Zhuo Kuang
Fair Federated Medical Image Classification Against Quality Shift via Inter-Client Progressive State Matching
Mar 12, 2025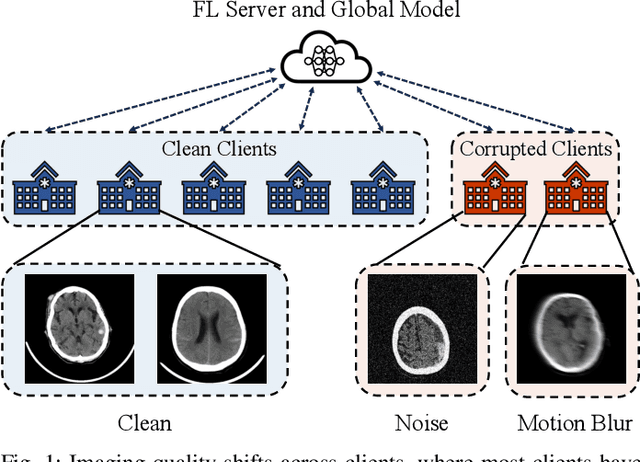
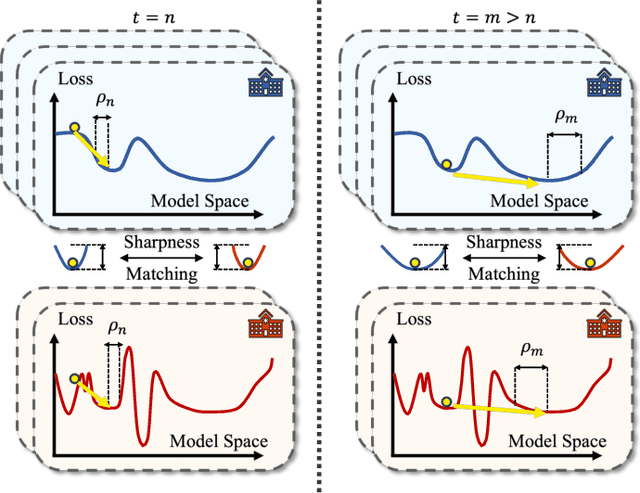
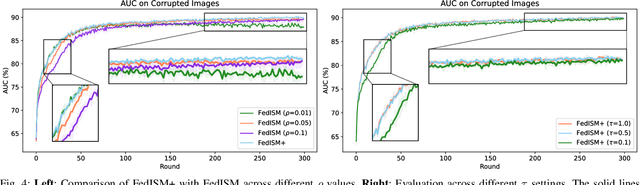
Abstract:Despite the potential of federated learning in medical applications, inconsistent imaging quality across institutions-stemming from lower-quality data from a minority of clients-biases federated models toward more common high-quality images. This raises significant fairness concerns. Existing fair federated learning methods have demonstrated some effectiveness in solving this problem by aligning a single 0th- or 1st-order state of convergence (e.g., training loss or sharpness). However, we argue in this work that fairness based on such a single state is still not an adequate surrogate for fairness during testing, as these single metrics fail to fully capture the convergence characteristics, making them suboptimal for guiding fair learning. To address this limitation, we develop a generalized framework. Specifically, we propose assessing convergence using multiple states, defined as sharpness or perturbed loss computed at varying search distances. Building on this comprehensive assessment, we propose promoting fairness for these states across clients to achieve our ultimate fairness objective. This is accomplished through the proposed method, FedISM+. In FedISM+, the search distance evolves over time, progressively focusing on different states. We then incorporate two components in local training and global aggregation to ensure cross-client fairness for each state. This gradually makes convergence equitable for all states, thereby improving fairness during testing. Our empirical evaluations, performed on the well-known RSNA ICH and ISIC 2019 datasets, demonstrate the superiority of FedISM+ over existing state-of-the-art methods for fair federated learning. The code is available at https://github.com/wnn2000/FFL4MIA.
From Optimization to Generalization: Fair Federated Learning against Quality Shift via Inter-Client Sharpness Matching
Apr 27, 2024
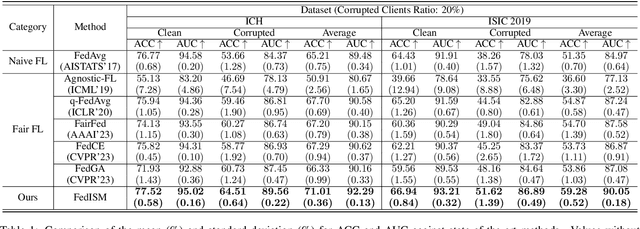


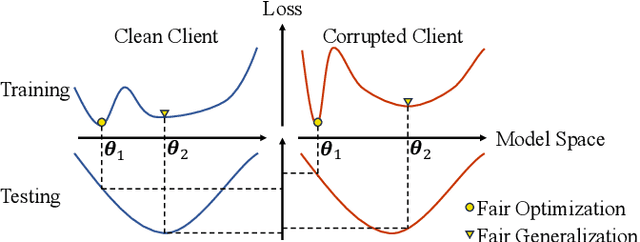
Abstract:Due to escalating privacy concerns, federated learning has been recognized as a vital approach for training deep neural networks with decentralized medical data. In practice, it is challenging to ensure consistent imaging quality across various institutions, often attributed to equipment malfunctions affecting a minority of clients. This imbalance in image quality can cause the federated model to develop an inherent bias towards higher-quality images, thus posing a severe fairness issue. In this study, we pioneer the identification and formulation of this new fairness challenge within the context of the imaging quality shift. Traditional methods for promoting fairness in federated learning predominantly focus on balancing empirical risks across diverse client distributions. This strategy primarily facilitates fair optimization across different training data distributions, yet neglects the crucial aspect of generalization. To address this, we introduce a solution termed Federated learning with Inter-client Sharpness Matching (FedISM). FedISM enhances both local training and global aggregation by incorporating sharpness-awareness, aiming to harmonize the sharpness levels across clients for fair generalization. Our empirical evaluations, conducted using the widely-used ICH and ISIC 2019 datasets, establish FedISM's superiority over current state-of-the-art federated learning methods in promoting fairness. Code is available at https://github.com/wnn2000/FFL4MIA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge