Erik Rodner
In Search of Grandmother Cells: Tracing Interpretable Neurons in Tabular Representations
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Foundation models are powerful yet often opaque in their decision-making. A topic of continued interest in both neuroscience and artificial intelligence is whether some neurons behave like grandmother cells, i.e., neurons that are inherently interpretable because they exclusively respond to single concepts. In this work, we propose two information-theoretic measures that quantify the neuronal saliency and selectivity for single concepts. We apply these metrics to the representations of TabPFN, a tabular foundation model, and perform a simple search across neuron-concept pairs to find the most salient and selective pair. Our analysis provides the first evidence that some neurons in such models show moderate, statistically significant saliency and selectivity for high-level concepts. These findings suggest that interpretable neurons can emerge naturally and that they can, in some cases, be identified without resorting to more complex interpretability techniques.
Is Visual in-Context Learning for Compositional Medical Tasks within Reach?
Jul 02, 2025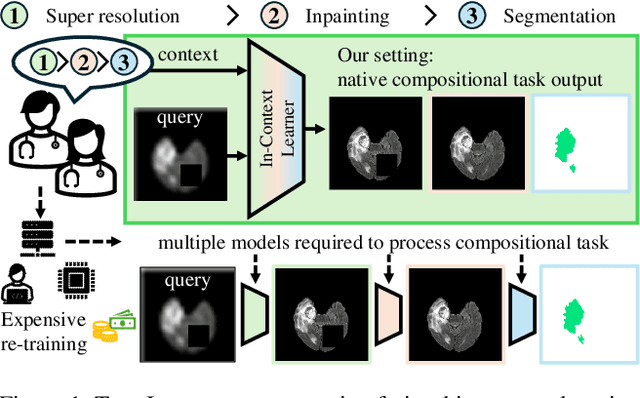
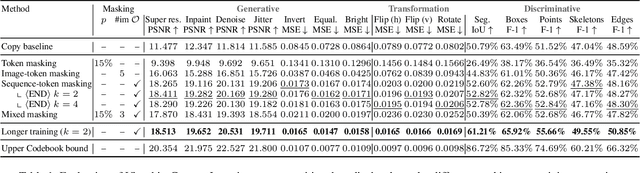
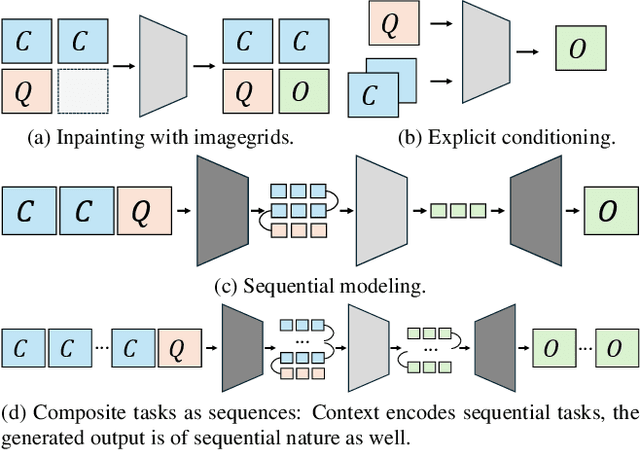
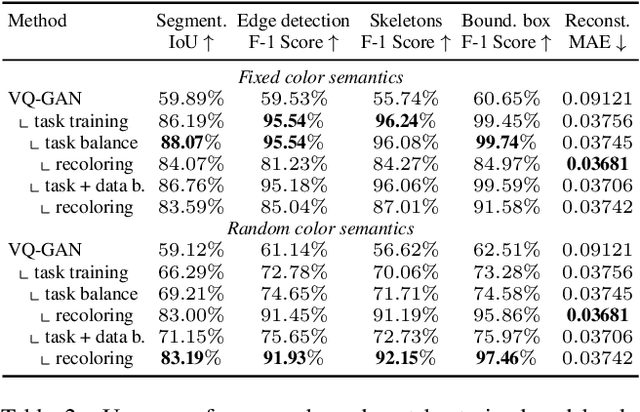
Abstract:In this paper, we explore the potential of visual in-context learning to enable a single model to handle multiple tasks and adapt to new tasks during test time without re-training. Unlike previous approaches, our focus is on training in-context learners to adapt to sequences of tasks, rather than individual tasks. Our goal is to solve complex tasks that involve multiple intermediate steps using a single model, allowing users to define entire vision pipelines flexibly at test time. To achieve this, we first examine the properties and limitations of visual in-context learning architectures, with a particular focus on the role of codebooks. We then introduce a novel method for training in-context learners using a synthetic compositional task generation engine. This engine bootstraps task sequences from arbitrary segmentation datasets, enabling the training of visual in-context learners for compositional tasks. Additionally, we investigate different masking-based training objectives to gather insights into how to train models better for solving complex, compositional tasks. Our exploration not only provides important insights especially for multi-modal medical task sequences but also highlights challenges that need to be addressed.
Robust Weight Imprinting: Insights from Neural Collapse and Proxy-Based Aggregation
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:The capacity of a foundation model allows for adaptation to new downstream tasks. Weight imprinting is a universal and efficient method to fulfill this purpose. It has been reinvented several times, but it has not been systematically studied. In this paper, we propose a framework for imprinting, identifying three main components: generation, normalization, and aggregation. This allows us to conduct an in-depth analysis of imprinting and a comparison of the existing work. We reveal the benefits of representing novel data with multiple proxies in the generation step and show the importance of proper normalization. We determine those proxies through clustering and propose a novel variant of imprinting that outperforms previous work. We motivate this by the neural collapse phenomenon -- an important connection that we can draw for the first time. Our results show an increase of up to 4% in challenging scenarios with complex data distributions for new classes.
Feedback-driven object detection and iterative model improvement
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Automated object detection has become increasingly valuable across diverse applications, yet efficient, high-quality annotation remains a persistent challenge. In this paper, we present the development and evaluation of a platform designed to interactively improve object detection models. The platform allows uploading and annotating images as well as fine-tuning object detection models. Users can then manually review and refine annotations, further creating improved snapshots that are used for automatic object detection on subsequent image uploads - a process we refer to as semi-automatic annotation resulting in a significant gain in annotation efficiency. Whereas iterative refinement of model results to speed up annotation has become common practice, we are the first to quantitatively evaluate its benefits with respect to time, effort, and interaction savings. Our experimental results show clear evidence for a significant time reduction of up to 53% for semi-automatic compared to manual annotation. Importantly, these efficiency gains did not compromise annotation quality, while matching or occasionally even exceeding the accuracy of manual annotations. These findings demonstrate the potential of our lightweight annotation platform for creating high-quality object detection datasets and provide best practices to guide future development of annotation platforms. The platform is open-source, with the frontend and backend repositories available on GitHub.
"Oh LLM, I'm Asking Thee, Please Give Me a Decision Tree": Zero-Shot Decision Tree Induction and Embedding with Large Language Models
Sep 27, 2024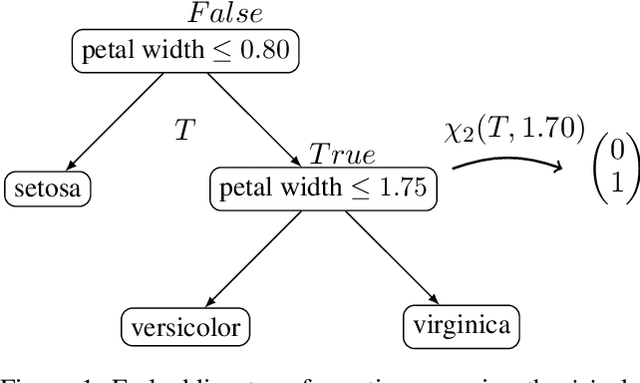
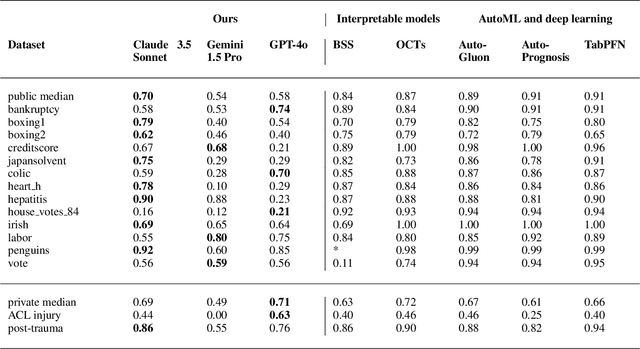
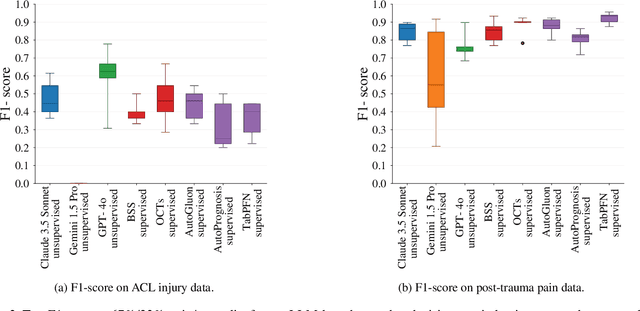
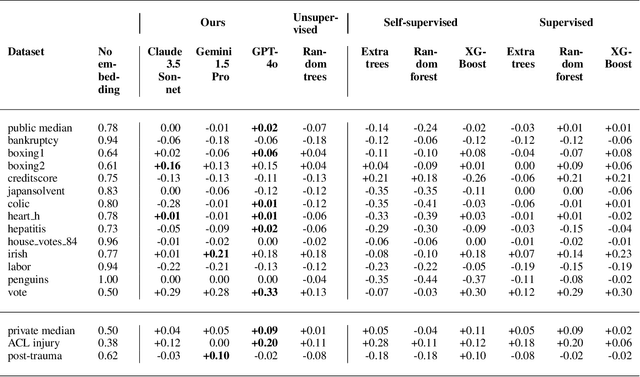
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) provide powerful means to leverage prior knowledge for predictive modeling when data is limited. In this work, we demonstrate how LLMs can use their compressed world knowledge to generate intrinsically interpretable machine learning models, i.e., decision trees, without any training data. We find that these zero-shot decision trees can surpass data-driven trees on some small-sized tabular datasets and that embeddings derived from these trees perform on par with data-driven tree-based embeddings on average. Our knowledge-driven decision tree induction and embedding approaches therefore serve as strong new baselines for data-driven machine learning methods in the low-data regime.
PMLBmini: A Tabular Classification Benchmark Suite for Data-Scarce Applications
Sep 03, 2024



Abstract:In practice, we are often faced with small-sized tabular data. However, current tabular benchmarks are not geared towards data-scarce applications, making it very difficult to derive meaningful conclusions from empirical comparisons. We introduce PMLBmini, a tabular benchmark suite of 44 binary classification datasets with sample sizes $\leq$ 500. We use our suite to thoroughly evaluate current automated machine learning (AutoML) frameworks, off-the-shelf tabular deep neural networks, as well as classical linear models in the low-data regime. Our analysis reveals that state-of-the-art AutoML and deep learning approaches often fail to appreciably outperform even a simple logistic regression baseline, but we also identify scenarios where AutoML and deep learning methods are indeed reasonable to apply. Our benchmark suite, available on https://github.com/RicardoKnauer/TabMini , allows researchers and practitioners to analyze their own methods and challenge their data efficiency.
Squeezing Lemons with Hammers: An Evaluation of AutoML and Tabular Deep Learning for Data-Scarce Classification Applications
May 13, 2024Abstract:Many industry verticals are confronted with small-sized tabular data. In this low-data regime, it is currently unclear whether the best performance can be expected from simple baselines, or more complex machine learning approaches that leverage meta-learning and ensembling. On 44 tabular classification datasets with sample sizes $\leq$ 500, we find that L2-regularized logistic regression performs similar to state-of-the-art automated machine learning (AutoML) frameworks (AutoPrognosis, AutoGluon) and off-the-shelf deep neural networks (TabPFN, HyperFast) on the majority of the benchmark datasets. We therefore recommend to consider logistic regression as the first choice for data-scarce applications with tabular data and provide practitioners with best practices for further method selection.
Cost-Sensitive Best Subset Selection for Logistic Regression: A Mixed-Integer Conic Optimization Perspective
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:A key challenge in machine learning is to design interpretable models that can reduce their inputs to the best subset for making transparent predictions, especially in the clinical domain. In this work, we propose a certifiably optimal feature selection procedure for logistic regression from a mixed-integer conic optimization perspective that can take an auxiliary cost to obtain features into account. Based on an extensive review of the literature, we carefully create a synthetic dataset generator for clinical prognostic model research. This allows us to systematically evaluate different heuristic and optimal cardinality- and budget-constrained feature selection procedures. The analysis shows key limitations of the methods for the low-data regime and when confronted with label noise. Our paper not only provides empirical recommendations for suitable methods and dataset designs, but also paves the way for future research in the area of meta-learning.
CAD Models to Real-World Images: A Practical Approach to Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Industrial Object Classification
Oct 07, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we systematically analyze unsupervised domain adaptation pipelines for object classification in a challenging industrial setting. In contrast to standard natural object benchmarks existing in the field, our results highlight the most important design choices when only category-labeled CAD models are available but classification needs to be done with real-world images. Our domain adaptation pipeline achieves SoTA performance on the VisDA benchmark, but more importantly, drastically improves recognition performance on our new open industrial dataset comprised of 102 mechanical parts. We conclude with a set of guidelines that are relevant for practitioners needing to apply state-of-the-art unsupervised domain adaptation in practice. Our code is available at https://github.com/dritter-bht/synthnet-transfer-learning.
Evaluating Zero-cost Active Learning for Object Detection
Dec 08, 2022Abstract:Object detection requires substantial labeling effort for learning robust models. Active learning can reduce this effort by intelligently selecting relevant examples to be annotated. However, selecting these examples properly without introducing a sampling bias with a negative impact on the generalization performance is not straightforward and most active learning techniques can not hold their promises on real-world benchmarks. In our evaluation paper, we focus on active learning techniques without a computational overhead besides inference, something we refer to as zero-cost active learning. In particular, we show that a key ingredient is not only the score on a bounding box level but also the technique used for aggregating the scores for ranking images. We outline our experimental setup and also discuss practical considerations when using active learning for object detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge