Siri Willems
Clinical Validation of Deep Learning for Real-Time Tissue Oxygenation Estimation Using Spectral Imaging
May 23, 2025Abstract:Accurate, real-time monitoring of tissue ischemia is crucial to understand tissue health and guide surgery. Spectral imaging shows great potential for contactless and intraoperative monitoring of tissue oxygenation. Due to the difficulty of obtaining direct reference oxygenation values, conventional methods are based on linear unmixing techniques. These are prone to assumptions and these linear relations may not always hold in practice. In this work, we present deep learning approaches for real-time tissue oxygenation estimation using Monte-Carlo simulated spectra. We train a fully connected neural network (FCN) and a convolutional neural network (CNN) for this task and propose a domain-adversarial training approach to bridge the gap between simulated and real clinical spectral data. Results demonstrate that these deep learning models achieve a higher correlation with capillary lactate measurements, a well-known marker of hypoxia, obtained during spectral imaging in surgery, compared to traditional linear unmixing. Notably, domain-adversarial training effectively reduces the domain gap, optimizing performance in real clinical settings.
OpenKBP-Opt: An international and reproducible evaluation of 76 knowledge-based planning pipelines
Feb 16, 2022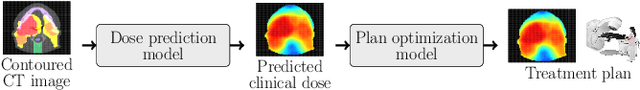

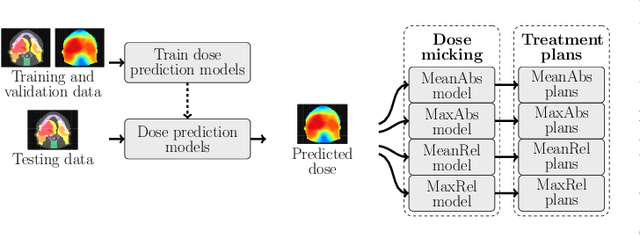
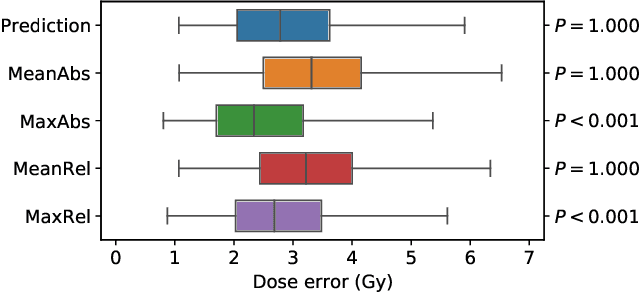
Abstract:We establish an open framework for developing plan optimization models for knowledge-based planning (KBP) in radiotherapy. Our framework includes reference plans for 100 patients with head-and-neck cancer and high-quality dose predictions from 19 KBP models that were developed by different research groups during the OpenKBP Grand Challenge. The dose predictions were input to four optimization models to form 76 unique KBP pipelines that generated 7600 plans. The predictions and plans were compared to the reference plans via: dose score, which is the average mean absolute voxel-by-voxel difference in dose a model achieved; the deviation in dose-volume histogram (DVH) criterion; and the frequency of clinical planning criteria satisfaction. We also performed a theoretical investigation to justify our dose mimicking models. The range in rank order correlation of the dose score between predictions and their KBP pipelines was 0.50 to 0.62, which indicates that the quality of the predictions is generally positively correlated with the quality of the plans. Additionally, compared to the input predictions, the KBP-generated plans performed significantly better (P<0.05; one-sided Wilcoxon test) on 18 of 23 DVH criteria. Similarly, each optimization model generated plans that satisfied a higher percentage of criteria than the reference plans. Lastly, our theoretical investigation demonstrated that the dose mimicking models generated plans that are also optimal for a conventional planning model. This was the largest international effort to date for evaluating the combination of KBP prediction and optimization models. In the interest of reproducibility, our data and code is freely available at https://github.com/ababier/open-kbp-opt.
Explainable-by-design Semi-Supervised Representation Learning for COVID-19 Diagnosis from CT Imaging
Dec 02, 2020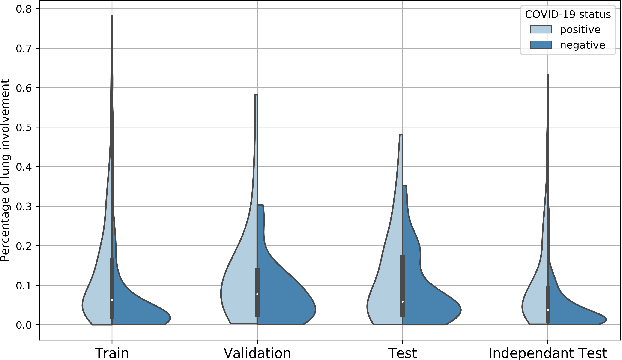
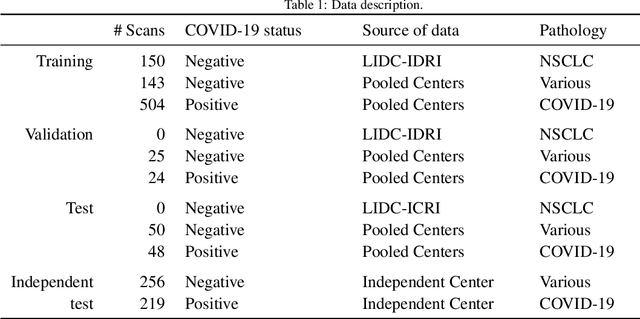
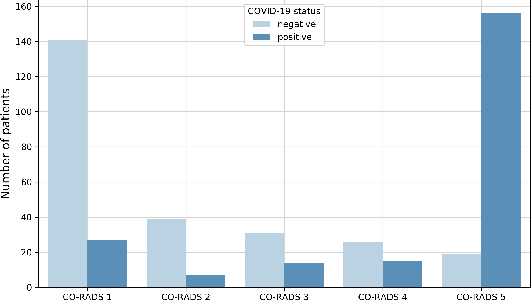
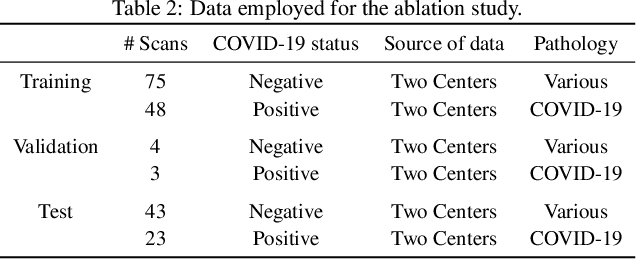
Abstract:Our motivating application is a real-world problem: COVID-19 classification from CT imaging, for which we present an explainable Deep Learning approach based on a semi-supervised classification pipeline that employs variational autoencoders to extract efficient feature embedding. We have optimized the architecture of two different networks for CT images: (i) a novel conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE) with a specific architecture that integrates the class labels inside the encoder layers and uses side information with shared attention layers for the encoder, which make the most of the contextual clues for representation learning, and (ii) a downstream convolutional neural network for supervised classification using the encoder structure of the CVAE. With the explainable classification results, the proposed diagnosis system is very effective for COVID-19 classification. Based on the promising results obtained qualitatively and quantitatively, we envisage a wide deployment of our developed technique in large-scale clinical studies.Code is available at https://git.etrovub.be/AVSP/ct-based-covid-19-diagnostic-tool.git.
Comparative study of deep learning methods for the automatic segmentation of lung, lesion and lesion type in CT scans of COVID-19 patients
Aug 21, 2020
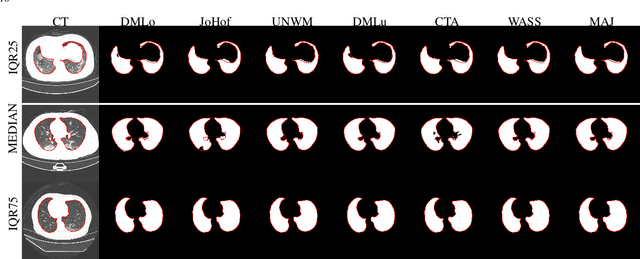
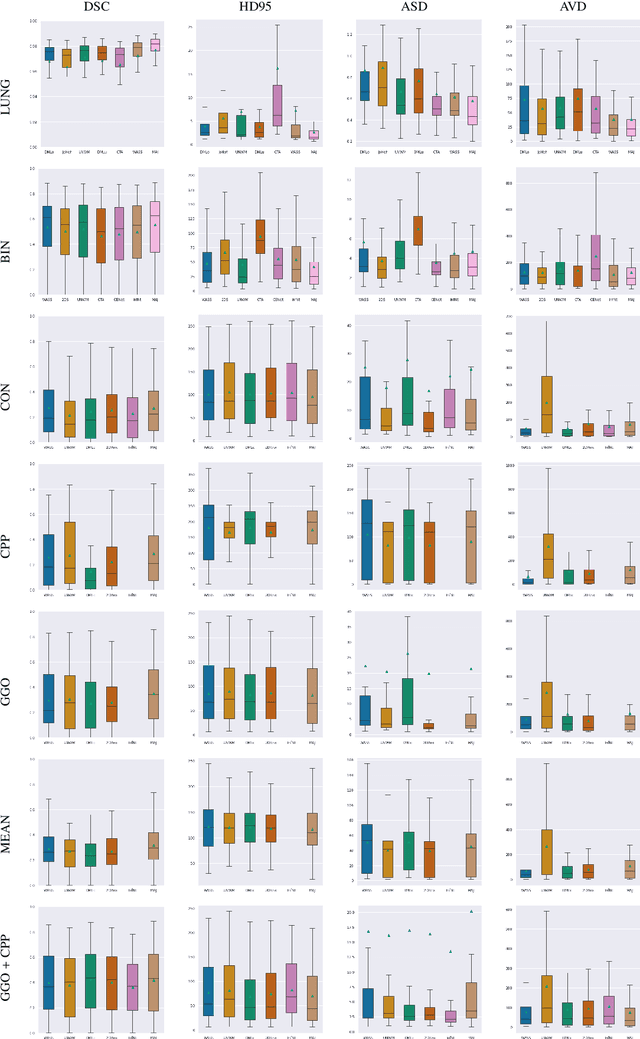
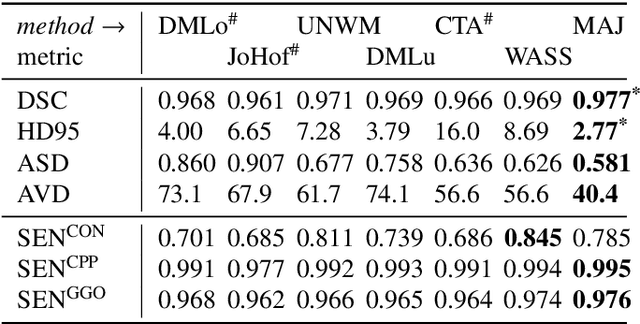
Abstract:Recent research on COVID-19 suggests that CT imaging provides useful information to assess disease progression and assist diagnosis, in addition to help understanding the disease. There is an increasing number of studies that propose to use deep learning to provide fast and accurate quantification of COVID-19 using chest CT scans. The main tasks of interest are the automatic segmentation of lung and lung lesions in chest CT scans of confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients. In this study, we compare twelve deep learning algorithms using a multi-center dataset, including both open-source and in-house developed algorithms. Results show that ensembling different methods can boost the overall test set performance for lung segmentation, binary lesion segmentation and multiclass lesion segmentation, resulting in mean Dice scores of 0.982, 0.724 and 0.469, respectively. The resulting binary lesions were segmented with a mean absolute volume error of 91.3 ml. In general, the task of distinguishing different lesion types was more difficult, with a mean absolute volume difference of 152 ml and mean Dice scores of 0.369 and 0.523 for consolidation and ground glass opacity, respectively. All methods perform binary lesion segmentation with an average volume error that is better than visual assessment by human raters, suggesting these methods are mature enough for a large-scale evaluation for use in clinical practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge