically, we first construct pixel-wise and semantic-wise self-distillation to balance the optimization objective of each modality. Then, we define relative preference to evaluate the dominance of each modality during training, based on which to design task-wise and gradient-wise regularization to balance the convergence rates of different modalities. Experimental results on two publicly available multi-modal datasets demonstrate the superiority of PASSION against existing approaches for modality balancing. More importantly, PASSION is validated to work as a plug-and-play module for consistent performance improvement across different backbones. Code is available at https://github.com/Jun-Jie-Shi/PASSION.
Non-parametric regularization for class imbalance federated medical image classification
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:Limited training data and severe class imbalance pose significant challenges to developing clinically robust deep learning models. Federated learning (FL) addresses the former by enabling different medical clients to collaboratively train a deep model without sharing privacy-sensitive data. However, class imbalance worsens due to variation in inter-client class distribution. We propose federated learning with non-parametric regularization (FedNPR and FedNPR-Per, a personalized version of FedNPR) to regularize the feature extractor and enhance useful and discriminative signal in the feature space. Our extensive experiments show that FedNPR outperform the existing state-of-the art FL approaches in class imbalance skin lesion classification and intracranial hemorrhage identification. Additionally, the non-parametric regularization module consistently improves the performance of existing state-of-the-art FL approaches. We believe that NPR is a valuable tool in FL under clinical settings.
FedIA: Federated Medical Image Segmentation with Heterogeneous Annotation Completeness
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:Federated learning has emerged as a compelling paradigm for medical image segmentation, particularly in light of increasing privacy concerns. However, most of the existing research relies on relatively stringent assumptions regarding the uniformity and completeness of annotations across clients. Contrary to this, this paper highlights a prevalent challenge in medical practice: incomplete annotations. Such annotations can introduce incorrectly labeled pixels, potentially undermining the performance of neural networks in supervised learning. To tackle this issue, we introduce a novel solution, named FedIA. Our insight is to conceptualize incomplete annotations as noisy data (\textit{i.e.}, low-quality data), with a focus on mitigating their adverse effects. We begin by evaluating the completeness of annotations at the client level using a designed indicator. Subsequently, we enhance the influence of clients with more comprehensive annotations and implement corrections for incomplete ones, thereby ensuring that models are trained on accurate data. Our method's effectiveness is validated through its superior performance on two extensively used medical image segmentation datasets, outperforming existing solutions. The code is available at https://github.com/HUSTxyy/FedIA.
FedMLP: Federated Multi-Label Medical Image Classification under Task Heterogeneity
Jun 27, 2024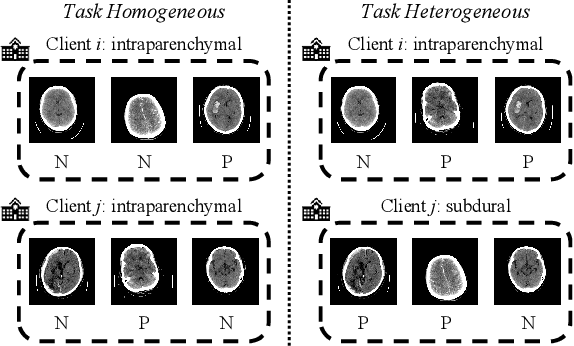
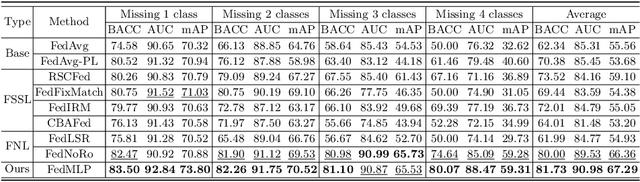
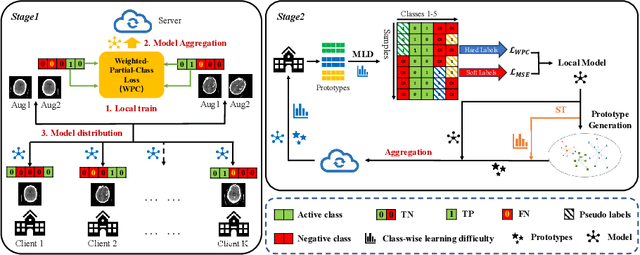
Abstract:Cross-silo federated learning (FL) enables decentralized organizations to collaboratively train models while preserving data privacy and has made significant progress in medical image classification. One common assumption is task homogeneity where each client has access to all classes during training. However, in clinical practice, given a multi-label classification task, constrained by the level of medical knowledge and the prevalence of diseases, each institution may diagnose only partial categories, resulting in task heterogeneity. How to pursue effective multi-label medical image classification under task heterogeneity is under-explored. In this paper, we first formulate such a realistic label missing setting in the multi-label FL domain and propose a two-stage method FedMLP to combat class missing from two aspects: pseudo label tagging and global knowledge learning. The former utilizes a warmed-up model to generate class prototypes and select samples with high confidence to supplement missing labels, while the latter uses a global model as a teacher for consistency regularization to prevent forgetting missing class knowledge. Experiments on two publicly-available medical datasets validate the superiority of FedMLP against the state-of-the-art both federated semi-supervised and noisy label learning approaches under task heterogeneity. Code is available at https://github.com/szbonaldo/FedMLP.
From Optimization to Generalization: Fair Federated Learning against Quality Shift via Inter-Client Sharpness Matching
Apr 27, 2024
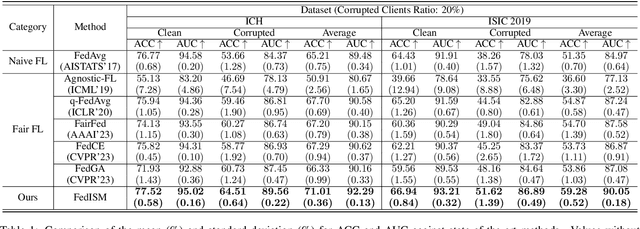


Abstract:Due to escalating privacy concerns, federated learning has been recognized as a vital approach for training deep neural networks with decentralized medical data. In practice, it is challenging to ensure consistent imaging quality across various institutions, often attributed to equipment malfunctions affecting a minority of clients. This imbalance in image quality can cause the federated model to develop an inherent bias towards higher-quality images, thus posing a severe fairness issue. In this study, we pioneer the identification and formulation of this new fairness challenge within the context of the imaging quality shift. Traditional methods for promoting fairness in federated learning predominantly focus on balancing empirical risks across diverse client distributions. This strategy primarily facilitates fair optimization across different training data distributions, yet neglects the crucial aspect of generalization. To address this, we introduce a solution termed Federated learning with Inter-client Sharpness Matching (FedISM). FedISM enhances both local training and global aggregation by incorporating sharpness-awareness, aiming to harmonize the sharpness levels across clients for fair generalization. Our empirical evaluations, conducted using the widely-used ICH and ISIC 2019 datasets, establish FedISM's superiority over current state-of-the-art federated learning methods in promoting fairness. Code is available at https://github.com/wnn2000/FFL4MIA.
SAMCT: Segment Any CT Allowing Labor-Free Task-Indicator Prompts
Mar 20, 2024



Abstract:Segment anything model (SAM), a foundation model with superior versatility and generalization across diverse segmentation tasks, has attracted widespread attention in medical imaging. However, it has been proved that SAM would encounter severe performance degradation due to the lack of medical knowledge in training and local feature encoding. Though several SAM-based models have been proposed for tuning SAM in medical imaging, they still suffer from insufficient feature extraction and highly rely on high-quality prompts. In this paper, we construct a large CT dataset consisting of 1.1M CT images and 5M masks from public datasets and propose a powerful foundation model SAMCT allowing labor-free prompts. Specifically, based on SAM, SAMCT is further equipped with a U-shaped CNN image encoder, a cross-branch interaction module, and a task-indicator prompt encoder. The U-shaped CNN image encoder works in parallel with the ViT image encoder in SAM to supplement local features. Cross-branch interaction enhances the feature expression capability of the CNN image encoder and the ViT image encoder by exchanging global perception and local features from one to the other. The task-indicator prompt encoder is a plug-and-play component to effortlessly encode task-related indicators into prompt embeddings. In this way, SAMCT can work in an automatic manner in addition to the semi-automatic interactive strategy in SAM. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of SAMCT against the state-of-the-art task-specific and SAM-based medical foundation models on various tasks. The code, data, and models are released at https://github.com/xianlin7/SAMCT.
FedA3I: Annotation Quality-Aware Aggregation for Federated Medical Image Segmentation Against Heterogeneous Annotation Noise
Dec 20, 2023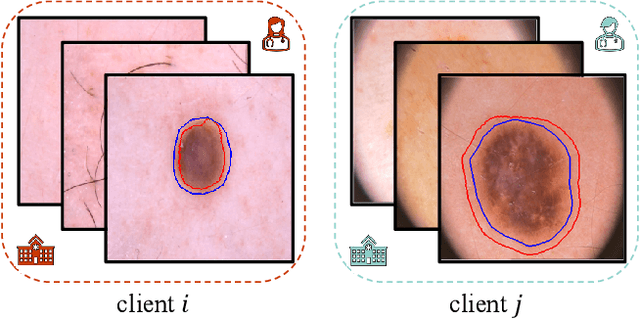

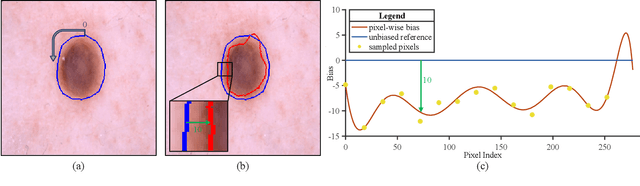
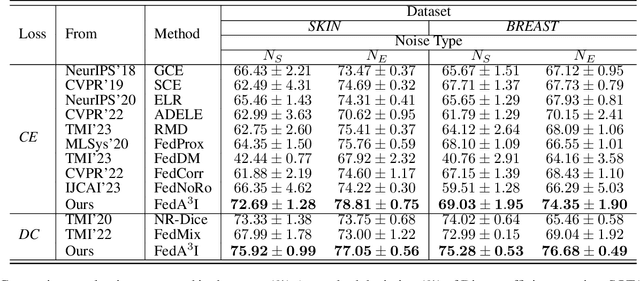
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a promising paradigm for training segmentation models on decentralized medical data, owing to its privacy-preserving property. However, existing research overlooks the prevalent annotation noise encountered in real-world medical datasets, which limits the performance ceilings of FL. In this paper, we, for the first time, identify and tackle this problem. For problem formulation, we propose a contour evolution for modeling non-independent and identically distributed (Non-IID) noise across pixels within each client and then extend it to the case of multi-source data to form a heterogeneous noise model (\textit{i.e.}, Non-IID annotation noise across clients). For robust learning from annotations with such two-level Non-IID noise, we emphasize the importance of data quality in model aggregation, allowing high-quality clients to have a greater impact on FL. To achieve this, we propose \textbf{Fed}erated learning with \textbf{A}nnotation qu\textbf{A}lity-aware \textbf{A}ggregat\textbf{I}on, named \textbf{FedA$^3$I}, by introducing a quality factor based on client-wise noise estimation. Specifically, noise estimation at each client is accomplished through the Gaussian mixture model and then incorporated into model aggregation in a layer-wise manner to up-weight high-quality clients. Extensive experiments on two real-world medical image segmentation datasets demonstrate the superior performance of FedA$^3$I against the state-of-the-art approaches in dealing with cross-client annotation noise. The code is available at \color{blue}{https://github.com/wnn2000/FedAAAI}.
SAMUS: Adapting Segment Anything Model for Clinically-Friendly and Generalizable Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Sep 13, 2023Abstract:Segment anything model (SAM), an eminent universal image segmentation model, has recently gathered considerable attention within the domain of medical image segmentation. Despite the remarkable performance of SAM on natural images, it grapples with significant performance degradation and limited generalization when confronted with medical images, particularly with those involving objects of low contrast, faint boundaries, intricate shapes, and diminutive sizes. In this paper, we propose SAMUS, a universal model tailored for ultrasound image segmentation. In contrast to previous SAM-based universal models, SAMUS pursues not only better generalization but also lower deployment cost, rendering it more suitable for clinical applications. Specifically, based on SAM, a parallel CNN branch is introduced to inject local features into the ViT encoder through cross-branch attention for better medical image segmentation. Then, a position adapter and a feature adapter are developed to adapt SAM from natural to medical domains and from requiring large-size inputs (1024x1024) to small-size inputs (256x256) for more clinical-friendly deployment. A comprehensive ultrasound dataset, comprising about 30k images and 69k masks and covering six object categories, is collected for verification. Extensive comparison experiments demonstrate SAMUS's superiority against the state-of-the-art task-specific models and universal foundation models under both task-specific evaluation and generalization evaluation. Moreover, SAMUS is deployable on entry-level GPUs, as it has been liberated from the constraints of long sequence encoding. The code, data, and models will be released at https://github.com/xianlin7/SAMUS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge