Christopher Michael Rytting
Terminal-Bench: Benchmarking Agents on Hard, Realistic Tasks in Command Line Interfaces
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:AI agents may soon become capable of autonomously completing valuable, long-horizon tasks in diverse domains. Current benchmarks either do not measure real-world tasks, or are not sufficiently difficult to meaningfully measure frontier models. To this end, we present Terminal-Bench 2.0: a carefully curated hard benchmark composed of 89 tasks in computer terminal environments inspired by problems from real workflows. Each task features a unique environment, human-written solution, and comprehensive tests for verification. We show that frontier models and agents score less than 65\% on the benchmark and conduct an error analysis to identify areas for model and agent improvement. We publish the dataset and evaluation harness to assist developers and researchers in future work at https://www.tbench.ai/ .
IMBUE: Improving Interpersonal Effectiveness through Simulation and Just-in-time Feedback with Human-Language Model Interaction
Feb 19, 2024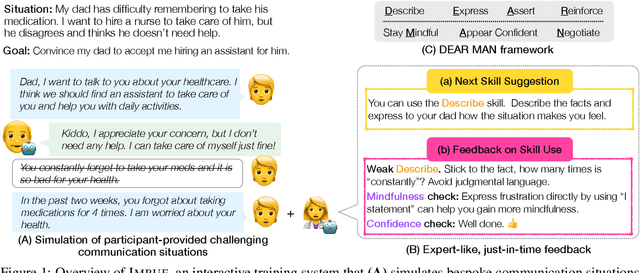
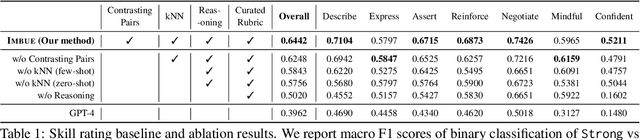
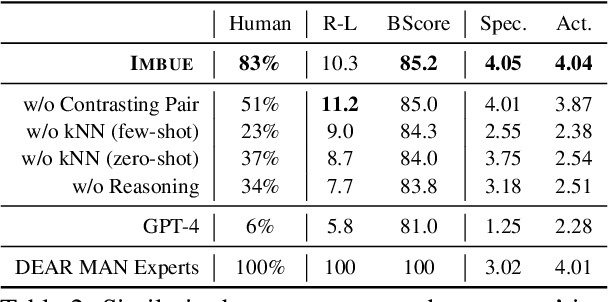
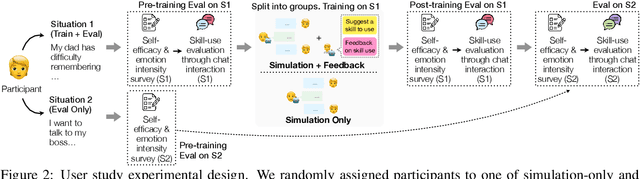
Abstract:Navigating certain communication situations can be challenging due to individuals' lack of skills and the interference of strong emotions. However, effective learning opportunities are rarely accessible. In this work, we conduct a human-centered study that uses language models to simulate bespoke communication training and provide just-in-time feedback to support the practice and learning of interpersonal effectiveness skills. We apply the interpersonal effectiveness framework from Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT), DEAR MAN, which focuses on both conversational and emotional skills. We present IMBUE, an interactive training system that provides feedback 25% more similar to experts' feedback, compared to that generated by GPT-4. IMBUE is the first to focus on communication skills and emotion management simultaneously, incorporate experts' domain knowledge in providing feedback, and be grounded in psychology theory. Through a randomized trial of 86 participants, we find that IMBUE's simulation-only variant significantly improves participants' self-efficacy (up to 17%) and reduces negative emotions (up to 25%). With IMBUE's additional just-in-time feedback, participants demonstrate 17% improvement in skill mastery, along with greater enhancements in self-efficacy (27% more) and reduction of negative emotions (16% more) compared to simulation-only. The improvement in skill mastery is the only measure that is transferred to new and more difficult situations; situation specific training is necessary for improving self-efficacy and emotion reduction.
A Roadmap to Pluralistic Alignment
Feb 07, 2024Abstract:With increased power and prevalence of AI systems, it is ever more critical that AI systems are designed to serve all, i.e., people with diverse values and perspectives. However, aligning models to serve pluralistic human values remains an open research question. In this piece, we propose a roadmap to pluralistic alignment, specifically using language models as a test bed. We identify and formalize three possible ways to define and operationalize pluralism in AI systems: 1) Overton pluralistic models that present a spectrum of reasonable responses; 2) Steerably pluralistic models that can steer to reflect certain perspectives; and 3) Distributionally pluralistic models that are well-calibrated to a given population in distribution. We also propose and formalize three possible classes of pluralistic benchmarks: 1) Multi-objective benchmarks, 2) Trade-off steerable benchmarks, which incentivize models to steer to arbitrary trade-offs, and 3) Jury-pluralistic benchmarks which explicitly model diverse human ratings. We use this framework to argue that current alignment techniques may be fundamentally limited for pluralistic AI; indeed, we highlight empirical evidence, both from our own experiments and from other work, that standard alignment procedures might reduce distributional pluralism in models, motivating the need for further research on pluralistic alignment.
Towards Coding Social Science Datasets with Language Models
Jun 03, 2023Abstract:Researchers often rely on humans to code (label, annotate, etc.) large sets of texts. This kind of human coding forms an important part of social science research, yet the coding process is both resource intensive and highly variable from application to application. In some cases, efforts to automate this process have achieved human-level accuracies, but to achieve this, these attempts frequently rely on thousands of hand-labeled training examples, which makes them inapplicable to small-scale research studies and costly for large ones. Recent advances in a specific kind of artificial intelligence tool - language models (LMs) - provide a solution to this problem. Work in computer science makes it clear that LMs are able to classify text, without the cost (in financial terms and human effort) of alternative methods. To demonstrate the possibilities of LMs in this area of political science, we use GPT-3, one of the most advanced LMs, as a synthetic coder and compare it to human coders. We find that GPT-3 can match the performance of typical human coders and offers benefits over other machine learning methods of coding text. We find this across a variety of domains using very different coding procedures. This provides exciting evidence that language models can serve as a critical advance in the coding of open-ended texts in a variety of applications.
An Information-theoretic Approach to Prompt Engineering Without Ground Truth Labels
Mar 21, 2022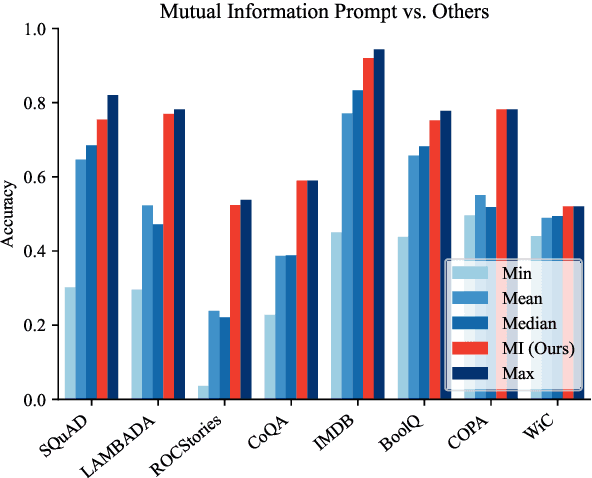
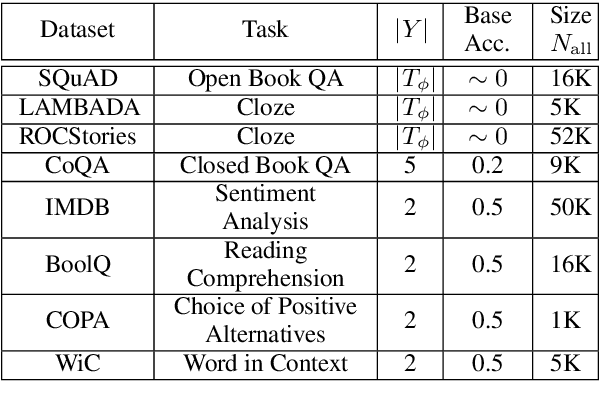
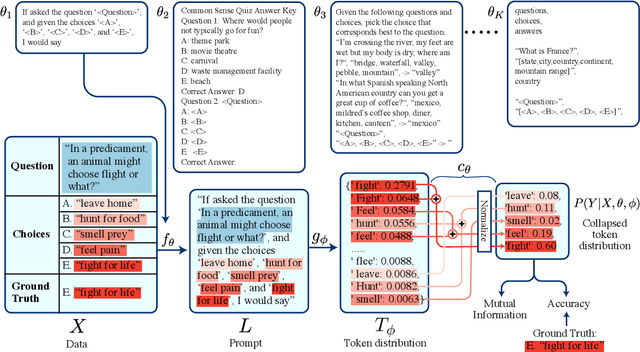
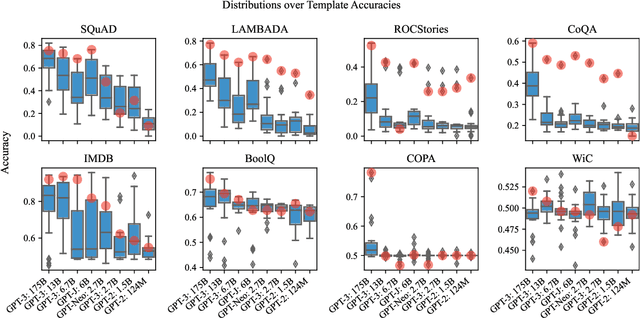
Abstract:Pre-trained language models derive substantial linguistic and factual knowledge from the massive corpora on which they are trained, and prompt engineering seeks to align these models to specific tasks. Unfortunately, existing prompt engineering methods require significant amounts of labeled data, access to model parameters, or both. We introduce a new method for selecting prompt templates \textit{without labeled examples} and \textit{without direct access to the model}. Specifically, over a set of candidate templates, we choose the template that maximizes the mutual information between the input and the corresponding model output. Across 8 datasets representing 7 distinct NLP tasks, we show that when a template has high mutual information, it also has high accuracy on the task. On the largest model, selecting prompts with our method gets 90\% of the way from the average prompt accuracy to the best prompt accuracy and requires no ground truth labels.
Leveraging the Inductive Bias of Large Language Models for Abstract Textual Reasoning
Oct 05, 2021
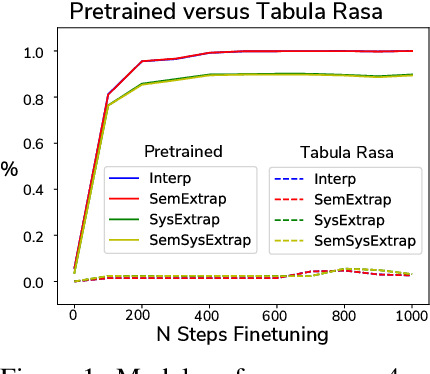
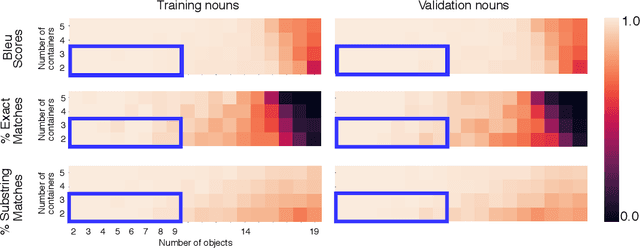
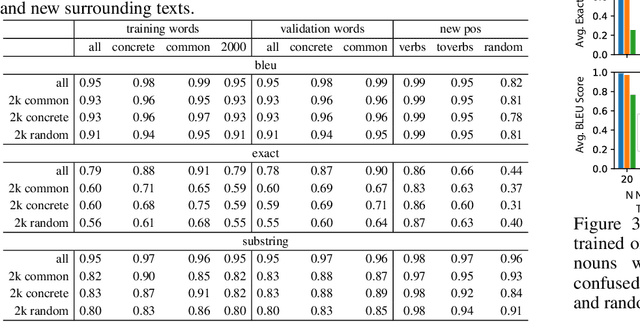
Abstract:Large natural language models (such as GPT-3 or T5) demonstrate impressive abilities across a range of general NLP tasks. Here, we show that the knowledge embedded in such models provides a useful inductive bias, not just on traditional NLP tasks, but also in the nontraditional task of training a symbolic reasoning engine. We observe that these engines learn quickly and generalize in a natural way that reflects human intuition. For example, training such a system to model block-stacking might naturally generalize to stacking other types of objects because of structure in the real world that has been partially captured by the language describing it. We study several abstract textual reasoning tasks, such as object manipulation and navigation, and demonstrate multiple types of generalization to novel scenarios and the symbols that comprise them. We also demonstrate the surprising utility of \textit{compositional learning}, where a learner dedicated to mastering a complicated task gains an advantage by training on relevant simpler tasks instead of jumping straight to the complicated task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge