Endri Kacupaj
OEKG: The Open Event Knowledge Graph
Feb 28, 2023



Abstract:Accessing and understanding contemporary and historical events of global impact such as the US elections and the Olympic Games is a major prerequisite for cross-lingual event analytics that investigate event causes, perception and consequences across country borders. In this paper, we present the Open Event Knowledge Graph (OEKG), a multilingual, event-centric, temporal knowledge graph composed of seven different data sets from multiple application domains, including question answering, entity recommendation and named entity recognition. These data sets are all integrated through an easy-to-use and robust pipeline and by linking to the event-centric knowledge graph EventKG. We describe their common schema and demonstrate the use of the OEKG at the example of three use cases: type-specific image retrieval, hybrid question answering over knowledge graphs and news articles, as well as language-specific event recommendation. The OEKG and its query endpoint are publicly available.
Contrastive Representation Learning for Conversational Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs
Oct 09, 2022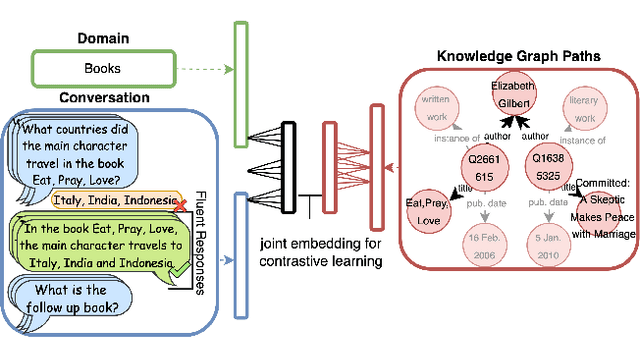
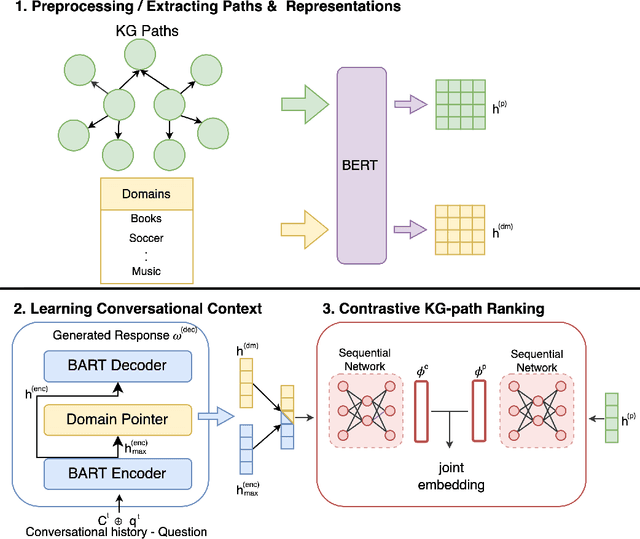
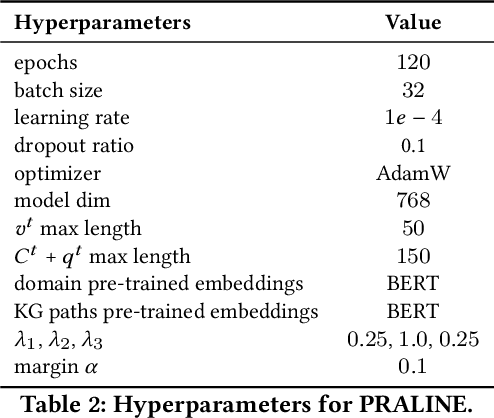
Abstract:This paper addresses the task of conversational question answering (ConvQA) over knowledge graphs (KGs). The majority of existing ConvQA methods rely on full supervision signals with a strict assumption of the availability of gold logical forms of queries to extract answers from the KG. However, creating such a gold logical form is not viable for each potential question in a real-world scenario. Hence, in the case of missing gold logical forms, the existing information retrieval-based approaches use weak supervision via heuristics or reinforcement learning, formulating ConvQA as a KG path ranking problem. Despite missing gold logical forms, an abundance of conversational contexts, such as entire dialog history with fluent responses and domain information, can be incorporated to effectively reach the correct KG path. This work proposes a contrastive representation learning-based approach to rank KG paths effectively. Our approach solves two key challenges. Firstly, it allows weak supervision-based learning that omits the necessity of gold annotations. Second, it incorporates the conversational context (entire dialog history and domain information) to jointly learn its homogeneous representation with KG paths to improve contrastive representations for effective path ranking. We evaluate our approach on standard datasets for ConvQA, on which it significantly outperforms existing baselines on all domains and overall. Specifically, in some cases, the Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR) and Hit@5 ranking metrics improve by absolute 10 and 18 points, respectively, compared to the state-of-the-art performance.
An Answer Verbalization Dataset for Conversational Question Answerings over Knowledge Graphs
Aug 13, 2022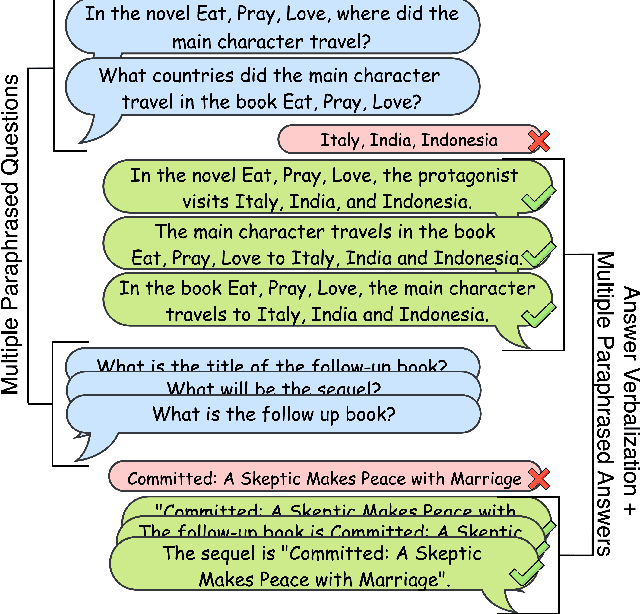

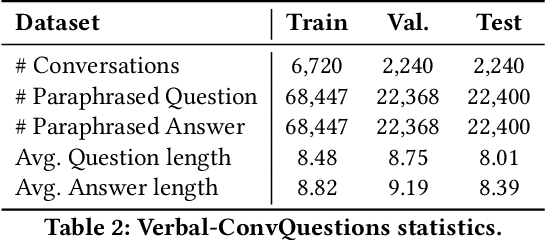
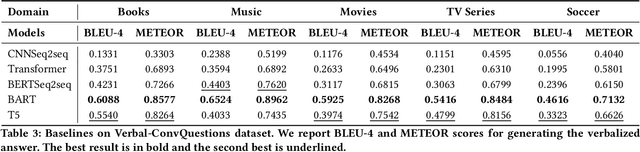
Abstract:We introduce a new dataset for conversational question answering over Knowledge Graphs (KGs) with verbalized answers. Question answering over KGs is currently focused on answer generation for single-turn questions (KGQA) or multiple-tun conversational question answering (ConvQA). However, in a real-world scenario (e.g., voice assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant), users prefer verbalized answers. This paper contributes to the state-of-the-art by extending an existing ConvQA dataset with multiple paraphrased verbalized answers. We perform experiments with five sequence-to-sequence models on generating answer responses while maintaining grammatical correctness. We additionally perform an error analysis that details the rates of models' mispredictions in specified categories. Our proposed dataset extended with answer verbalization is publicly available with detailed documentation on its usage for wider utility.
VOGUE: Answer Verbalization through Multi-Task Learning
Jun 28, 2021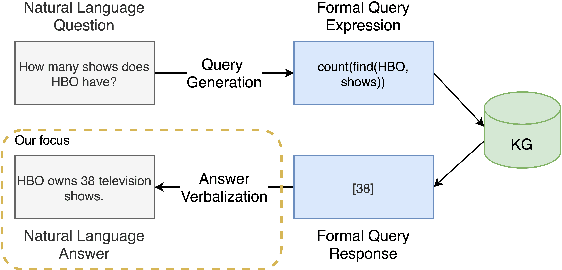
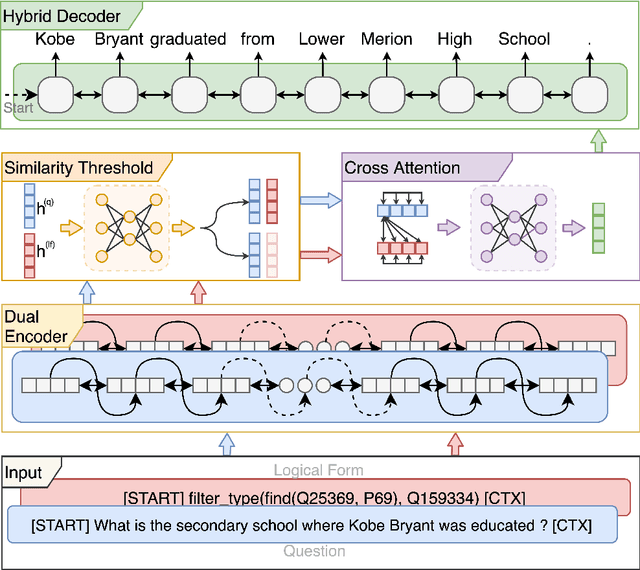
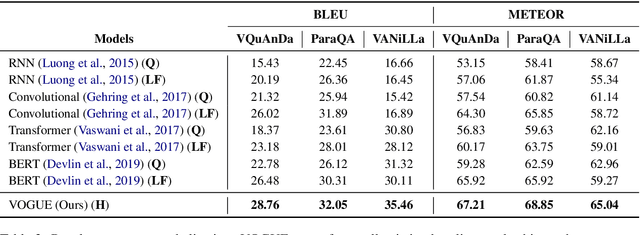
Abstract:In recent years, there have been significant developments in Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs (KGQA). Despite all the notable advancements, current KGQA systems only focus on answer generation techniques and not on answer verbalization. However, in real-world scenarios (e.g., voice assistants such as Alexa, Siri, etc.), users prefer verbalized answers instead of a generated response. This paper addresses the task of answer verbalization for (complex) question answering over knowledge graphs. In this context, we propose a multi-task-based answer verbalization framework: VOGUE (Verbalization thrOuGh mUlti-task lEarning). The VOGUE framework attempts to generate a verbalized answer using a hybrid approach through a multi-task learning paradigm. Our framework can generate results based on using questions and queries as inputs concurrently. VOGUE comprises four modules that are trained simultaneously through multi-task learning. We evaluate our framework on existing datasets for answer verbalization, and it outperforms all current baselines on both BLEU and METEOR scores.
GeoWINE: Geolocation based Wiki, Image,News and Event Retrieval
May 04, 2021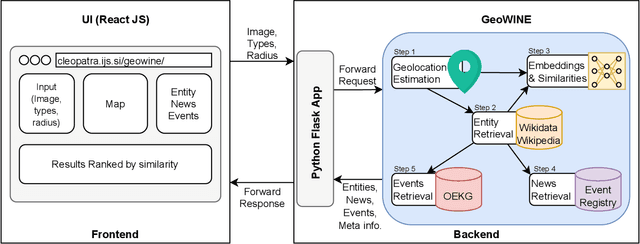
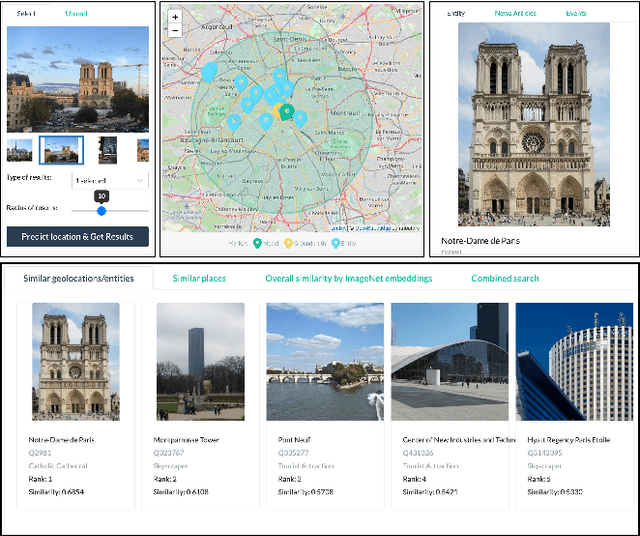
Abstract:In the context of social media, geolocation inference on news or events has become a very important task. In this paper, we present the GeoWINE (Geolocation-based Wiki-Image-News-Event retrieval) demonstrator, an effective modular system for multimodal retrieval which expects only a single image as input. The GeoWINE system consists of five modules in order to retrieve related information from various sources. The first module is a state-of-the-art model for geolocation estimation of images. The second module performs a geospatial-based query for entity retrieval using the Wikidata knowledge graph. The third module exploits four different image embedding representations, which are used to retrieve most similar entities compared to the input image. The embeddings are derived from the tasks of geolocation estimation, place recognition, ImageNet-based image classification, and their combination. The last two modules perform news and event retrieval from EventRegistry and the Open Event Knowledge Graph (OEKG). GeoWINE provides an intuitive interface for end-users and is insightful for experts for reconfiguration to individual setups. The GeoWINE achieves promising results in entity label prediction for images on Google Landmarks dataset. The demonstrator is publicly available at http://cleopatra.ijs.si/geowine/.
Conversational Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs with Transformer and Graph Attention Networks
Apr 04, 2021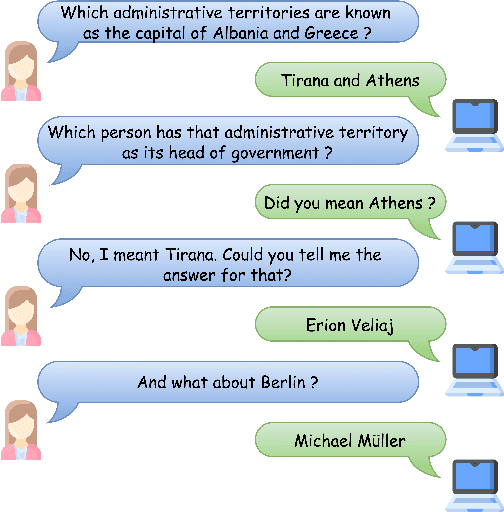
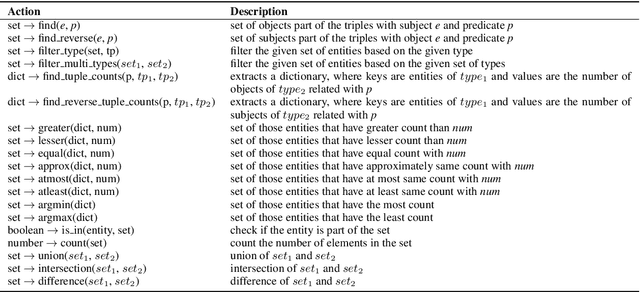
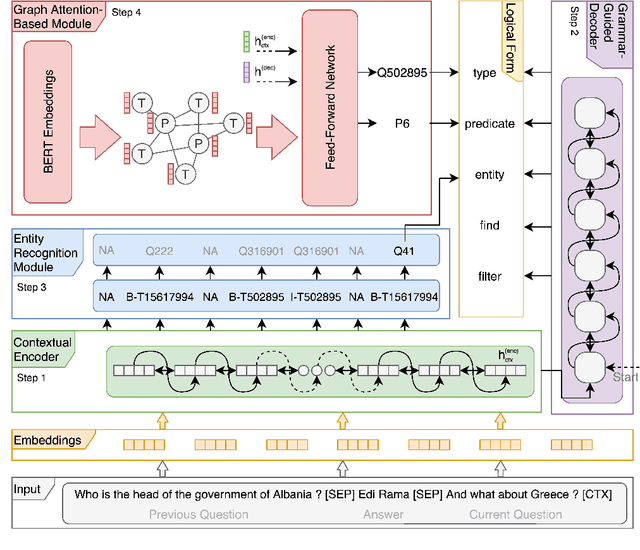
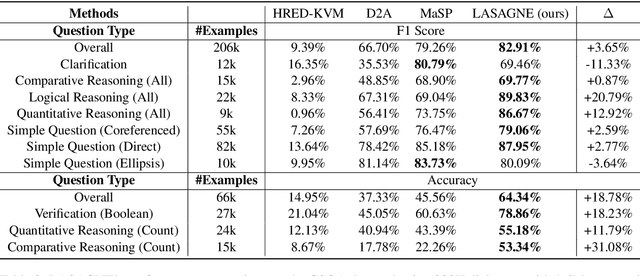
Abstract:This paper addresses the task of (complex) conversational question answering over a knowledge graph. For this task, we propose LASAGNE (muLti-task semAntic parSing with trAnsformer and Graph atteNtion nEtworks). It is the first approach, which employs a transformer architecture extended with Graph Attention Networks for multi-task neural semantic parsing. LASAGNE uses a transformer model for generating the base logical forms, while the Graph Attention model is used to exploit correlations between (entity) types and predicates to produce node representations. LASAGNE also includes a novel entity recognition module which detects, links, and ranks all relevant entities in the question context. We evaluate LASAGNE on a standard dataset for complex sequential question answering, on which it outperforms existing baseline averages on all question types. Specifically, we show that LASAGNE improves the F1-score on eight out of ten question types; in some cases, the increase in F1-score is more than 20% compared to the state of the art.
Demographic Aware Probabilistic Medical Knowledge Graph Embeddings of Electronic Medical Records
Apr 03, 2021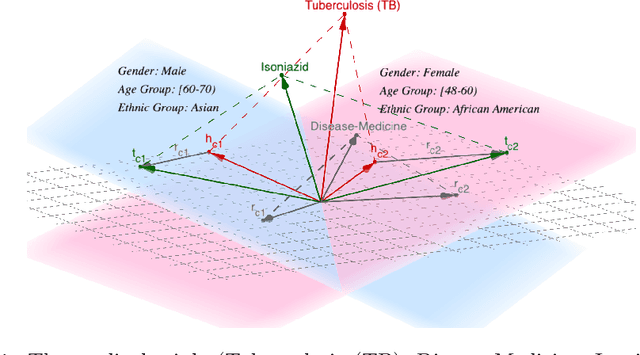
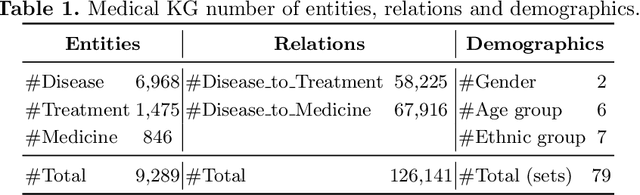
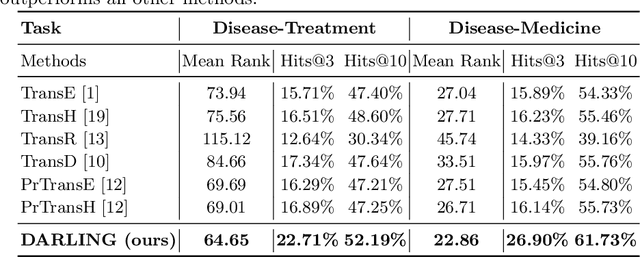
Abstract:Medical knowledge graphs (KGs) constructed from Electronic Medical Records (EMR) contain abundant information about patients and medical entities. The utilization of KG embedding models on these data has proven to be efficient for different medical tasks. However, existing models do not properly incorporate patient demographics and most of them ignore the probabilistic features of the medical KG. In this paper, we propose DARLING (Demographic Aware pRobabiListic medIcal kNowledge embeddinG), a demographic-aware medical KG embedding framework that explicitly incorporates demographics in the medical entities space by associating patient demographics with a corresponding hyperplane. Our framework leverages the probabilistic features within the medical entities for learning their representations through demographic guidance. We evaluate DARLING through link prediction for treatments and medicines, on a medical KG constructed from EMR data, and illustrate its superior performance compared to existing KG embedding models.
ParaQA: A Question Answering Dataset with Paraphrase Responses for Single-Turn Conversation
Mar 13, 2021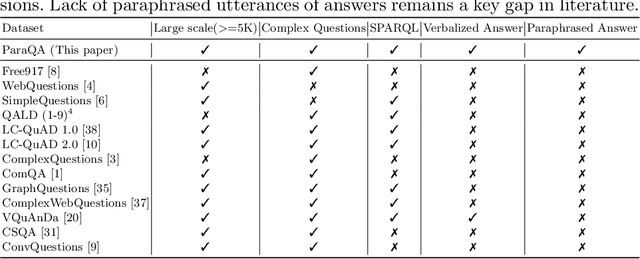
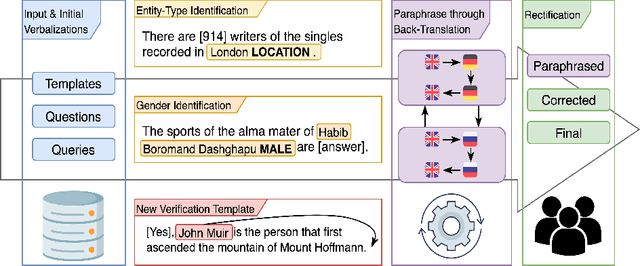
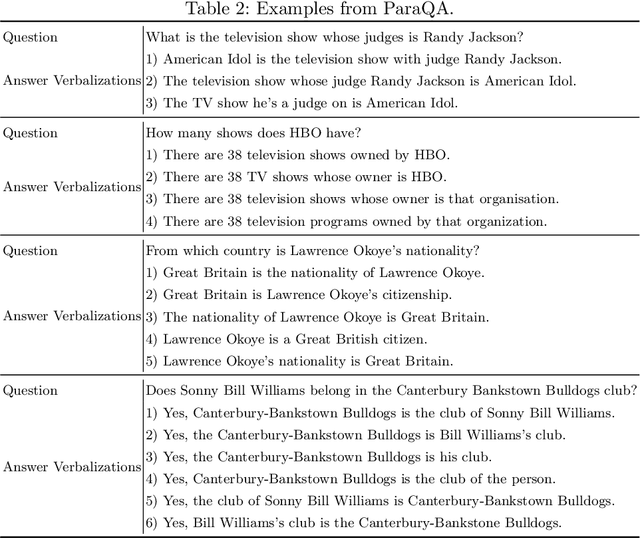
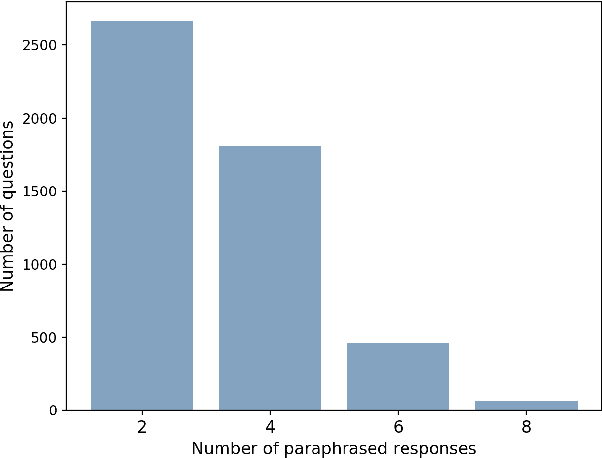
Abstract:This paper presents ParaQA, a question answering (QA) dataset with multiple paraphrased responses for single-turn conversation over knowledge graphs (KG). The dataset was created using a semi-automated framework for generating diverse paraphrasing of the answers using techniques such as back-translation. The existing datasets for conversational question answering over KGs (single-turn/multi-turn) focus on question paraphrasing and provide only up to one answer verbalization. However, ParaQA contains 5000 question-answer pairs with a minimum of two and a maximum of eight unique paraphrased responses for each question. We complement the dataset with baseline models and illustrate the advantage of having multiple paraphrased answers through commonly used metrics such as BLEU and METEOR. The ParaQA dataset is publicly available on a persistent URI for broader usage and adaptation in the research community.
Context Transformer with Stacked Pointer Networks for Conversational Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs
Mar 13, 2021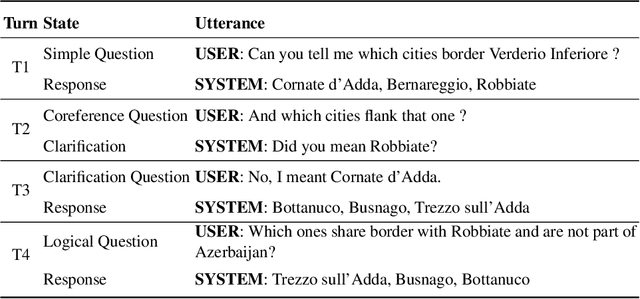
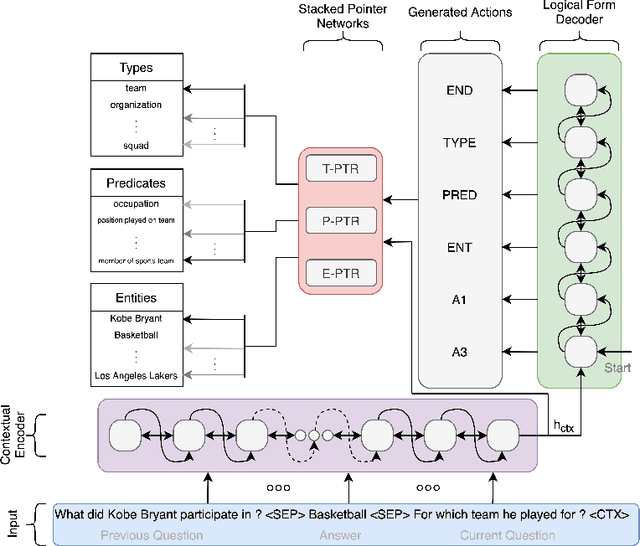
Abstract:Neural semantic parsing approaches have been widely used for Question Answering (QA) systems over knowledge graphs. Such methods provide the flexibility to handle QA datasets with complex queries and a large number of entities. In this work, we propose a novel framework named CARTON, which performs multi-task semantic parsing for handling the problem of conversational question answering over a large-scale knowledge graph. Our framework consists of a stack of pointer networks as an extension of a context transformer model for parsing the input question and the dialog history. The framework generates a sequence of actions that can be executed on the knowledge graph. We evaluate CARTON on a standard dataset for complex sequential question answering on which CARTON outperforms all baselines. Specifically, we observe performance improvements in F1-score on eight out of ten question types compared to the previous state of the art. For logical reasoning questions, an improvement of 11 absolute points is reached.
MLM: A Benchmark Dataset for Multitask Learning with Multiple Languages and Modalities
Sep 04, 2020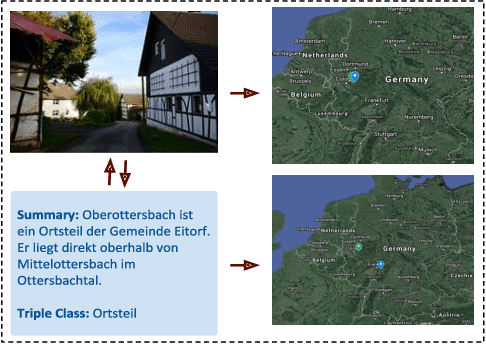
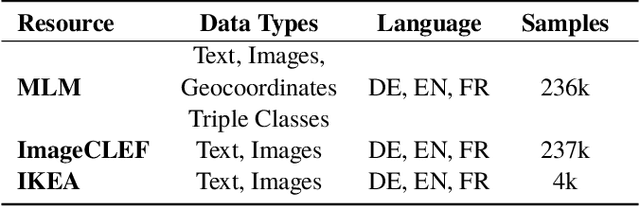
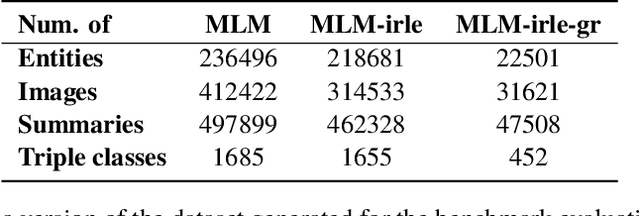
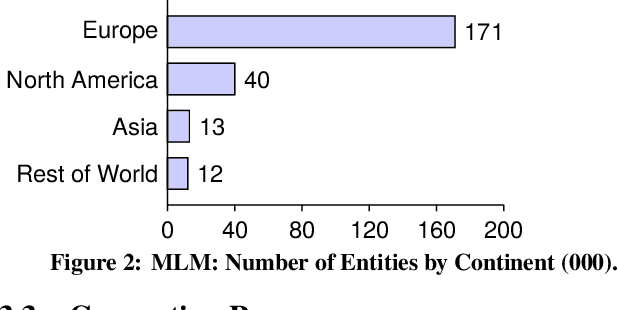
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the MLM (Multiple Languages and Modalities) dataset - a new resource to train and evaluate multitask systems on samples in multiple modalities and three languages. The generation process and inclusion of semantic data provide a resource that further tests the ability for multitask systems to learn relationships between entities. The dataset is designed for researchers and developers who build applications that perform multiple tasks on data encountered on the web and in digital archives. A second version of MLM provides a geo-representative subset of the data with weighted samples for countries of the European Union. We demonstrate the value of the resource in developing novel applications in the digital humanities with a motivating use case and specify a benchmark set of tasks to retrieve modalities and locate entities in the dataset. Evaluation of baseline multitask and single task systems on the full and geo-representative versions of MLM demonstrate the challenges of generalising on diverse data. In addition to the digital humanities, we expect the resource to contribute to research in multimodal representation learning, location estimation, and scene understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge