Inna Wanyin Lin
IMBUE: Improving Interpersonal Effectiveness through Simulation and Just-in-time Feedback with Human-Language Model Interaction
Feb 19, 2024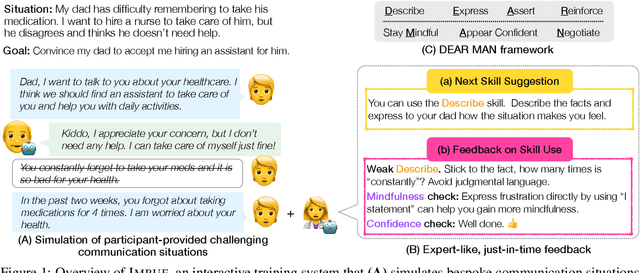
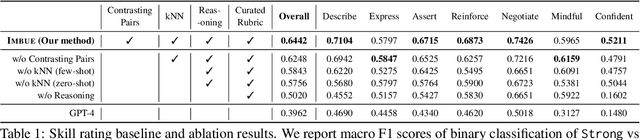
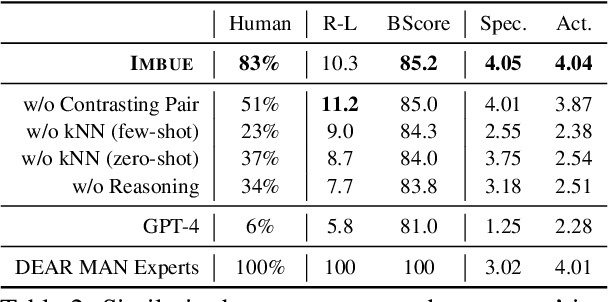
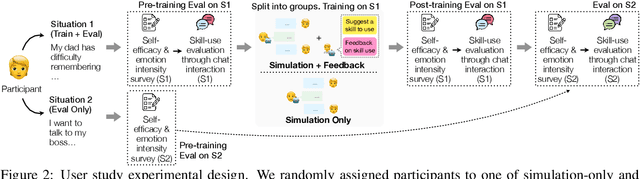
Abstract:Navigating certain communication situations can be challenging due to individuals' lack of skills and the interference of strong emotions. However, effective learning opportunities are rarely accessible. In this work, we conduct a human-centered study that uses language models to simulate bespoke communication training and provide just-in-time feedback to support the practice and learning of interpersonal effectiveness skills. We apply the interpersonal effectiveness framework from Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT), DEAR MAN, which focuses on both conversational and emotional skills. We present IMBUE, an interactive training system that provides feedback 25% more similar to experts' feedback, compared to that generated by GPT-4. IMBUE is the first to focus on communication skills and emotion management simultaneously, incorporate experts' domain knowledge in providing feedback, and be grounded in psychology theory. Through a randomized trial of 86 participants, we find that IMBUE's simulation-only variant significantly improves participants' self-efficacy (up to 17%) and reduces negative emotions (up to 25%). With IMBUE's additional just-in-time feedback, participants demonstrate 17% improvement in skill mastery, along with greater enhancements in self-efficacy (27% more) and reduction of negative emotions (16% more) compared to simulation-only. The improvement in skill mastery is the only measure that is transferred to new and more difficult situations; situation specific training is necessary for improving self-efficacy and emotion reduction.
A Computational Framework for Behavioral Assessment of LLM Therapists
Jan 01, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of ChatGPT and other large language models (LLMs) has greatly increased interest in utilizing LLMs as therapists to support individuals struggling with mental health challenges. However, due to the lack of systematic studies, our understanding of how LLM therapists behave, i.e., ways in which they respond to clients, is significantly limited. Understanding their behavior across a wide range of clients and situations is crucial to accurately assess their capabilities and limitations in the high-risk setting of mental health, where undesirable behaviors can lead to severe consequences. In this paper, we propose BOLT, a novel computational framework to study the conversational behavior of LLMs when employed as therapists. We develop an in-context learning method to quantitatively measure the behavior of LLMs based on 13 different psychotherapy techniques including reflections, questions, solutions, normalizing, and psychoeducation. Subsequently, we compare the behavior of LLM therapists against that of high- and low-quality human therapy, and study how their behavior can be modulated to better reflect behaviors observed in high-quality therapy. Our analysis of GPT and Llama-variants reveals that these LLMs often resemble behaviors more commonly exhibited in low-quality therapy rather than high-quality therapy, such as offering a higher degree of problem-solving advice when clients share emotions, which is against typical recommendations. At the same time, unlike low-quality therapy, LLMs reflect significantly more upon clients' needs and strengths. Our analysis framework suggests that despite the ability of LLMs to generate anecdotal examples that appear similar to human therapists, LLM therapists are currently not fully consistent with high-quality care, and thus require additional research to ensure quality care.
Facilitating Self-Guided Mental Health Interventions Through Human-Language Model Interaction: A Case Study of Cognitive Restructuring
Oct 24, 2023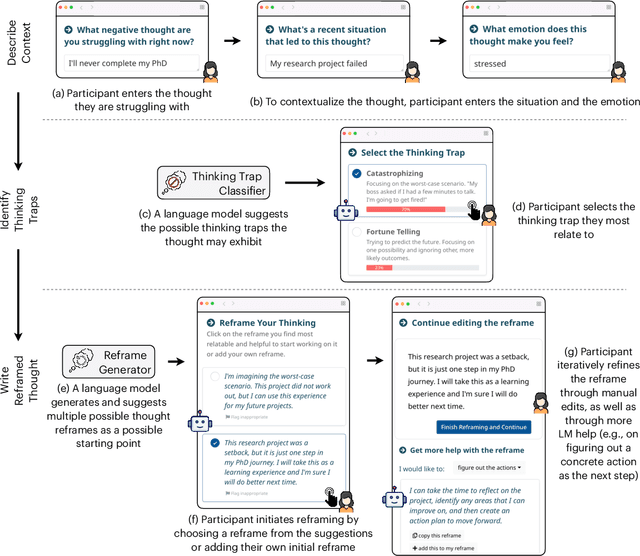
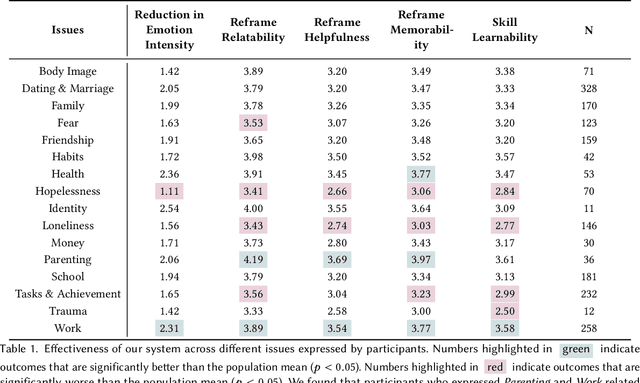
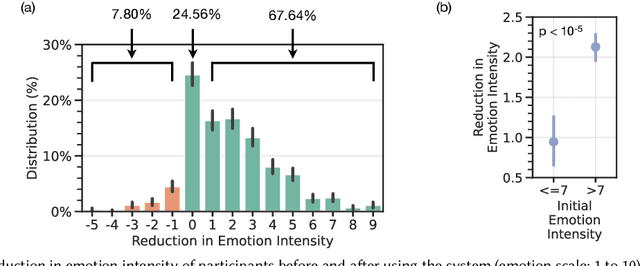
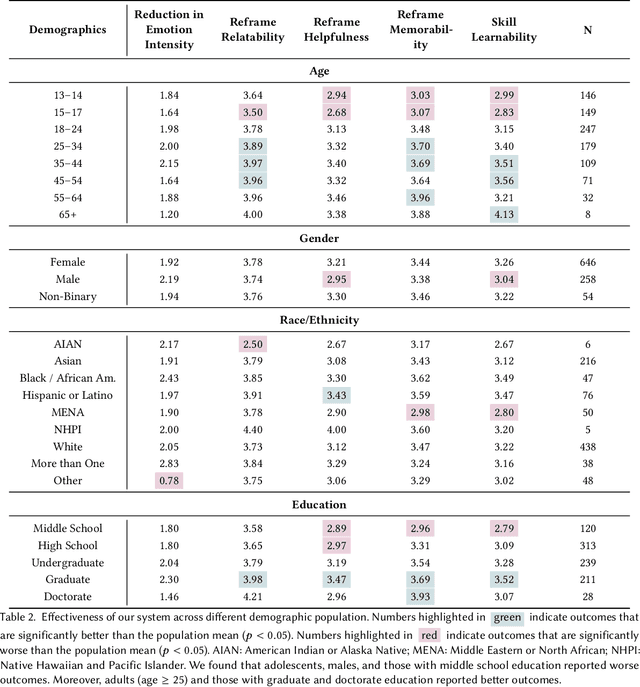
Abstract:Self-guided mental health interventions, such as "do-it-yourself" tools to learn and practice coping strategies, show great promise to improve access to mental health care. However, these interventions are often cognitively demanding and emotionally triggering, creating accessibility barriers that limit their wide-scale implementation and adoption. In this paper, we study how human-language model interaction can support self-guided mental health interventions. We take cognitive restructuring, an evidence-based therapeutic technique to overcome negative thinking, as a case study. In an IRB-approved randomized field study on a large mental health website with 15,531 participants, we design and evaluate a system that uses language models to support people through various steps of cognitive restructuring. Our findings reveal that our system positively impacts emotional intensity for 67% of participants and helps 65% overcome negative thoughts. Although adolescents report relatively worse outcomes, we find that tailored interventions that simplify language model generations improve overall effectiveness and equity.
Cognitive Reframing of Negative Thoughts through Human-Language Model Interaction
May 04, 2023



Abstract:A proven therapeutic technique to overcome negative thoughts is to replace them with a more hopeful "reframed thought." Although therapy can help people practice and learn this Cognitive Reframing of Negative Thoughts, clinician shortages and mental health stigma commonly limit people's access to therapy. In this paper, we conduct a human-centered study of how language models may assist people in reframing negative thoughts. Based on psychology literature, we define a framework of seven linguistic attributes that can be used to reframe a thought. We develop automated metrics to measure these attributes and validate them with expert judgements from mental health practitioners. We collect a dataset of 600 situations, thoughts and reframes from practitioners and use it to train a retrieval-enhanced in-context learning model that effectively generates reframed thoughts and controls their linguistic attributes. To investigate what constitutes a "high-quality" reframe, we conduct an IRB-approved randomized field study on a large mental health website with over 2,000 participants. Amongst other findings, we show that people prefer highly empathic or specific reframes, as opposed to reframes that are overly positive. Our findings provide key implications for the use of LMs to assist people in overcoming negative thoughts.
Gendered Mental Health Stigma in Masked Language Models
Oct 27, 2022Abstract:Mental health stigma prevents many individuals from receiving the appropriate care, and social psychology studies have shown that mental health tends to be overlooked in men. In this work, we investigate gendered mental health stigma in masked language models. In doing so, we operationalize mental health stigma by developing a framework grounded in psychology research: we use clinical psychology literature to curate prompts, then evaluate the models' propensity to generate gendered words. We find that masked language models capture societal stigma about gender in mental health: models are consistently more likely to predict female subjects than male in sentences about having a mental health condition (32% vs. 19%), and this disparity is exacerbated for sentences that indicate treatment-seeking behavior. Furthermore, we find that different models capture dimensions of stigma differently for men and women, associating stereotypes like anger, blame, and pity more with women with mental health conditions than with men. In showing the complex nuances of models' gendered mental health stigma, we demonstrate that context and overlapping dimensions of identity are important considerations when assessing computational models' social biases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge