David Tian
Dima
Gemma 3 Technical Report
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:We introduce Gemma 3, a multimodal addition to the Gemma family of lightweight open models, ranging in scale from 1 to 27 billion parameters. This version introduces vision understanding abilities, a wider coverage of languages and longer context - at least 128K tokens. We also change the architecture of the model to reduce the KV-cache memory that tends to explode with long context. This is achieved by increasing the ratio of local to global attention layers, and keeping the span on local attention short. The Gemma 3 models are trained with distillation and achieve superior performance to Gemma 2 for both pre-trained and instruction finetuned versions. In particular, our novel post-training recipe significantly improves the math, chat, instruction-following and multilingual abilities, making Gemma3-4B-IT competitive with Gemma2-27B-IT and Gemma3-27B-IT comparable to Gemini-1.5-Pro across benchmarks. We release all our models to the community.
On-device Real-time Custom Hand Gesture Recognition
Sep 19, 2023



Abstract:Most existing hand gesture recognition (HGR) systems are limited to a predefined set of gestures. However, users and developers often want to recognize new, unseen gestures. This is challenging due to the vast diversity of all plausible hand shapes, e.g. it is impossible for developers to include all hand gestures in a predefined list. In this paper, we present a user-friendly framework that lets users easily customize and deploy their own gesture recognition pipeline. Our framework provides a pre-trained single-hand embedding model that can be fine-tuned for custom gesture recognition. Users can perform gestures in front of a webcam to collect a small amount of images per gesture. We also offer a low-code solution to train and deploy the custom gesture recognition model. This makes it easy for users with limited ML expertise to use our framework. We further provide a no-code web front-end for users without any ML expertise. This makes it even easier to build and test the end-to-end pipeline. The resulting custom HGR is then ready to be run on-device for real-time scenarios. This can be done by calling a simple function in our open-sourced model inference API, MediaPipe Tasks. This entire process only takes a few minutes.
Efficient Heterogeneous Video Segmentation at the Edge
Aug 24, 2022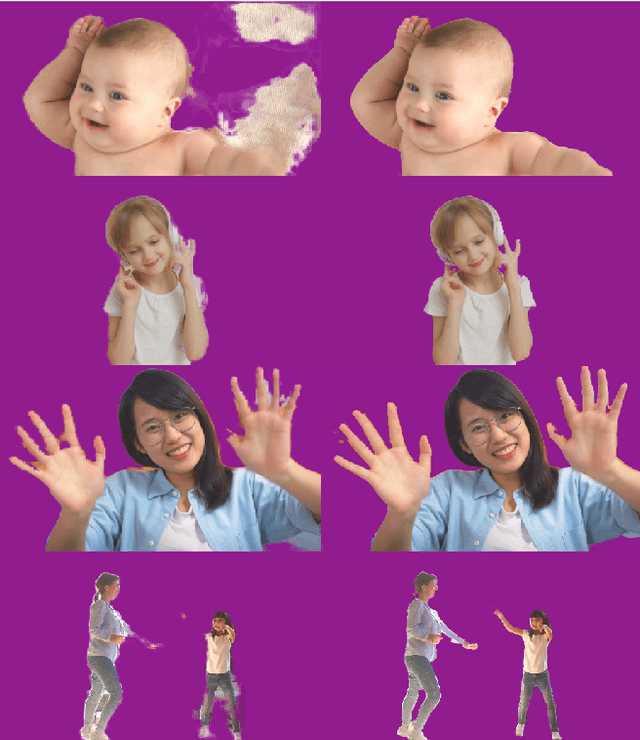
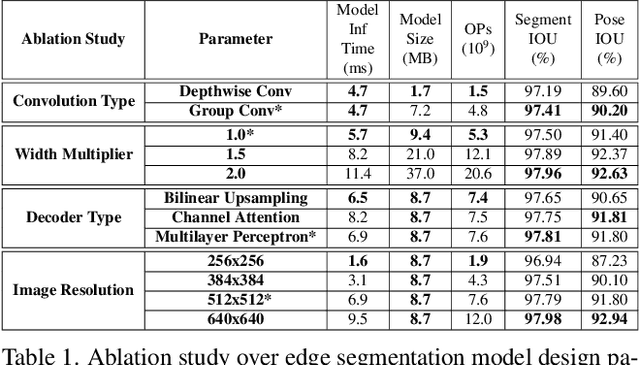
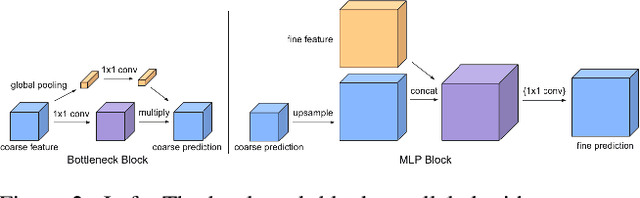
Abstract:We introduce an efficient video segmentation system for resource-limited edge devices leveraging heterogeneous compute. Specifically, we design network models by searching across multiple dimensions of specifications for the neural architectures and operations on top of already light-weight backbones, targeting commercially available edge inference engines. We further analyze and optimize the heterogeneous data flows in our systems across the CPU, the GPU and the NPU. Our approach has empirically factored well into our real-time AR system, enabling remarkably higher accuracy with quadrupled effective resolutions, yet at much shorter end-to-end latency, much higher frame rate, and even lower power consumption on edge platforms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge