Abhay Jha
Learning Personalized User Preference from Cold Start in Multi-turn Conversations
Sep 10, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a novel teachable conversation interaction system that is capable of learning users preferences from cold start by gradually adapting to personal preferences. In particular, the TAI system is able to automatically identify and label user preference in live interactions, manage dialogue flows for interactive teaching sessions, and reuse learned preference for preference elicitation. We develop the TAI system by leveraging BERT encoder models to encode both dialogue and relevant context information, and build action prediction (AP), argument filling (AF) and named entity recognition (NER) models to understand the teaching session. We adopt a seeker-provider interaction loop mechanism to generate diverse dialogues from cold-start. TAI is capable of learning user preference, which achieves 0.9122 turn level accuracy on out-of-sample dataset, and has been successfully adopted in production.
Alexa Conversations: An Extensible Data-driven Approach for Building Task-oriented Dialogue Systems
Apr 19, 2021
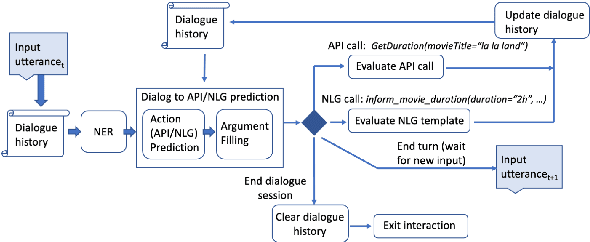
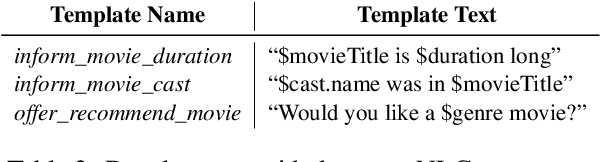
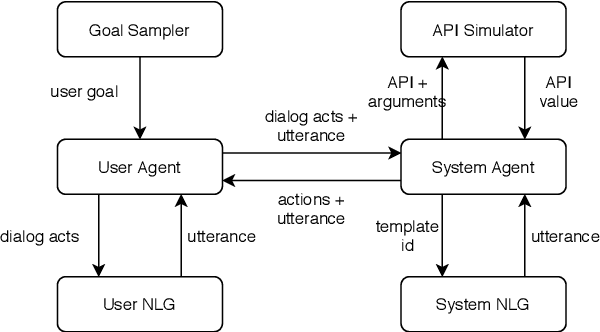
Abstract:Traditional goal-oriented dialogue systems rely on various components such as natural language understanding, dialogue state tracking, policy learning and response generation. Training each component requires annotations which are hard to obtain for every new domain, limiting scalability of such systems. Similarly, rule-based dialogue systems require extensive writing and maintenance of rules and do not scale either. End-to-End dialogue systems, on the other hand, do not require module-specific annotations but need a large amount of data for training. To overcome these problems, in this demo, we present Alexa Conversations, a new approach for building goal-oriented dialogue systems that is scalable, extensible as well as data efficient. The components of this system are trained in a data-driven manner, but instead of collecting annotated conversations for training, we generate them using a novel dialogue simulator based on a few seed dialogues and specifications of APIs and entities provided by the developer. Our approach provides out-of-the-box support for natural conversational phenomena like entity sharing across turns or users changing their mind during conversation without requiring developers to provide any such dialogue flows. We exemplify our approach using a simple pizza ordering task and showcase its value in reducing the developer burden for creating a robust experience. Finally, we evaluate our system using a typical movie ticket booking task and show that the dialogue simulator is an essential component of the system that leads to over $50\%$ improvement in turn-level action signature prediction accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge