Dongxu Guo
STEVE Series: Step-by-Step Construction of Agent Systems in Minecraft
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Building an embodied agent system with a large language model (LLM) as its core is a promising direction. Due to the significant costs and uncontrollable factors associated with deploying and training such agents in the real world, we have decided to begin our exploration within the Minecraft environment. Our STEVE Series agents can complete basic tasks in a virtual environment and more challenging tasks such as navigation and even creative tasks, with an efficiency far exceeding previous state-of-the-art methods by a factor of $2.5\times$ to $7.3\times$. We begin our exploration with a vanilla large language model, augmenting it with a vision encoder and an action codebase trained on our collected high-quality dataset STEVE-21K. Subsequently, we enhanced it with a Critic and memory to transform it into a complex system. Finally, we constructed a hierarchical multi-agent system. Our recent work explored how to prune the agent system through knowledge distillation. In the future, we will explore more potential applications of STEVE agents in the real world.
Do We Really Need a Complex Agent System? Distill Embodied Agent into a Single Model
Apr 06, 2024Abstract:With the power of large language models (LLMs), open-ended embodied agents can flexibly understand human instructions, generate interpretable guidance strategies, and output executable actions. Nowadays, Multi-modal Language Models~(MLMs) integrate multi-modal signals into LLMs, further bringing richer perception to entity agents and allowing embodied agents to perceive world-understanding tasks more delicately. However, existing works: 1) operate independently by agents, each containing multiple LLMs, from perception to action, resulting in gaps between complex tasks and execution; 2) train MLMs on static data, struggling with dynamics in open-ended scenarios; 3) input prior knowledge directly as prompts, suppressing application flexibility. We propose STEVE-2, a hierarchical knowledge distillation framework for open-ended embodied tasks, characterized by 1) a hierarchical system for multi-granular task division, 2) a mirrored distillation method for parallel simulation data, and 3) an extra expert model for bringing additional knowledge into parallel simulation. After distillation, embodied agents can complete complex, open-ended tasks without additional expert guidance, utilizing the performance and knowledge of a versatile MLM. Extensive evaluations on navigation and creation tasks highlight the superior performance of STEVE-2 in open-ended tasks, with $1.4 \times$ - $7.3 \times$ in performance.
Hierarchical Auto-Organizing System for Open-Ended Multi-Agent Navigation
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:Due to the dynamic and unpredictable open-world setting, navigating complex environments in Minecraft poses significant challenges for multi-agent systems. Agents must interact with the environment and coordinate their actions with other agents to achieve common objectives. However, traditional approaches often struggle to efficiently manage inter-agent communication and task distribution, crucial for effective multi-agent navigation. Furthermore, processing and integrating multi-modal information (such as visual, textual, and auditory data) is essential for agents to comprehend their goals and navigate the environment successfully and fully. To address this issue, we design the HAS framework to auto-organize groups of LLM-based agents to complete navigation tasks. In our approach, we devise a hierarchical auto-organizing navigation system, which is characterized by 1) a hierarchical system for multi-agent organization, ensuring centralized planning and decentralized execution; 2) an auto-organizing and intra-communication mechanism, enabling dynamic group adjustment under subtasks; 3) a multi-modal information platform, facilitating multi-modal perception to perform the three navigation tasks with one system. To assess organizational behavior, we design a series of navigation tasks in the Minecraft environment, which includes searching and exploring. We aim to develop embodied organizations that push the boundaries of embodied AI, moving it towards a more human-like organizational structure.
Pedestrian Stop and Go Forecasting with Hybrid Feature Fusion
Mar 04, 2022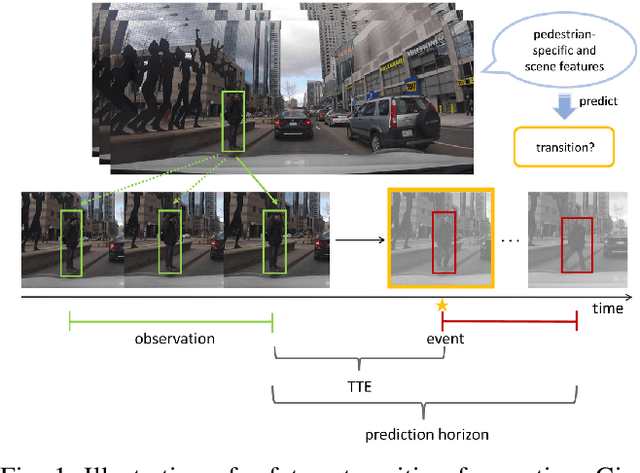
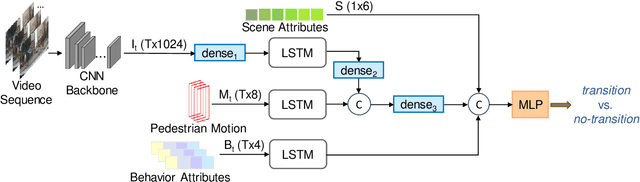
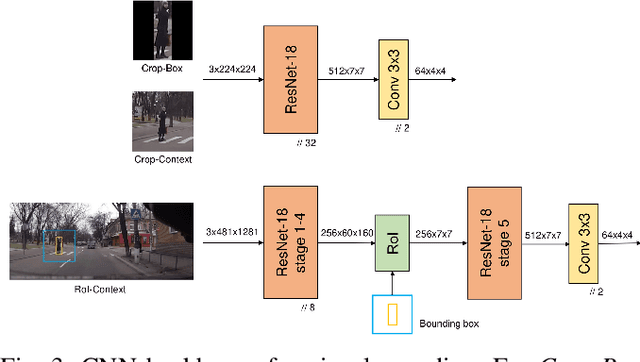
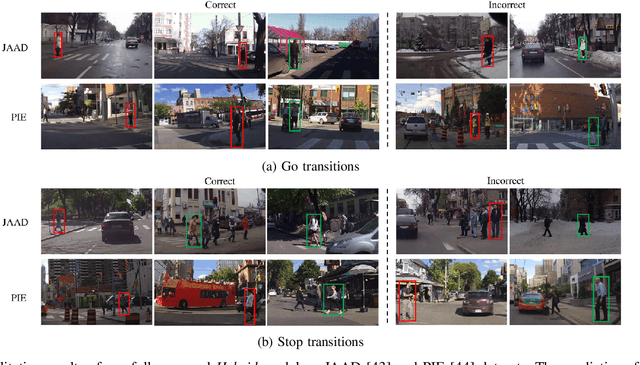
Abstract:Forecasting pedestrians' future motions is essential for autonomous driving systems to safely navigate in urban areas. However, existing prediction algorithms often overly rely on past observed trajectories and tend to fail around abrupt dynamic changes, such as when pedestrians suddenly start or stop walking. We suggest that predicting these highly non-linear transitions should form a core component to improve the robustness of motion prediction algorithms. In this paper, we introduce the new task of pedestrian stop and go forecasting. Considering the lack of suitable existing datasets for it, we release TRANS, a benchmark for explicitly studying the stop and go behaviors of pedestrians in urban traffic. We build it from several existing datasets annotated with pedestrians' walking motions, in order to have various scenarios and behaviors. We also propose a novel hybrid model that leverages pedestrian-specific and scene features from several modalities, both video sequences and high-level attributes, and gradually fuses them to integrate multiple levels of context. We evaluate our model and several baselines on TRANS, and set a new benchmark for the community to work on pedestrian stop and go forecasting.
Detecting Electric Vehicle Battery Failure via Dynamic-VAE
Jan 28, 2022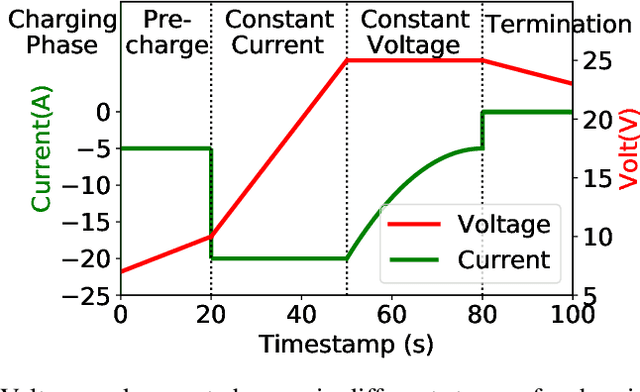
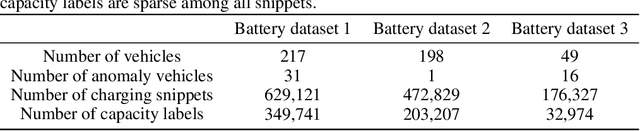
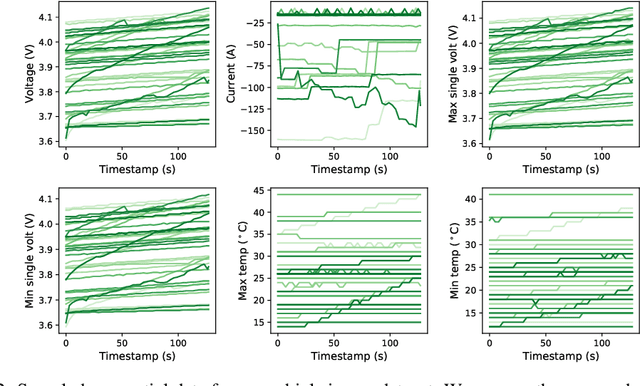
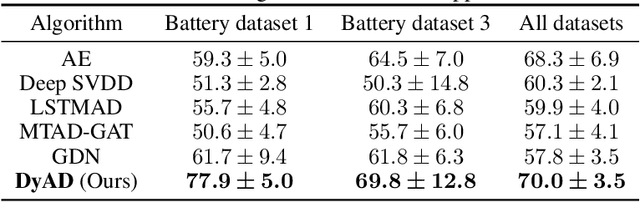
Abstract:In this note, we describe a battery failure detection pipeline backed up by deep learning models. We first introduce a large-scale Electric vehicle (EV) battery dataset including cleaned battery-charging data from hundreds of vehicles. We then formulate battery failure detection as an outlier detection problem, and propose a new algorithm named Dynamic-VAE based on dynamic system and variational autoencoders. We validate the performance of our proposed algorithm against several baselines on our released dataset and demonstrated the effectiveness of Dynamic-VAE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge