Debasis Ganguly
LURE-RAG: Lightweight Utility-driven Reranking for Efficient RAG
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Most conventional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines rely on relevance-based retrieval, which often misaligns with utility -- that is, whether the retrieved passages actually improve the quality of the generated text specific to a downstream task such as question answering or query-based summarization. The limitations of existing utility-driven retrieval approaches for RAG are that, firstly, they are resource-intensive typically requiring query encoding, and that secondly, they do not involve listwise ranking loss during training. The latter limitation is particularly critical, as the relative order between documents directly affects generation in RAG. To address this gap, we propose Lightweight Utility-driven Reranking for Efficient RAG (LURE-RAG), a framework that augments any black-box retriever with an efficient LambdaMART-based reranker. Unlike prior methods, LURE-RAG trains the reranker with a listwise ranking loss guided by LLM utility, thereby directly optimizing the ordering of retrieved documents. Experiments on two standard datasets demonstrate that LURE-RAG achieves competitive performance, reaching 97-98% of the state-of-the-art dense neural baseline, while remaining efficient in both training and inference. Moreover, its dense variant, UR-RAG, significantly outperforms the best existing baseline by up to 3%.
Beyond Correlations: A Downstream Evaluation Framework for Query Performance Prediction
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:The standard practice of query performance prediction (QPP) evaluation is to measure a set-level correlation between the estimated retrieval qualities and the true ones. However, neither this correlation-based evaluation measure quantifies QPP effectiveness at the level of individual queries, nor does this connect to a downstream application, meaning that QPP methods yielding high correlation values may not find a practical application in query-specific decisions in an IR pipeline. In this paper, we propose a downstream-focussed evaluation framework where a distribution of QPP estimates across a list of top-documents retrieved with several rankers is used as priors for IR fusion. While on the one hand, a distribution of these estimates closely matching that of the true retrieval qualities indicates the quality of the predictor, their usage as priors on the other hand indicates a predictor's ability to make informed choices in an IR pipeline. Our experiments firstly establish the importance of QPP estimates in weighted IR fusion, yielding substantial improvements of over 4.5% over unweighted CombSUM and RRF fusion strategies, and secondly, reveal new insights that the downstream effectiveness of QPP does not correlate well with the standard correlation-based QPP evaluation.
Breaking Flat: A Generalised Query Performance Prediction Evaluation Framework
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:The traditional use-case of query performance prediction (QPP) is to identify which queries perform well and which perform poorly for a given ranking model. A more fine-grained and arguably more challenging extension of this task is to determine which ranking models are most effective for a given query. In this work, we generalize the QPP task and its evaluation into three settings: (i) SingleRanker MultiQuery (SRMQ-PP), corresponding to the standard use case; (ii) MultiRanker SingleQuery (MRSQ-PP), which evaluates a QPP model's ability to select the most effective ranker for a query; and (iii) MultiRanker MultiQuery (MRMQ-PP), which considers predictions jointly across all query ranker pairs. Our results show that (a) the relative effectiveness of QPP models varies substantially across tasks (SRMQ-PP vs. MRSQ-PP), and (b) predicting the best ranker for a query is considerably more difficult than predicting the relative difficulty of queries for a given ranker.
Predicting Retrieval Utility and Answer Quality in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:The quality of answers generated by large language models (LLMs) in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is largely influenced by the contextual information contained in the retrieved documents. A key challenge for improving RAG is to predict both the utility of retrieved documents -- quantified as the performance gain from using context over generation without context -- and the quality of the final answers in terms of correctness and relevance. In this paper, we define two prediction tasks within RAG. The first is retrieval performance prediction (RPP), which estimates the utility of retrieved documents. The second is generation performance prediction (GPP), which estimates the final answer quality. We hypothesise that in RAG, the topical relevance of retrieved documents correlates with their utility, suggesting that query performance prediction (QPP) approaches can be adapted for RPP and GPP. Beyond these retriever-centric signals, we argue that reader-centric features, such as the LLM's perplexity of the retrieved context conditioned on the input query, can further enhance prediction accuracy for both RPP and GPP. Finally, we propose that features reflecting query-agnostic document quality and readability can also provide useful signals to the predictions. We train linear regression models with the above categories of predictors for both RPP and GPP. Experiments on the Natural Questions (NQ) dataset show that combining predictors from multiple feature categories yields the most accurate estimates of RAG performance.
T-Retrievability: A Topic-Focused Approach to Measure Fair Document Exposure in Information Retrieval
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:Retrievability of a document is a collection-based statistic that measures its expected (reciprocal) rank of being retrieved within a specific rank cut-off. A collection with uniformly distributed retrievability scores across documents is an indicator of fair document exposure. While retrievability scores have been used to quantify the fairness of exposure for a collection, in our work, we use the distribution of retrievability scores to measure the exposure bias of retrieval models. We hypothesise that an uneven distribution of retrievability scores across the entire collection may not accurately reflect exposure bias but rather indicate variations in topical relevance. As a solution, we propose a topic-focused localised retrievability measure, which we call \textit{T-Retrievability} (topic-retrievability), which first computes retrievability scores over multiple groups of topically-related documents, and then aggregates these localised values to obtain the collection-level statistics. Our analysis using this proposed T-Retrievability measure uncovers new insights into the exposure characteristics of various neural ranking models. The findings suggest that this localised measure provides a more nuanced understanding of exposure fairness, offering a more reliable approach for assessing document accessibility in IR systems.
Disentangling Locality and Entropy in Ranking Distillation
May 27, 2025Abstract:The training process of ranking models involves two key data selection decisions: a sampling strategy, and a labeling strategy. Modern ranking systems, especially those for performing semantic search, typically use a ``hard negative'' sampling strategy to identify challenging items using heuristics and a distillation labeling strategy to transfer ranking "knowledge" from a more capable model. In practice, these approaches have grown increasingly expensive and complex, for instance, popular pretrained rankers from SentenceTransformers involve 12 models in an ensemble with data provenance hampering reproducibility. Despite their complexity, modern sampling and labeling strategies have not been fully ablated, leaving the underlying source of effectiveness gains unclear. Thus, to better understand why models improve and potentially reduce the expense of training effective models, we conduct a broad ablation of sampling and distillation processes in neural ranking. We frame and theoretically derive the orthogonal nature of model geometry affected by example selection and the effect of teacher ranking entropy on ranking model optimization, establishing conditions in which data augmentation can effectively improve bias in a ranking model. Empirically, our investigation on established benchmarks and common architectures shows that sampling processes that were once highly effective in contrastive objectives may be spurious or harmful under distillation. We further investigate how data augmentation, in terms of inputs and targets, can affect effectiveness and the intrinsic behavior of models in ranking. Through this work, we aim to encourage more computationally efficient approaches that reduce focus on contrastive pairs and instead directly understand training dynamics under rankings, which better represent real-world settings.
Modeling Ranking Properties with In-Context Learning
May 23, 2025Abstract:While standard IR models are mainly designed to optimize relevance, real-world search often needs to balance additional objectives such as diversity and fairness. These objectives depend on inter-document interactions and are commonly addressed using post-hoc heuristics or supervised learning methods, which require task-specific training for each ranking scenario and dataset. In this work, we propose an in-context learning (ICL) approach that eliminates the need for such training. Instead, our method relies on a small number of example rankings that demonstrate the desired trade-offs between objectives for past queries similar to the current input. We evaluate our approach on four IR test collections to investigate multiple auxiliary objectives: group fairness (TREC Fairness), polarity diversity (Touch\'e), and topical diversity (TREC Deep Learning 2019/2020). We empirically validate that our method enables control over ranking behavior through demonstration engineering, allowing nuanced behavioral adjustments without explicit optimization.
Exploring the Role of Diversity in Example Selection for In-Context Learning
May 03, 2025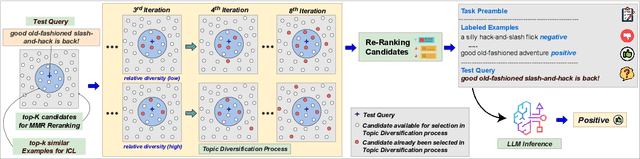
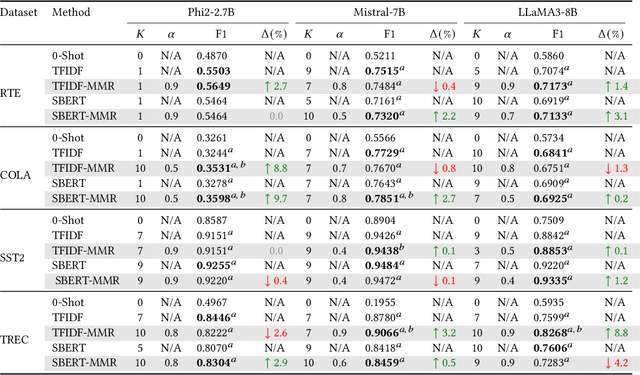
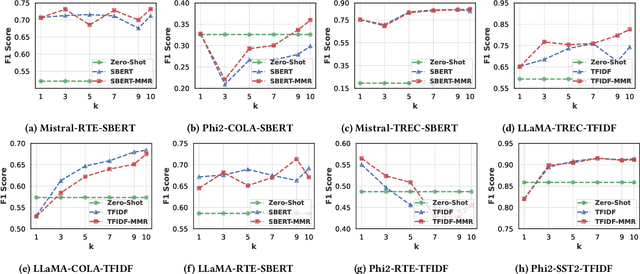
Abstract:In-Context Learning (ICL) has gained prominence due to its ability to perform tasks without requiring extensive training data and its robustness to noisy labels. A typical ICL workflow involves selecting localized examples relevant to a given input using sparse or dense embedding-based similarity functions. However, relying solely on similarity-based selection may introduce topical biases in the retrieved contexts, potentially leading to suboptimal downstream performance. We posit that reranking the retrieved context to enhance topical diversity can improve downstream task performance. To achieve this, we leverage maximum marginal relevance (MMR) which balances topical similarity with inter-example diversity. Our experimental results demonstrate that diversifying the selected examples leads to consistent improvements in downstream performance across various context sizes and similarity functions. The implementation of our approach is made available at https://github.com/janak11111/Diverse-ICL.
Is Relevance Propagated from Retriever to Generator in RAG?
Feb 20, 2025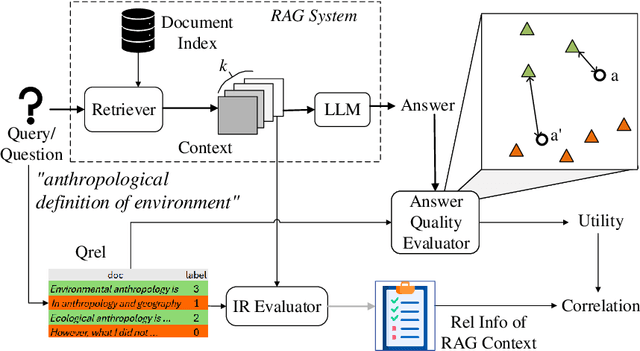
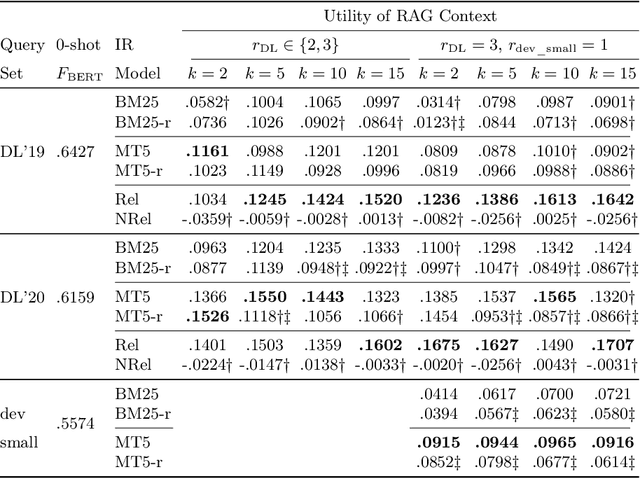
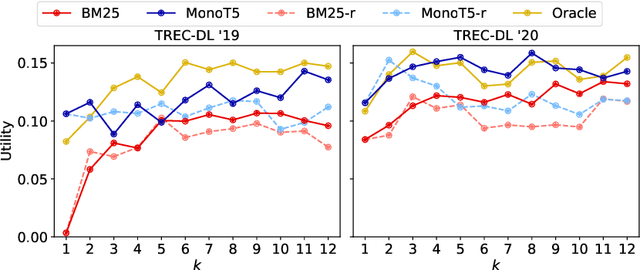
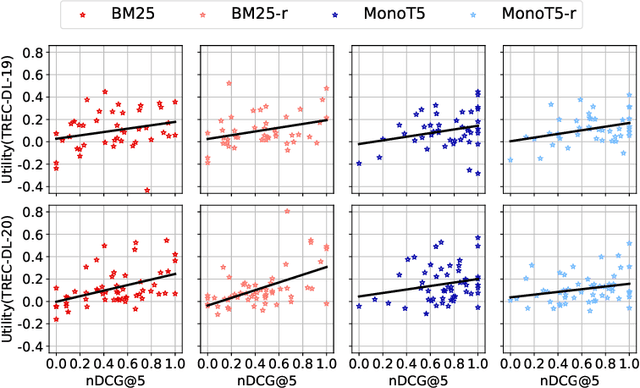
Abstract:Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a framework for incorporating external knowledge, usually in the form of a set of documents retrieved from a collection, as a part of a prompt to a large language model (LLM) to potentially improve the performance of a downstream task, such as question answering. Different from a standard retrieval task's objective of maximising the relevance of a set of top-ranked documents, a RAG system's objective is rather to maximise their total utility, where the utility of a document indicates whether including it as a part of the additional contextual information in an LLM prompt improves a downstream task. Existing studies investigate the role of the relevance of a RAG context for knowledge-intensive language tasks (KILT), where relevance essentially takes the form of answer containment. In contrast, in our work, relevance corresponds to that of topical overlap between a query and a document for an information seeking task. Specifically, we make use of an IR test collection to empirically investigate whether a RAG context comprised of topically relevant documents leads to improved downstream performance. Our experiments lead to the following findings: (a) there is a small positive correlation between relevance and utility; (b) this correlation decreases with increasing context sizes (higher values of k in k-shot); and (c) a more effective retrieval model generally leads to better downstream RAG performance.
Few-shot Pairwise Rank Prompting: An Effective Non-Parametric Retrieval Model
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:A supervised ranking model, despite its advantage of being effective, usually involves complex processing - typically multiple stages of task-specific pre-training and fine-tuning. This has motivated researchers to explore simpler pipelines leveraging large language models (LLMs) that are capable of working in a zero-shot manner. However, since zero-shot inference does not make use of a training set of pairs of queries and their relevant documents, its performance is mostly worse than that of supervised models, which are trained on such example pairs. Motivated by the existing findings that training examples generally improve zero-shot performance, in our work, we explore if this also applies to ranking models. More specifically, given a query and a pair of documents, the preference prediction task is improved by augmenting examples of preferences for similar queries from a training set. Our proposed pairwise few-shot ranker demonstrates consistent improvements over the zero-shot baseline on both in-domain (TREC DL) and out-domain (BEIR subset) retrieval benchmarks. Our method also achieves a close performance to that of a supervised model without requiring any complex training pipeline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge