Dwaipayan Roy
Cultural Analytics for Good: Building Inclusive Evaluation Frameworks for Historical IR
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:This work bridges the fields of information retrieval and cultural analytics to support equitable access to historical knowledge. Using the British Library BL19 digital collection (more than 35,000 works from 1700-1899), we construct a benchmark for studying changes in language, terminology and retrieval in the 19th-century fiction and non-fiction. Our approach combines expert-driven query design, paragraph-level relevance annotation, and Large Language Model (LLM) assistance to create a scalable evaluation framework grounded in human expertise. We focus on knowledge transfer from fiction to non-fiction, investigating how narrative understanding and semantic richness in fiction can improve retrieval for scholarly and factual materials. This interdisciplinary framework not only improves retrieval accuracy but also fosters interpretability, transparency, and cultural inclusivity in digital archives. Our work provides both practical evaluation resources and a methodological paradigm for developing retrieval systems that support richer, historically aware engagement with digital archives, ultimately working towards more emancipatory knowledge infrastructures.
FACTors: A New Dataset for Studying the Fact-checking Ecosystem
May 14, 2025Abstract:Our fight against false information is spearheaded by fact-checkers. They investigate the veracity of claims and document their findings as fact-checking reports. With the rapid increase in the amount of false information circulating online, the use of automation in fact-checking processes aims to strengthen this ecosystem by enhancing scalability. Datasets containing fact-checked claims play a key role in developing such automated solutions. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no fact-checking dataset at the ecosystem level, covering claims from a sufficiently long period of time and sourced from a wide range of actors reflecting the entire ecosystem that admittedly follows widely-accepted codes and principles of fact-checking. We present a new dataset FACTors, the first to fill this gap by presenting ecosystem-level data on fact-checking. It contains 118,112 claims from 117,993 fact-checking reports in English (co-)authored by 1,953 individuals and published during the period of 1995-2025 by 39 fact-checking organisations that are active signatories of the IFCN (International Fact-Checking Network) and/or EFCSN (European Fact-Checking Standards Network). It contains 7,327 overlapping claims investigated by multiple fact-checking organisations, corresponding to 2,977 unique claims. It allows to conduct new ecosystem-level studies of the fact-checkers (organisations and individuals). To demonstrate the usefulness of FACTors, we present three example applications, including a first-of-its-kind statistical analysis of the fact-checking ecosystem, examining the political inclinations of the fact-checking organisations, and attempting to assign a credibility score to each organisation based on the findings of the statistical analysis and political leanings. Our methods for constructing FACTors are generic and can be used to maintain a live dataset that can be updated dynamically.
Combining Query Performance Predictors: A Reproducibility Study
Mar 31, 2025



Abstract:A large number of approaches to Query Performance Prediction (QPP) have been proposed over the last two decades. As early as 2009, Hauff et al. [28] explored whether different QPP methods may be combined to improve prediction quality. Since then, significant research has been done both on QPP approaches, as well as their evaluation. This study revisits Hauff et al.s work to assess the reproducibility of their findings in the light of new prediction methods, evaluation metrics, and datasets. We expand the scope of the earlier investigation by: (i) considering post-retrieval methods, including supervised neural techniques (only pre-retrieval techniques were studied in [28]); (ii) using sMARE for evaluation, in addition to the traditional correlation coefficients and RMSE; and (iii) experimenting with additional datasets (Clueweb09B and TREC DL). Our results largely support previous claims, but we also present several interesting findings. We interpret these findings by taking a more nuanced look at the correlation between QPP methods, examining whether they capture diverse information or rely on overlapping factors.
Unveiling Temporal Trends in 19th Century Literature: An Information Retrieval Approach
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:In English literature, the 19th century witnessed a significant transition in styles, themes, and genres. Consequently, the novels from this period display remarkable diversity. This paper explores these variations by examining the evolution of term usage in 19th century English novels through the lens of information retrieval. By applying a query expansion-based approach to a decade-segmented collection of fiction from the British Library, we examine how related terms vary over time. Our analysis employs multiple standard metrics including Kendall's tau, Jaccard similarity, and Jensen-Shannon divergence to assess overlaps and shifts in expanded query term sets. Our results indicate a significant degree of divergence in the related terms across decades as selected by the query expansion technique, suggesting substantial linguistic and conceptual changes throughout the 19th century novels.
Navigating Nuance: In Quest for Political Truth
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:This study investigates the several nuanced rationales for countering the rise of political bias. We evaluate the performance of the Llama-3 (70B) language model on the Media Bias Identification Benchmark (MBIB), based on a novel prompting technique that incorporates subtle reasons for identifying political leaning. Our findings underscore the challenges of detecting political bias and highlight the potential of transfer learning methods to enhance future models. Through our framework, we achieve a comparable performance with the supervised and fully fine-tuned ConvBERT model, which is the state-of-the-art model, performing best among other baseline models for the political bias task on MBIB. By demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach, we contribute to the development of more robust tools for mitigating the spread of misinformation and polarization. Our codes and dataset are made publicly available in github.
Exploring the Nexus Between Retrievability and Query Generation Strategies
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Quantifying bias in retrieval functions through document retrievability scores is vital for assessing recall-oriented retrieval systems. However, many studies investigating retrieval model bias lack validation of their query generation methods as accurate representations of retrievability for real users and their queries. This limitation results from the absence of established criteria for query generation in retrievability assessments. Typically, researchers resort to using frequent collocations from document corpora when no query log is available. In this study, we address the issue of reproducibility and seek to validate query generation methods by comparing retrievability scores generated from artificially generated queries to those derived from query logs. Our findings demonstrate a minimal or negligible correlation between retrievability scores from artificial queries and those from query logs. This suggests that artificially generated queries may not accurately reflect retrievability scores as derived from query logs. We further explore alternative query generation techniques, uncovering a variation that exhibits the highest correlation. This alternative approach holds promise for improving reproducibility when query logs are unavailable.
A Comparative Analysis of Retrievability and PageRank Measures
Nov 17, 2023

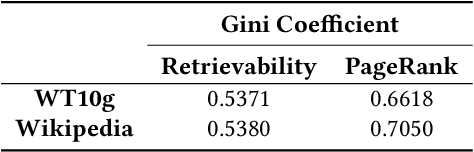

Abstract:The accessibility of documents within a collection holds a pivotal role in Information Retrieval, signifying the ease of locating specific content in a collection of documents. This accessibility can be achieved via two distinct avenues. The first is through some retrieval model using a keyword or other feature-based search, and the other is where a document can be navigated using links associated with them, if available. Metrics such as PageRank, Hub, and Authority illuminate the pathways through which documents can be discovered within the network of content while the concept of Retrievability is used to quantify the ease with which a document can be found by a retrieval model. In this paper, we compare these two perspectives, PageRank and retrievability, as they quantify the importance and discoverability of content in a corpus. Through empirical experimentation on benchmark datasets, we demonstrate a subtle similarity between retrievability and PageRank particularly distinguishable for larger datasets.
Automated Attribute Extraction from Legal Proceedings
Oct 18, 2023


Abstract:The escalating number of pending cases is a growing concern world-wide. Recent advancements in digitization have opened up possibilities for leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) tools in the processing of legal documents. Adopting a structured representation for legal documents, as opposed to a mere bag-of-words flat text representation, can significantly enhance processing capabilities. With the aim of achieving this objective, we put forward a set of diverse attributes for criminal case proceedings. We use a state-of-the-art sequence labeling framework to automatically extract attributes from the legal documents. Moreover, we demonstrate the efficacy of the extracted attributes in a downstream task, namely legal judgment prediction.
Findability: A Novel Measure of Information Accessibility
Oct 14, 2023
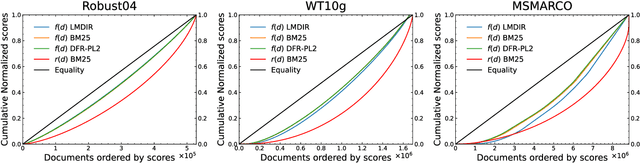
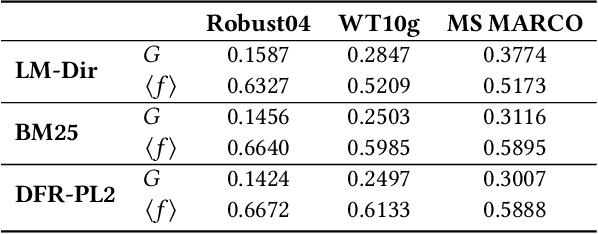
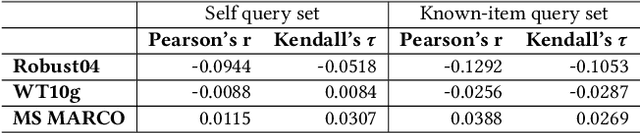
Abstract:The overwhelming volume of data generated and indexed by search engines poses a significant challenge in retrieving documents from the index efficiently and effectively. Even with a well-crafted query, several relevant documents often get buried among a multitude of competing documents, resulting in reduced accessibility or `findability' of the desired document. Consequently, it is crucial to develop a robust methodology for assessing this dimension of Information Retrieval (IR) system performance. While previous studies have focused on measuring document accessibility disregarding user queries and document relevance, there exists no metric to quantify the findability of a document within a given IR system without resorting to manual labor. This paper aims to address this gap by defining and deriving a metric to evaluate the findability of documents as perceived by end-users. Through experiments, we demonstrate the varying impact of different retrieval models and collections on the findability of documents. Furthermore, we establish the findability measure as an independent metric distinct from retrievability, an accessibility measure introduced in prior literature.
Retrievability in an Integrated Retrieval System: An Extended Study
Mar 27, 2023Abstract:Retrievability measures the influence a retrieval system has on the access to information in a given collection of items. This measure can help in making an evaluation of the search system based on which insights can be drawn. In this paper, we investigate the retrievability in an integrated search system consisting of items from various categories, particularly focussing on datasets, publications \ijdl{and variables} in a real-life Digital Library (DL). The traditional metrics, that is, the Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient, are employed to visualize the diversity in retrievability scores of the \ijdl{three} retrievable document types (specifically datasets, publications, and variables). Our results show a significant popularity bias with certain items being retrieved more often than others. Particularly, it has been shown that certain datasets are more likely to be retrieved than other datasets in the same category. In contrast, the retrievability scores of items from the variable or publication category are more evenly distributed. We have observed that the distribution of document retrievability is more diverse for datasets as compared to publications and variables.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge