Suchana Datta
Cultural Analytics for Good: Building Inclusive Evaluation Frameworks for Historical IR
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:This work bridges the fields of information retrieval and cultural analytics to support equitable access to historical knowledge. Using the British Library BL19 digital collection (more than 35,000 works from 1700-1899), we construct a benchmark for studying changes in language, terminology and retrieval in the 19th-century fiction and non-fiction. Our approach combines expert-driven query design, paragraph-level relevance annotation, and Large Language Model (LLM) assistance to create a scalable evaluation framework grounded in human expertise. We focus on knowledge transfer from fiction to non-fiction, investigating how narrative understanding and semantic richness in fiction can improve retrieval for scholarly and factual materials. This interdisciplinary framework not only improves retrieval accuracy but also fosters interpretability, transparency, and cultural inclusivity in digital archives. Our work provides both practical evaluation resources and a methodological paradigm for developing retrieval systems that support richer, historically aware engagement with digital archives, ultimately working towards more emancipatory knowledge infrastructures.
Combining Query Performance Predictors: A Reproducibility Study
Mar 31, 2025



Abstract:A large number of approaches to Query Performance Prediction (QPP) have been proposed over the last two decades. As early as 2009, Hauff et al. [28] explored whether different QPP methods may be combined to improve prediction quality. Since then, significant research has been done both on QPP approaches, as well as their evaluation. This study revisits Hauff et al.s work to assess the reproducibility of their findings in the light of new prediction methods, evaluation metrics, and datasets. We expand the scope of the earlier investigation by: (i) considering post-retrieval methods, including supervised neural techniques (only pre-retrieval techniques were studied in [28]); (ii) using sMARE for evaluation, in addition to the traditional correlation coefficients and RMSE; and (iii) experimenting with additional datasets (Clueweb09B and TREC DL). Our results largely support previous claims, but we also present several interesting findings. We interpret these findings by taking a more nuanced look at the correlation between QPP methods, examining whether they capture diverse information or rely on overlapping factors.
Unveiling Temporal Trends in 19th Century Literature: An Information Retrieval Approach
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:In English literature, the 19th century witnessed a significant transition in styles, themes, and genres. Consequently, the novels from this period display remarkable diversity. This paper explores these variations by examining the evolution of term usage in 19th century English novels through the lens of information retrieval. By applying a query expansion-based approach to a decade-segmented collection of fiction from the British Library, we examine how related terms vary over time. Our analysis employs multiple standard metrics including Kendall's tau, Jaccard similarity, and Jensen-Shannon divergence to assess overlaps and shifts in expanded query term sets. Our results indicate a significant degree of divergence in the related terms across decades as selected by the query expansion technique, suggesting substantial linguistic and conceptual changes throughout the 19th century novels.
A Deep Learning Approach for Selective Relevance Feedback
Jan 20, 2024



Abstract:Pseudo-relevance feedback (PRF) can enhance average retrieval effectiveness over a sufficiently large number of queries. However, PRF often introduces a drift into the original information need, thus hurting the retrieval effectiveness of several queries. While a selective application of PRF can potentially alleviate this issue, previous approaches have largely relied on unsupervised or feature-based learning to determine whether a query should be expanded. In contrast, we revisit the problem of selective PRF from a deep learning perspective, presenting a model that is entirely data-driven and trained in an end-to-end manner. The proposed model leverages a transformer-based bi-encoder architecture. Additionally, to further improve retrieval effectiveness with this selective PRF approach, we make use of the model's confidence estimates to combine the information from the original and expanded queries. In our experiments, we apply this selective feedback on a number of different combinations of ranking and feedback models, and show that our proposed approach consistently improves retrieval effectiveness for both sparse and dense ranking models, with the feedback models being either sparse, dense or generative.
On the Feasibility and Robustness of Pointwise Evaluation of Query Performance Prediction
Apr 01, 2023Abstract:Despite the retrieval effectiveness of queries being mutually independent of one another, the evaluation of query performance prediction (QPP) systems has been carried out by measuring rank correlation over an entire set of queries. Such a listwise approach has a number of disadvantages, notably that it does not support the common requirement of assessing QPP for individual queries. In this paper, we propose a pointwise QPP framework that allows us to evaluate the quality of a QPP system for individual queries by measuring the deviations between each prediction versus the corresponding true value, and then aggregating the results over a set of queries. Our experiments demonstrate that this new approach leads to smaller variances in QPP evaluations across a range of different target metrics and retrieval models.
Deep-QPP: A Pairwise Interaction-based Deep Learning Model for Supervised Query Performance Prediction
Feb 15, 2022
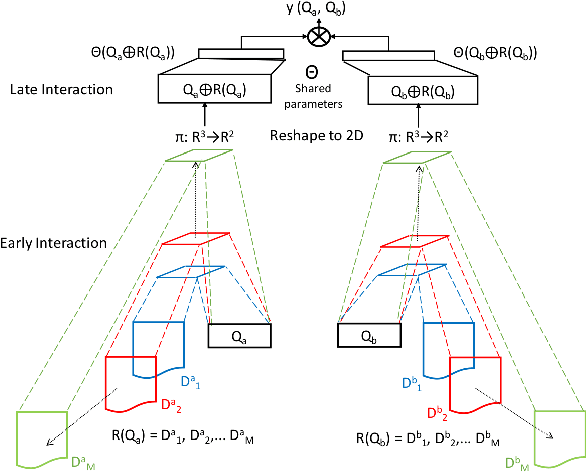
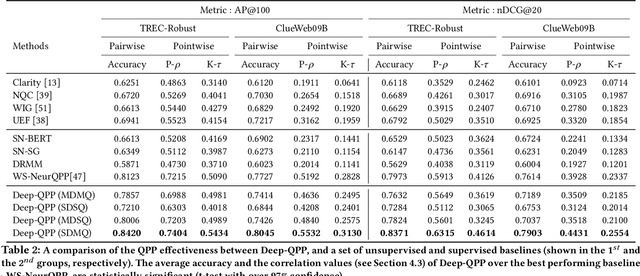
Abstract:Motivated by the recent success of end-to-end deep neural models for ranking tasks, we present here a supervised end-to-end neural approach for query performance prediction (QPP). In contrast to unsupervised approaches that rely on various statistics of document score distributions, our approach is entirely data-driven. Further, in contrast to weakly supervised approaches, our method also does not rely on the outputs from different QPP estimators. In particular, our model leverages information from the semantic interactions between the terms of a query and those in the top-documents retrieved with it. The architecture of the model comprises multiple layers of 2D convolution filters followed by a feed-forward layer of parameters. Experiments on standard test collections demonstrate that our proposed supervised approach outperforms other state-of-the-art supervised and unsupervised approaches.
An Analysis of Variations in the Effectiveness of Query Performance Prediction
Feb 13, 2022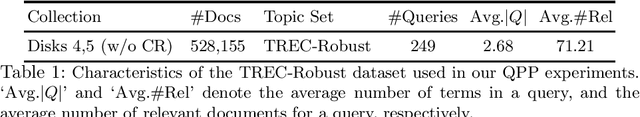
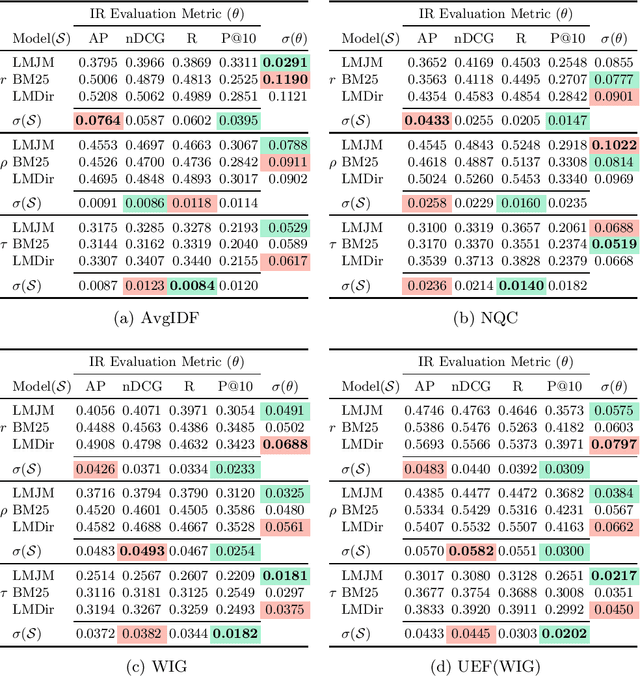
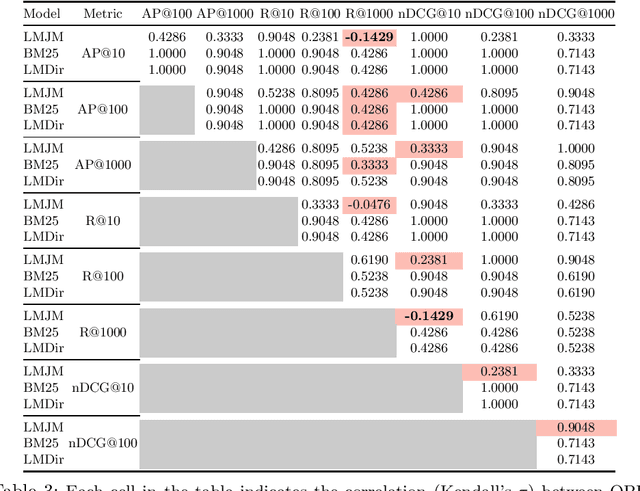
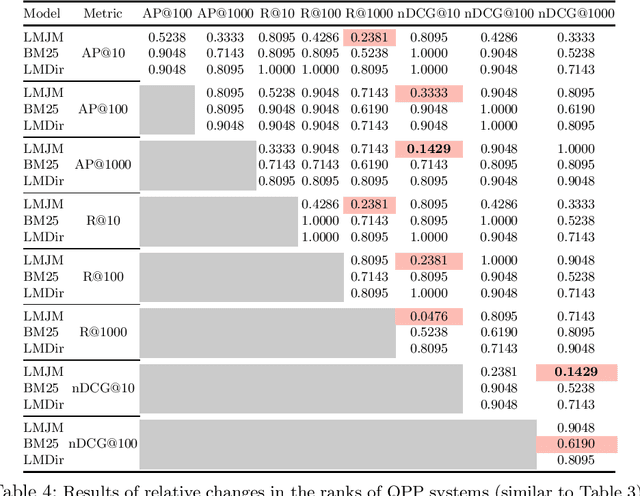
Abstract:A query performance predictor estimates the retrieval effectiveness of an IR system for a given query. An important characteristic of QPP evaluation is that, since the ground truth retrieval effectiveness for QPP evaluation can be measured with different metrics, the ground truth itself is not absolute, which is in contrast to other retrieval tasks, such as that of ad-hoc retrieval. Motivated by this argument, the objective of this paper is to investigate how such variances in the ground truth for QPP evaluation can affect the outcomes of QPP experiments. We consider this not only in terms of the absolute values of the evaluation metrics being reported (e.g. Pearson's $r$, Kendall's $\tau$), but also with respect to the changes in the ranks of different QPP systems when ordered by the QPP metric scores. Our experiments reveal that the observed QPP outcomes can vary considerably, both in terms of the absolute evaluation metric values and also in terms of the relative system ranks. Through our analysis, we report the optimal combinations of QPP evaluation metric and experimental settings that are likely to lead to smaller variations in the observed results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge