Deguang Kong
The University of Texas at Arlington
Personalized Search Via Neural Contextual Semantic Relevance Ranking
Sep 10, 2023



Abstract:Existing neural relevance models do not give enough consideration for query and item context information which diversifies the search results to adapt for personal preference. To bridge this gap, this paper presents a neural learning framework to personalize document ranking results by leveraging the signals to capture how the document fits into users' context. In particular, it models the relationships between document content and user query context using both lexical representations and semantic embeddings such that the user's intent can be better understood by data enrichment of personalized query context information. Extensive experiments performed on the search dataset, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Learning Personalized User Preference from Cold Start in Multi-turn Conversations
Sep 10, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a novel teachable conversation interaction system that is capable of learning users preferences from cold start by gradually adapting to personal preferences. In particular, the TAI system is able to automatically identify and label user preference in live interactions, manage dialogue flows for interactive teaching sessions, and reuse learned preference for preference elicitation. We develop the TAI system by leveraging BERT encoder models to encode both dialogue and relevant context information, and build action prediction (AP), argument filling (AF) and named entity recognition (NER) models to understand the teaching session. We adopt a seeker-provider interaction loop mechanism to generate diverse dialogues from cold-start. TAI is capable of learning user preference, which achieves 0.9122 turn level accuracy on out-of-sample dataset, and has been successfully adopted in production.
STREET: A Multi-Task Structured Reasoning and Explanation Benchmark
Feb 13, 2023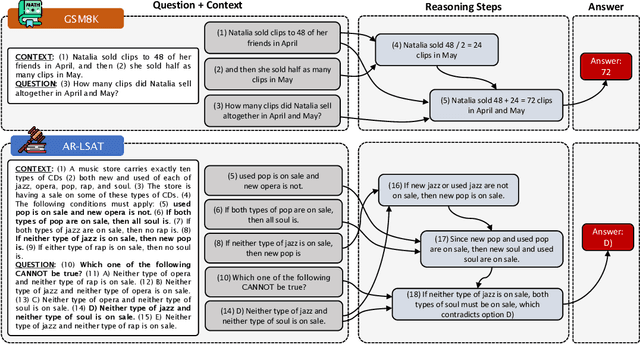
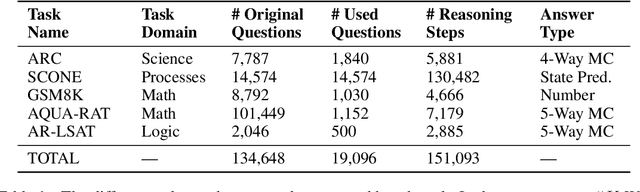
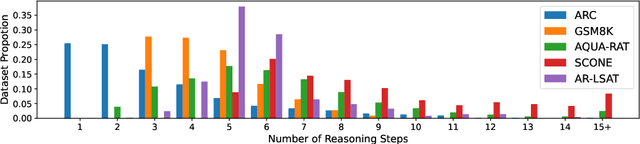
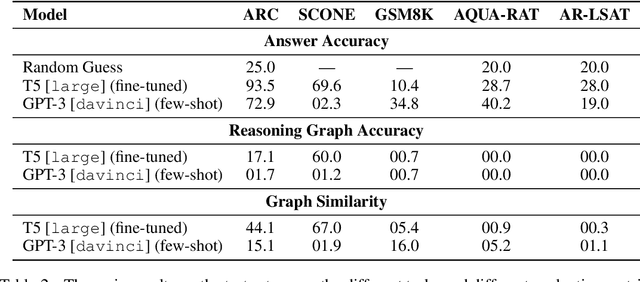
Abstract:We introduce STREET, a unified multi-task and multi-domain natural language reasoning and explanation benchmark. Unlike most existing question-answering (QA) datasets, we expect models to not only answer questions, but also produce step-by-step structured explanations describing how premises in the question are used to produce intermediate conclusions that can prove the correctness of a certain answer. We perform extensive evaluation with popular language models such as few-shot prompting GPT-3 and fine-tuned T5. We find that these models still lag behind human performance when producing such structured reasoning steps. We believe this work will provide a way for the community to better train and test systems on multi-step reasoning and explanations in natural language.
Robust Consensus Clustering and its Applications for Advertising Forecasting
Dec 27, 2022Abstract:Consensus clustering aggregates partitions in order to find a better fit by reconciling clustering results from different sources/executions. In practice, there exist noise and outliers in clustering task, which, however, may significantly degrade the performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel algorithm -- robust consensus clustering that can find common ground truth among experts' opinions, which tends to be minimally affected by the bias caused by the outliers. In particular, we formalize the robust consensus clustering problem as a constraint optimization problem, and then derive an effective algorithm upon alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) with rigorous convergence guarantee. Our method outperforms the baselines on benchmarks. We apply the proposed method to the real-world advertising campaign segmentation and forecasting tasks using the proposed consensus clustering results based on the similarity computed via Kolmogorov-Smirnov Statistics. The accurate clustering result is helpful for building the advertiser profiles so as to perform the forecasting.
Do not Waste Money on Advertising Spend: Bid Recommendation via Concavity Changes
Dec 26, 2022



Abstract:In computational advertising, a challenging problem is how to recommend the bid for advertisers to achieve the best return on investment (ROI) given budget constraint. This paper presents a bid recommendation scenario that discovers the concavity changes in click prediction curves. The recommended bid is derived based on the turning point from significant increase (i.e. concave downward) to slow increase (convex upward). Parametric learning based method is applied by solving the corresponding constraint optimization problem. Empirical studies on real-world advertising scenarios clearly demonstrate the performance gains for business metrics (including revenue increase, click increase and advertiser ROI increase).
Demystifying Advertising Campaign Bid Recommendation: A Constraint target CPA Goal Optimization
Dec 26, 2022Abstract:In cost-per-click (CPC) or cost-per-impression (CPM) advertising campaigns, advertisers always run the risk of spending the budget without getting enough conversions. Moreover, the bidding on advertising inventory has few connections with propensity one that can reach to target cost-per-acquisition (tCPA) goals. To address this problem, this paper presents a bid optimization scenario to achieve the desired tCPA goals for advertisers. In particular, we build the optimization engine to make a decision by solving the rigorously formalized constrained optimization problem, which leverages the bid landscape model learned from rich historical auction data using non-parametric learning. The proposed model can naturally recommend the bid that meets the advertisers' expectations by making inference over advertisers' historical auction behaviors, which essentially deals with the data challenges commonly faced by bid landscape modeling: incomplete logs in auctions, and uncertainty due to the variation and fluctuations in advertising bidding behaviors. The bid optimization model outperforms the baseline methods on real-world campaigns, and has been applied into a wide range of scenarios for performance improvement and revenue liftup.
Language Agnostic Multilingual Information Retrieval with Contrastive Learning
Oct 12, 2022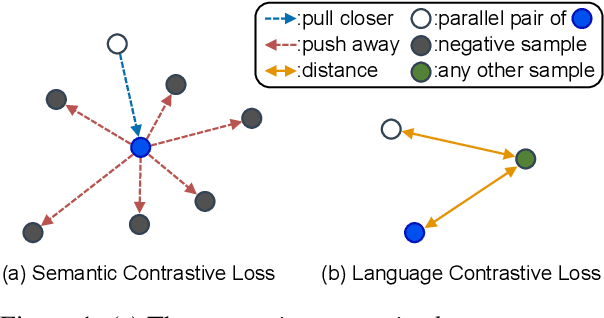
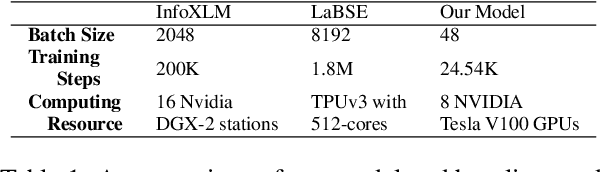
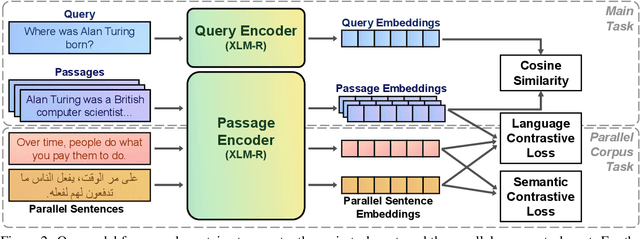
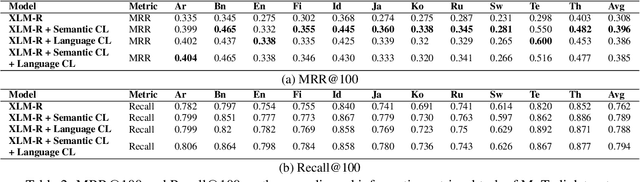
Abstract:Multilingual information retrieval is challenging due to the lack of training datasets for many low-resource languages. We present an effective method by leveraging parallel and non-parallel corpora to improve the pretrained multilingual language models' cross-lingual transfer ability for information retrieval. We design the semantic contrastive loss as regular contrastive learning to improve the cross-lingual alignment of parallel sentence pairs, and we propose a new contrastive loss, the language contrastive loss, to leverage both parallel corpora and non-parallel corpora to further improve multilingual representation learning. We train our model on an English information retrieval dataset, and test its zero-shot transfer ability to other languages. Our experiment results show that our method brings significant improvement to prior work on retrieval performance, while it requires much less computational effort. Our model can work well even with a small number of parallel corpora. And it can be used as an add-on module to any backbone and other tasks. Our code is available at: https://github.com/xiyanghu/multilingualIR.
DeepRebirth: Accelerating Deep Neural Network Execution on Mobile Devices
Jan 10, 2018



Abstract:Deploying deep neural networks on mobile devices is a challenging task. Current model compression methods such as matrix decomposition effectively reduce the deployed model size, but still cannot satisfy real-time processing requirement. This paper first discovers that the major obstacle is the excessive execution time of non-tensor layers such as pooling and normalization without tensor-like trainable parameters. This motivates us to design a novel acceleration framework: DeepRebirth through "slimming" existing consecutive and parallel non-tensor and tensor layers. The layer slimming is executed at different substructures: (a) streamline slimming by merging the consecutive non-tensor and tensor layer vertically; (b) branch slimming by merging non-tensor and tensor branches horizontally. The proposed optimization operations significantly accelerate the model execution and also greatly reduce the run-time memory cost since the slimmed model architecture contains less hidden layers. To maximally avoid accuracy loss, the parameters in new generated layers are learned with layer-wise fine-tuning based on both theoretical analysis and empirical verification. As observed in the experiment, DeepRebirth achieves more than 3x speed-up and 2.5x run-time memory saving on GoogLeNet with only 0.4% drop of top-5 accuracy on ImageNet. Furthermore, by combining with other model compression techniques, DeepRebirth offers an average of 65ms inference time on the CPU of Samsung Galaxy S6 with 86.5% top-5 accuracy, 14% faster than SqueezeNet which only has a top-5 accuracy of 80.5%.
An Iterative Locally Linear Embedding Algorithm
Jun 27, 2012

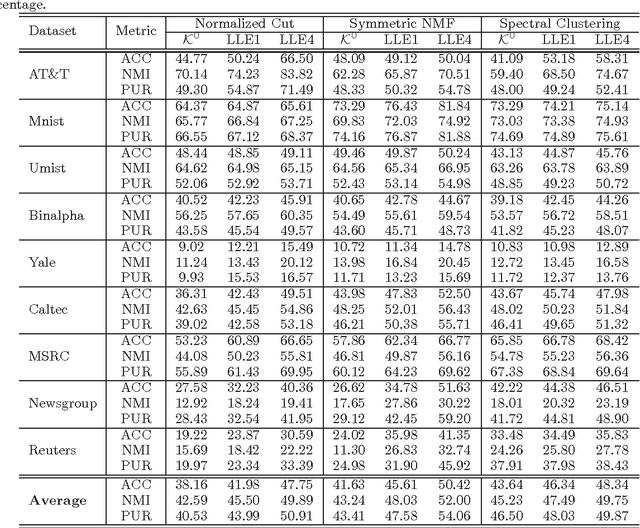

Abstract:Local Linear embedding (LLE) is a popular dimension reduction method. In this paper, we first show LLE with nonnegative constraint is equivalent to the widely used Laplacian embedding. We further propose to iterate the two steps in LLE repeatedly to improve the results. Thirdly, we relax the kNN constraint of LLE and present a sparse similarity learning algorithm. The final Iterative LLE combines these three improvements. Extensive experiment results show that iterative LLE algorithm significantly improve both classification and clustering results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge