Dirk Vandermeulen
Attention Maps in 3D Shape Classification for Dental Stage Estimation with Class Node Graph Attention Networks
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Deep learning offers a promising avenue for automating many recognition tasks in fields such as medicine and forensics. However, the black-box nature of these models hinders their adoption in high-stakes applications where trust and accountability are required. For 3D shape recognition tasks in particular, this paper introduces the Class Node Graph Attention Network (CGAT) architecture to address this need. Applied to 3D meshes of third molars derived from CBCT images, for Demirjian stage allocation, CGAT utilizes graph attention convolutions and an inherent attention mechanism, visualized via attention rollout, to explain its decision-making process. We evaluated the local mean curvature and distance to centroid node features, both individually and in combination, as well as model depth, finding that models incorporating directed edges to a global CLS node produced more intuitive attention maps, while also yielding desirable classification performance. We analyzed the attention-based explanations of the models, and their predictive performances to propose optimal settings for the CGAT. The combination of local mean curvature and distance to centroid as node features yielded a slight performance increase with 0.76 weighted F1 score, and more comprehensive attention visualizations. The CGAT architecture's ability to generate human-understandable attention maps can enhance trust and facilitate expert validation of model decisions. While demonstrated on dental data, CGAT is broadly applicable to graph-based classification and regression tasks, promoting wider adoption of transparent and competitive deep learning models in high-stakes environments.
Convolutional neural networks for medical image segmentation
Nov 17, 2022



Abstract:In this article, we look into some essential aspects of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with the focus on medical image segmentation. First, we discuss the CNN architecture, thereby highlighting the spatial origin of the data, voxel-wise classification and the receptive field. Second, we discuss the sampling of input-output pairs, thereby highlighting the interaction between voxel-wise classification, patch size and the receptive field. Finally, we give a historical overview of crucial changes to CNN architectures for classification and segmentation, giving insights in the relation between three pivotal CNN architectures: FCN, U-Net and DeepMedic.
DeepVoxNet2: Yet another CNN framework
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:We know that both the CNN mapping function and the sampling scheme are of paramount importance for CNN-based image analysis. It is clear that both functions operate in the same space, with an image axis $\mathcal{I}$ and a feature axis $\mathcal{F}$. Remarkably, we found that no frameworks existed that unified the two and kept track of the spatial origin of the data automatically. Based on our own practical experience, we found the latter to often result in complex coding and pipelines that are difficult to exchange. This article introduces our framework for 1, 2 or 3D image classification or segmentation: DeepVoxNet2 (DVN2). This article serves as an interactive tutorial, and a pre-compiled version, including the outputs of the code blocks, can be found online in the public DVN2 repository. This tutorial uses data from the multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark (BRATS) of 2018 to show an example of a 3D segmentation pipeline.
Final infarct prediction in acute ischemic stroke
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:This article focuses on the control center of each human body: the brain. We will point out the pivotal role of the cerebral vasculature and how its complex mechanisms may vary between subjects. We then emphasize a specific acute pathological state, i.e., acute ischemic stroke, and show how medical imaging and its analysis can be used to define the treatment. We show how the core-penumbra concept is used in practice using mismatch criteria and how machine learning can be used to make predictions of the final infarct, either via deconvolution or convolutional neural networks.
Theoretical analysis and experimental validation of volume bias of soft Dice optimized segmentation maps in the context of inherent uncertainty
Nov 08, 2022



Abstract:The clinical interest is often to measure the volume of a structure, which is typically derived from a segmentation. In order to evaluate and compare segmentation methods, the similarity between a segmentation and a predefined ground truth is measured using popular discrete metrics, such as the Dice score. Recent segmentation methods use a differentiable surrogate metric, such as soft Dice, as part of the loss function during the learning phase. In this work, we first briefly describe how to derive volume estimates from a segmentation that is, potentially, inherently uncertain or ambiguous. This is followed by a theoretical analysis and an experimental validation linking the inherent uncertainty to common loss functions for training CNNs, namely cross-entropy and soft Dice. We find that, even though soft Dice optimization leads to an improved performance with respect to the Dice score and other measures, it may introduce a volume bias for tasks with high inherent uncertainty. These findings indicate some of the method's clinical limitations and suggest doing a closer ad-hoc volume analysis with an optional re-calibration step.
* 18 pages, 7 figures, 3 tables, published in Elsevier Medical Image Analysis (2021)
The Dice loss in the context of missing or empty labels: Introducing $Φ$ and $ε$
Jul 19, 2022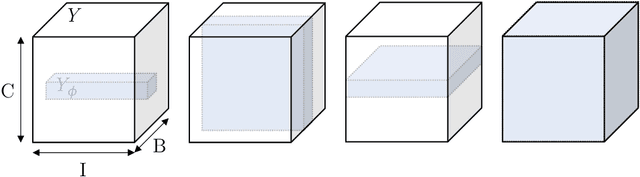
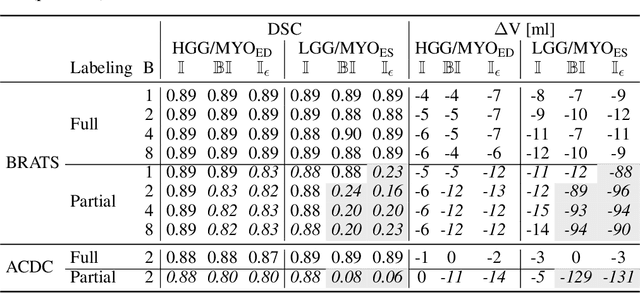
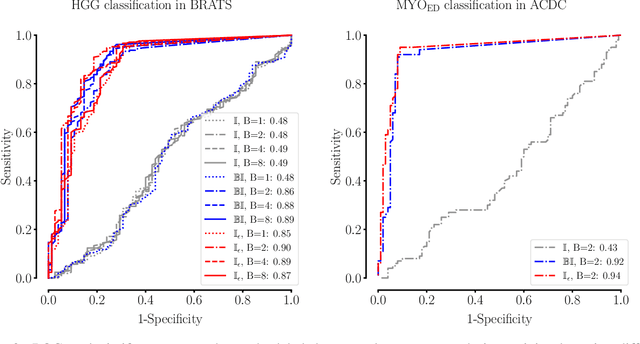
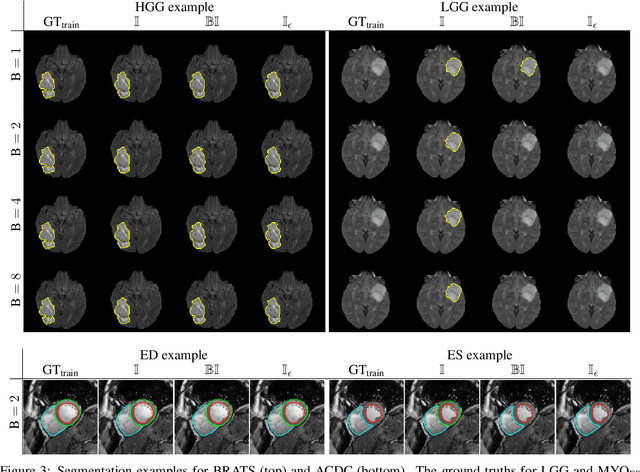
Abstract:Albeit the Dice loss is one of the dominant loss functions in medical image segmentation, most research omits a closer look at its derivative, i.e. the real motor of the optimization when using gradient descent. In this paper, we highlight the peculiar action of the Dice loss in the presence of missing or empty labels. First, we formulate a theoretical basis that gives a general description of the Dice loss and its derivative. It turns out that the choice of the reduction dimensions $\Phi$ and the smoothing term $\epsilon$ is non-trivial and greatly influences its behavior. We find and propose heuristic combinations of $\Phi$ and $\epsilon$ that work in a segmentation setting with either missing or empty labels. Second, we empirically validate these findings in a binary and multiclass segmentation setting using two publicly available datasets. We confirm that the choice of $\Phi$ and $\epsilon$ is indeed pivotal. With $\Phi$ chosen such that the reductions happen over a single batch (and class) element and with a negligible $\epsilon$, the Dice loss deals with missing labels naturally and performs similarly compared to recent adaptations specific for missing labels. With $\Phi$ chosen such that the reductions happen over multiple batch elements or with a heuristic value for $\epsilon$, the Dice loss handles empty labels correctly. We believe that this work highlights some essential perspectives and hope that it encourages researchers to better describe their exact implementation of the Dice loss in future work.
On the relationship between calibrated predictors and unbiased volume estimation
Dec 23, 2021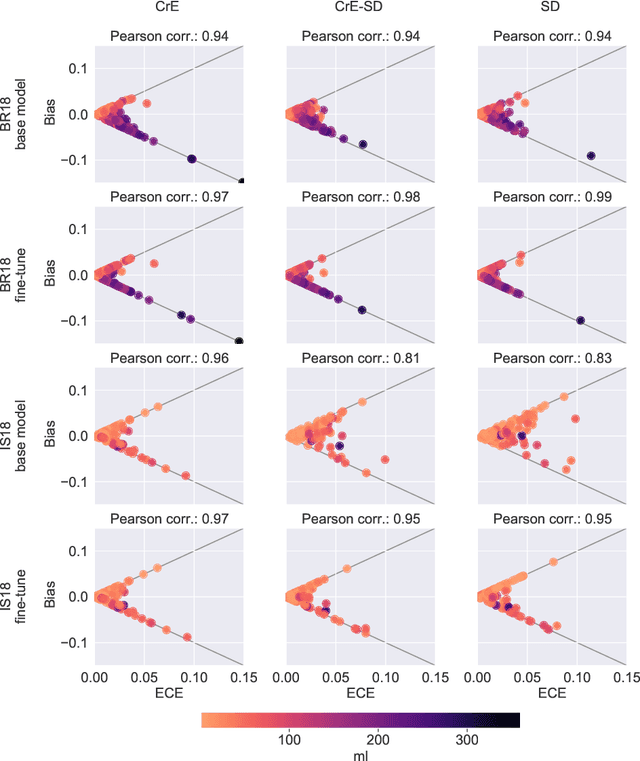
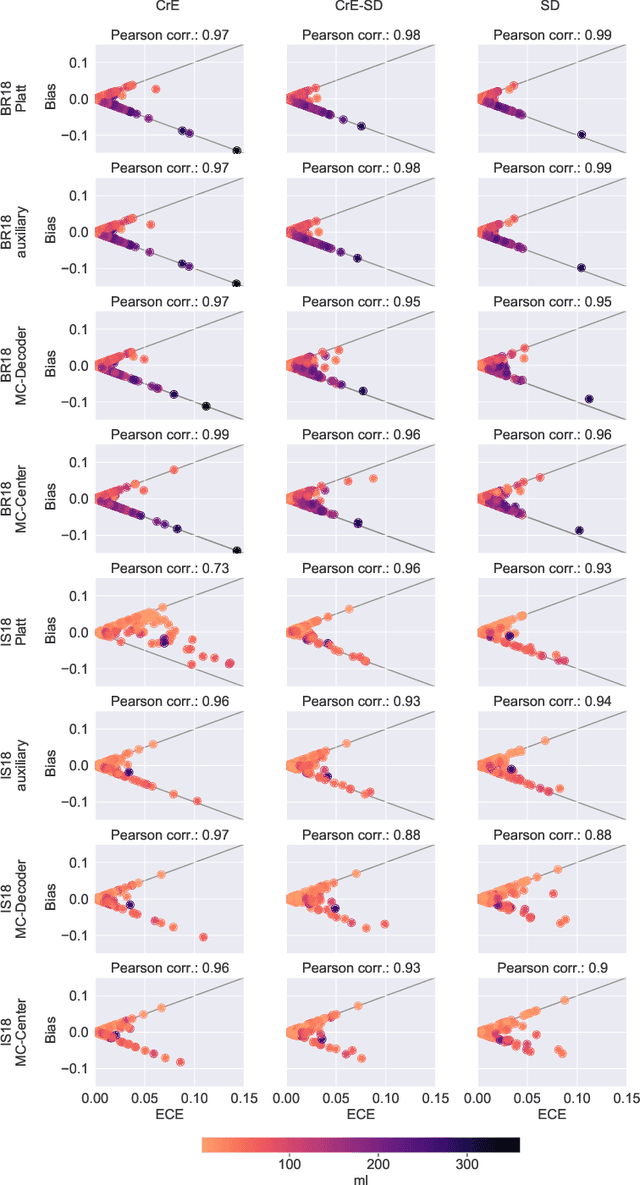
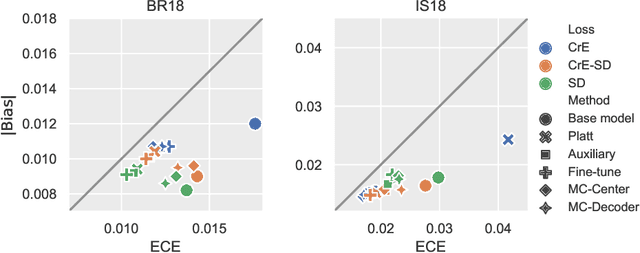
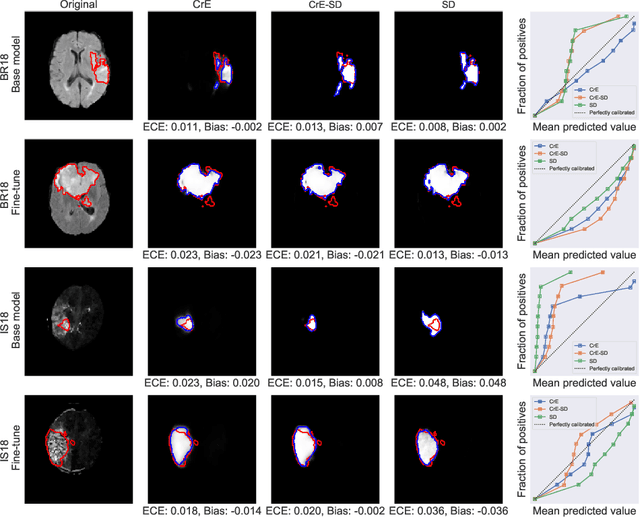
Abstract:Machine learning driven medical image segmentation has become standard in medical image analysis. However, deep learning models are prone to overconfident predictions. This has led to a renewed focus on calibrated predictions in the medical imaging and broader machine learning communities. Calibrated predictions are estimates of the probability of a label that correspond to the true expected value of the label conditioned on the confidence. Such calibrated predictions have utility in a range of medical imaging applications, including surgical planning under uncertainty and active learning systems. At the same time it is often an accurate volume measurement that is of real importance for many medical applications. This work investigates the relationship between model calibration and volume estimation. We demonstrate both mathematically and empirically that if the predictor is calibrated per image, we can obtain the correct volume by taking an expectation of the probability scores per pixel/voxel of the image. Furthermore, we show that convex combinations of calibrated classifiers preserve volume estimation, but do not preserve calibration. Therefore, we conclude that having a calibrated predictor is a sufficient, but not necessary condition for obtaining an unbiased estimate of the volume. We validate our theoretical findings empirically on a collection of 18 different (calibrated) training strategies on the tasks of glioma volume estimation on BraTS 2018, and ischemic stroke lesion volume estimation on ISLES 2018 datasets.
Unsupervised Diffeomorphic Surface Registration and Non-Linear Modelling
Sep 28, 2021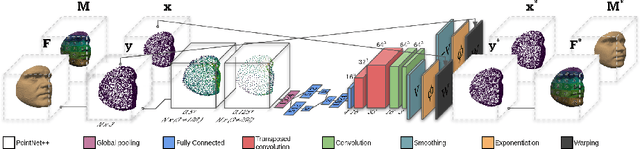

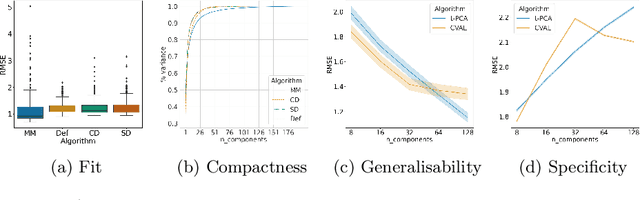
Abstract:Registration is an essential tool in image analysis. Deep learning based alternatives have recently become popular, achieving competitive performance at a faster speed. However, many contemporary techniques are limited to volumetric representations, despite increased popularity of 3D surface and shape data in medical image analysis. We propose a one-step registration model for 3D surfaces that internalises a lower dimensional probabilistic deformation model (PDM) using conditional variational autoencoders (CVAE). The deformations are constrained to be diffeomorphic using an exponentiation layer. The one-step registration model is benchmarked against iterative techniques, trading in a slightly lower performance in terms of shape fit for a higher compactness. We experiment with two distance metrics, Chamfer distance (CD) and Sinkhorn divergence (SD), as specific distance functions for surface data in real-world registration scenarios. The internalised deformation model is benchmarked against linear principal component analysis (PCA) achieving competitive results and improved generalisability from lower dimensions.
Explainable-by-design Semi-Supervised Representation Learning for COVID-19 Diagnosis from CT Imaging
Dec 02, 2020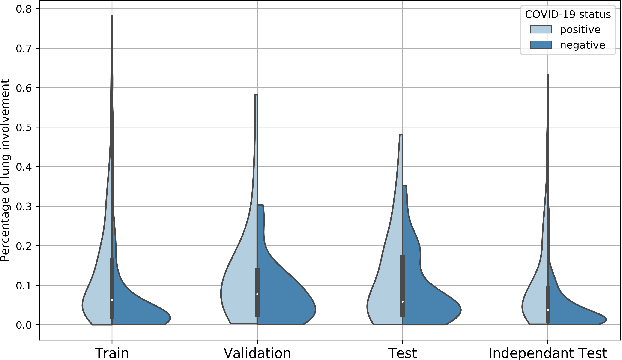
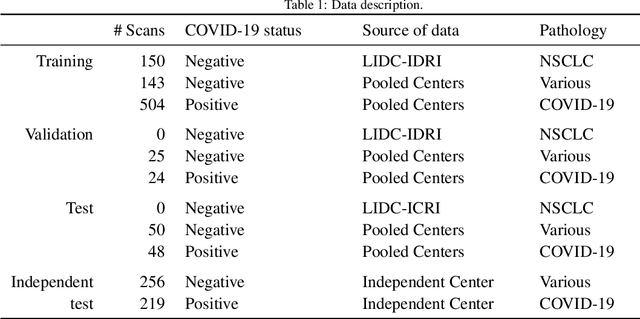
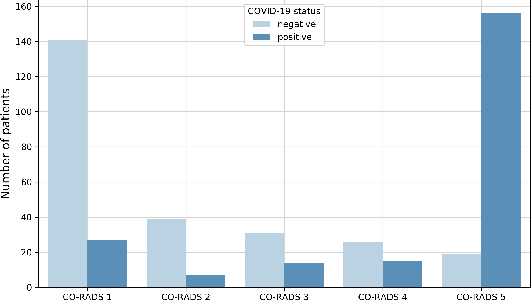
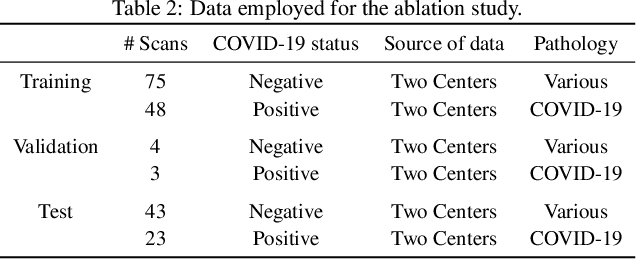
Abstract:Our motivating application is a real-world problem: COVID-19 classification from CT imaging, for which we present an explainable Deep Learning approach based on a semi-supervised classification pipeline that employs variational autoencoders to extract efficient feature embedding. We have optimized the architecture of two different networks for CT images: (i) a novel conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE) with a specific architecture that integrates the class labels inside the encoder layers and uses side information with shared attention layers for the encoder, which make the most of the contextual clues for representation learning, and (ii) a downstream convolutional neural network for supervised classification using the encoder structure of the CVAE. With the explainable classification results, the proposed diagnosis system is very effective for COVID-19 classification. Based on the promising results obtained qualitatively and quantitatively, we envisage a wide deployment of our developed technique in large-scale clinical studies.Code is available at https://git.etrovub.be/AVSP/ct-based-covid-19-diagnostic-tool.git.
Optimization for Medical Image Segmentation: Theory and Practice when evaluating with Dice Score or Jaccard Index
Oct 26, 2020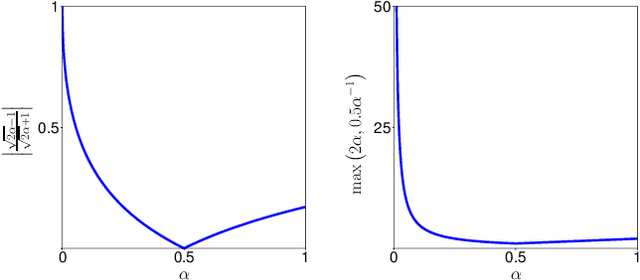
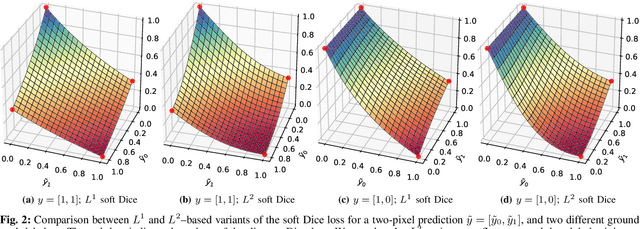
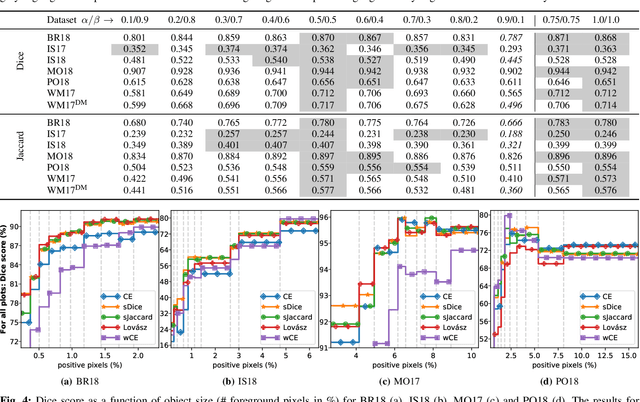
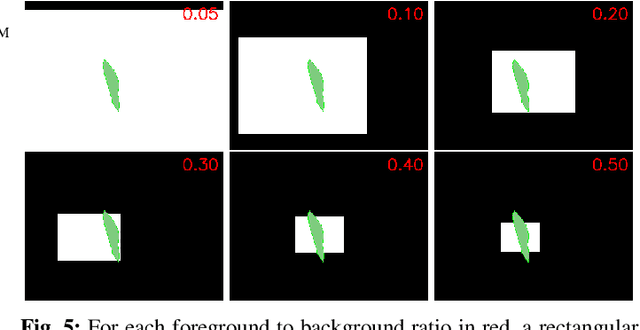
Abstract:In many medical imaging and classical computer vision tasks, the Dice score and Jaccard index are used to evaluate the segmentation performance. Despite the existence and great empirical success of metric-sensitive losses, i.e. relaxations of these metrics such as soft Dice, soft Jaccard and Lovasz-Softmax, many researchers still use per-pixel losses, such as (weighted) cross-entropy to train CNNs for segmentation. Therefore, the target metric is in many cases not directly optimized. We investigate from a theoretical perspective, the relation within the group of metric-sensitive loss functions and question the existence of an optimal weighting scheme for weighted cross-entropy to optimize the Dice score and Jaccard index at test time. We find that the Dice score and Jaccard index approximate each other relatively and absolutely, but we find no such approximation for a weighted Hamming similarity. For the Tversky loss, the approximation gets monotonically worse when deviating from the trivial weight setting where soft Tversky equals soft Dice. We verify these results empirically in an extensive validation on six medical segmentation tasks and can confirm that metric-sensitive losses are superior to cross-entropy based loss functions in case of evaluation with Dice Score or Jaccard Index. This further holds in a multi-class setting, and across different object sizes and foreground/background ratios. These results encourage a wider adoption of metric-sensitive loss functions for medical segmentation tasks where the performance measure of interest is the Dice score or Jaccard index.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge