Chien-Yao Wang
YOLO-RD: Introducing Relevant and Compact Explicit Knowledge to YOLO by Retriever-Dictionary
Oct 20, 2024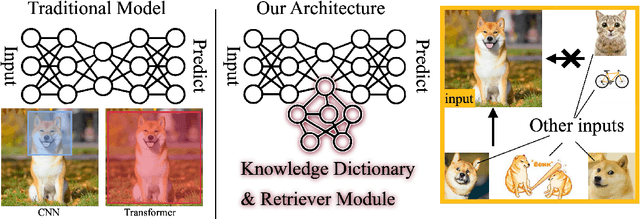
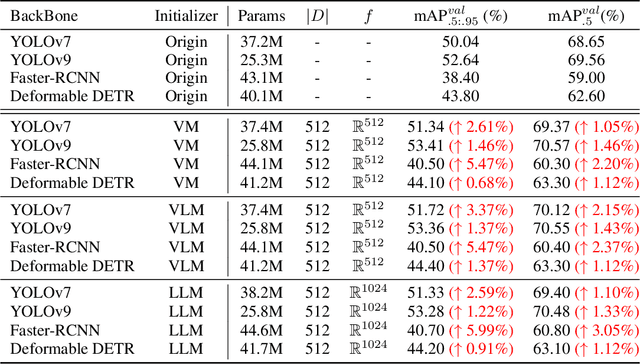
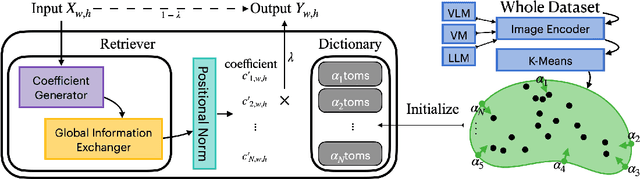
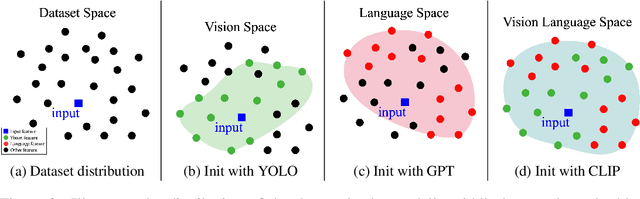
Abstract:Identifying and localizing objects within images is a fundamental challenge, and numerous efforts have been made to enhance model accuracy by experimenting with diverse architectures and refining training strategies. Nevertheless, a prevalent limitation in existing models is overemphasizing the current input while ignoring the information from the entire dataset. We introduce an innovative {\em \textbf{R}etriever}-{\em\textbf{D}ictionary} (RD) module to address this issue. This architecture enables YOLO-based models to efficiently retrieve features from a Dictionary that contains the insight of the dataset, which is built by the knowledge from Visual Models (VM), Large Language Models (LLM), or Visual Language Models (VLM). The flexible RD enables the model to incorporate such explicit knowledge that enhances the ability to benefit multiple tasks, specifically, segmentation, detection, and classification, from pixel to image level. The experiments show that using the RD significantly improves model performance, achieving more than a 3\% increase in mean Average Precision for object detection with less than a 1\% increase in model parameters. Beyond 1-stage object detection models, the RD module improves the effectiveness of 2-stage models and DETR-based architectures, such as Faster R-CNN and Deformable DETR
YOLOv1 to YOLOv10: The fastest and most accurate real-time object detection systems
Aug 18, 2024Abstract:This is a comprehensive review of the YOLO series of systems. Different from previous literature surveys, this review article re-examines the characteristics of the YOLO series from the latest technical point of view. At the same time, we also analyzed how the YOLO series continued to influence and promote real-time computer vision-related research and led to the subsequent development of computer vision and language models.We take a closer look at how the methods proposed by the YOLO series in the past ten years have affected the development of subsequent technologies and show the applications of YOLO in various fields. We hope this article can play a good guiding role in subsequent real-time computer vision development.
YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:Today's deep learning methods focus on how to design the most appropriate objective functions so that the prediction results of the model can be closest to the ground truth. Meanwhile, an appropriate architecture that can facilitate acquisition of enough information for prediction has to be designed. Existing methods ignore a fact that when input data undergoes layer-by-layer feature extraction and spatial transformation, large amount of information will be lost. This paper will delve into the important issues of data loss when data is transmitted through deep networks, namely information bottleneck and reversible functions. We proposed the concept of programmable gradient information (PGI) to cope with the various changes required by deep networks to achieve multiple objectives. PGI can provide complete input information for the target task to calculate objective function, so that reliable gradient information can be obtained to update network weights. In addition, a new lightweight network architecture -- Generalized Efficient Layer Aggregation Network (GELAN), based on gradient path planning is designed. GELAN's architecture confirms that PGI has gained superior results on lightweight models. We verified the proposed GELAN and PGI on MS COCO dataset based object detection. The results show that GELAN only uses conventional convolution operators to achieve better parameter utilization than the state-of-the-art methods developed based on depth-wise convolution. PGI can be used for variety of models from lightweight to large. It can be used to obtain complete information, so that train-from-scratch models can achieve better results than state-of-the-art models pre-trained using large datasets, the comparison results are shown in Figure 1. The source codes are at: https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov9.
YOLOR-Based Multi-Task Learning
Sep 29, 2023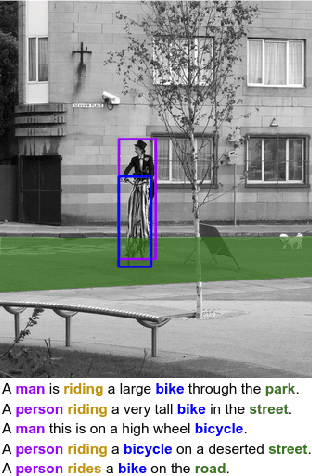

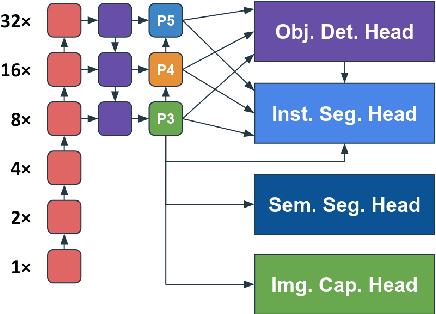

Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) aims to learn multiple tasks using a single model and jointly improve all of them assuming generalization and shared semantics. Reducing conflicts between tasks during joint learning is difficult and generally requires careful network design and extremely large models. We propose building on You Only Learn One Representation (YOLOR), a network architecture specifically designed for multitasking. YOLOR leverages both explicit and implicit knowledge, from data observations and learned latents, respectively, to improve a shared representation while minimizing the number of training parameters. However, YOLOR and its follow-up, YOLOv7, only trained two tasks at once. In this paper, we jointly train object detection, instance segmentation, semantic segmentation, and image captioning. We analyze tradeoffs and attempt to maximize sharing of semantic information. Through our architecture and training strategies, we find that our method achieves competitive performance on all tasks while maintaining a low parameter count and without any pre-training. We will release code soon.
MVA2023 Small Object Detection Challenge for Spotting Birds: Dataset, Methods, and Results
Jul 18, 2023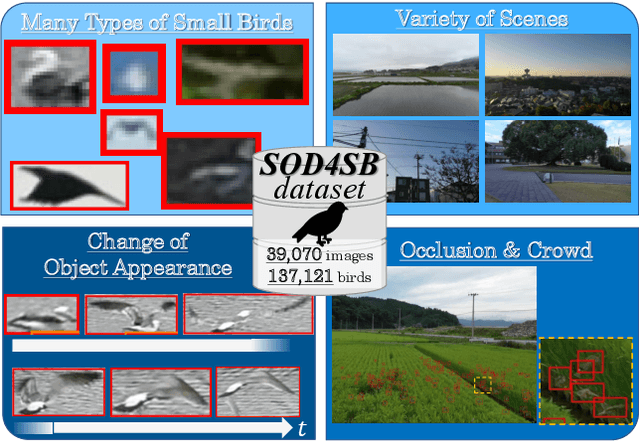
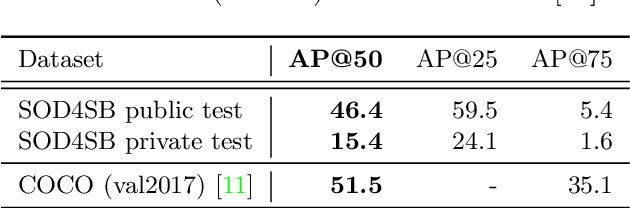
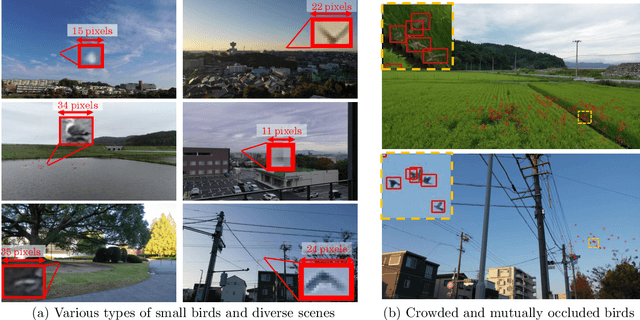
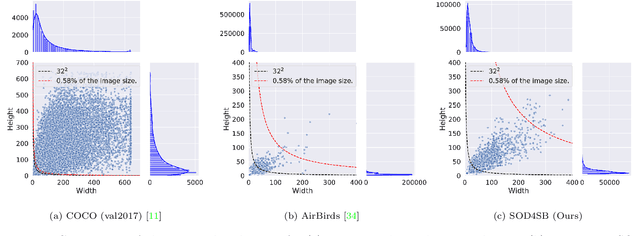
Abstract:Small Object Detection (SOD) is an important machine vision topic because (i) a variety of real-world applications require object detection for distant objects and (ii) SOD is a challenging task due to the noisy, blurred, and less-informative image appearances of small objects. This paper proposes a new SOD dataset consisting of 39,070 images including 137,121 bird instances, which is called the Small Object Detection for Spotting Birds (SOD4SB) dataset. The detail of the challenge with the SOD4SB dataset is introduced in this paper. In total, 223 participants joined this challenge. This paper briefly introduces the award-winning methods. The dataset, the baseline code, and the website for evaluation on the public testset are publicly available.
NeighborTrack: Improving Single Object Tracking by Bipartite Matching with Neighbor Tracklets
Nov 12, 2022Abstract:We propose a post-processor, called NeighborTrack, that leverages neighbor information of the tracking target to validate and improve single-object tracking (SOT) results. It requires no additional data or retraining. Instead, it uses the confidence score predicted by the backbone SOT network to automatically derive neighbor information and then uses this information to improve the tracking results. When tracking an occluded target, its appearance features are untrustworthy. However, a general siamese network often cannot tell whether the tracked object is occluded by reading the confidence score alone, because it could be misled by neighbors with high confidence scores. Our proposed NeighborTrack takes advantage of unoccluded neighbors' information to reconfirm the tracking target and reduces false tracking when the target is occluded. It not only reduces the impact caused by occlusion, but also fixes tracking problems caused by object appearance changes. NeighborTrack is agnostic to SOT networks and post-processing methods. For the VOT challenge dataset commonly used in short-term object tracking, we improve three famous SOT networks, Ocean, TransT, and OSTrack, by an average of ${1.92\%}$ EAO and ${2.11\%}$ robustness. For the mid- and long-term tracking experiments based on OSTrack, we achieve state-of-the-art ${72.25\%}$ AUC on LaSOT and ${75.7\%}$ AO on GOT-10K.
Designing Network Design Strategies Through Gradient Path Analysis
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Designing a high-efficiency and high-quality expressive network architecture has always been the most important research topic in the field of deep learning. Most of today's network design strategies focus on how to integrate features extracted from different layers, and how to design computing units to effectively extract these features, thereby enhancing the expressiveness of the network. This paper proposes a new network design strategy, i.e., to design the network architecture based on gradient path analysis. On the whole, most of today's mainstream network design strategies are based on feed forward path, that is, the network architecture is designed based on the data path. In this paper, we hope to enhance the expressive ability of the trained model by improving the network learning ability. Due to the mechanism driving the network parameter learning is the backward propagation algorithm, we design network design strategies based on back propagation path. We propose the gradient path design strategies for the layer-level, the stage-level, and the network-level, and the design strategies are proved to be superior and feasible from theoretical analysis and experiments.
SearchTrack: Multiple Object Tracking with Object-Customized Search and Motion-Aware Features
Oct 29, 2022



Abstract:The paper presents a new method, SearchTrack, for multiple object tracking and segmentation (MOTS). To address the association problem between detected objects, SearchTrack proposes object-customized search and motion-aware features. By maintaining a Kalman filter for each object, we encode the predicted motion into the motion-aware feature, which includes both motion and appearance cues. For each object, a customized fully convolutional search engine is created by SearchTrack by learning a set of weights for dynamic convolutions specific to the object. Experiments demonstrate that our SearchTrack method outperforms competitive methods on both MOTS and MOT tasks, particularly in terms of association accuracy. Our method achieves 71.5 HOTA (car) and 57.6 HOTA (pedestrian) on the KITTI MOTS and 53.4 HOTA on MOT17. In terms of association accuracy, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance among 2D online methods on the KITTI MOTS. Our code is available at https://github.com/qa276390/SearchTrack.
YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors
Jul 06, 2022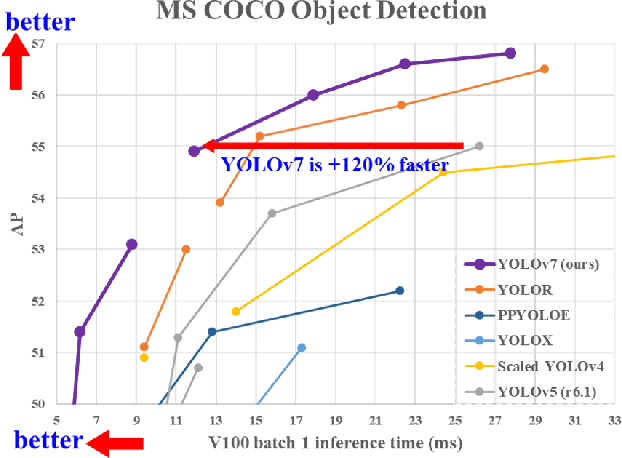
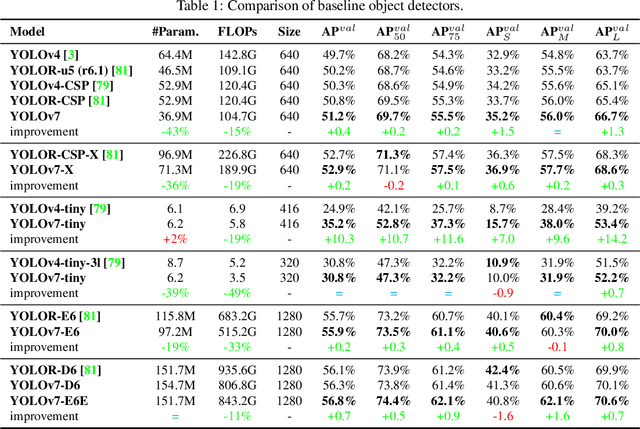
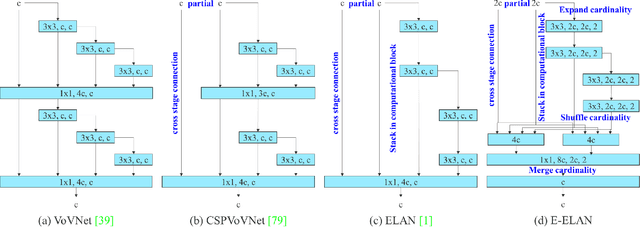
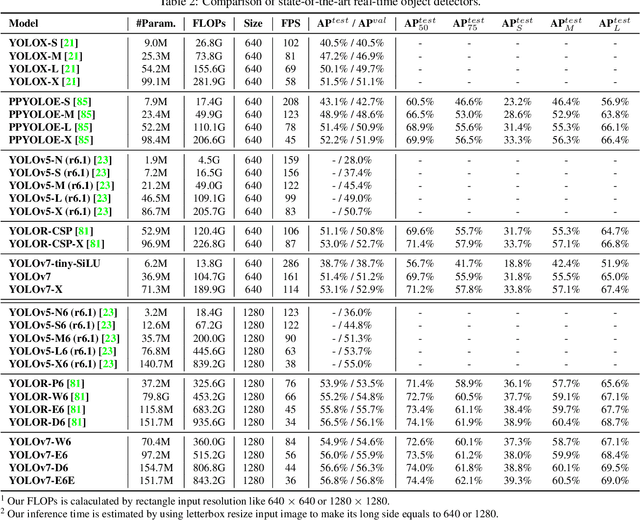
Abstract:YOLOv7 surpasses all known object detectors in both speed and accuracy in the range from 5 FPS to 160 FPS and has the highest accuracy 56.8% AP among all known real-time object detectors with 30 FPS or higher on GPU V100. YOLOv7-E6 object detector (56 FPS V100, 55.9% AP) outperforms both transformer-based detector SWIN-L Cascade-Mask R-CNN (9.2 FPS A100, 53.9% AP) by 509% in speed and 2% in accuracy, and convolutional-based detector ConvNeXt-XL Cascade-Mask R-CNN (8.6 FPS A100, 55.2% AP) by 551% in speed and 0.7% AP in accuracy, as well as YOLOv7 outperforms: YOLOR, YOLOX, Scaled-YOLOv4, YOLOv5, DETR, Deformable DETR, DINO-5scale-R50, ViT-Adapter-B and many other object detectors in speed and accuracy. Moreover, we train YOLOv7 only on MS COCO dataset from scratch without using any other datasets or pre-trained weights. Source code is released in https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7.
You Only Learn One Representation: Unified Network for Multiple Tasks
May 10, 2021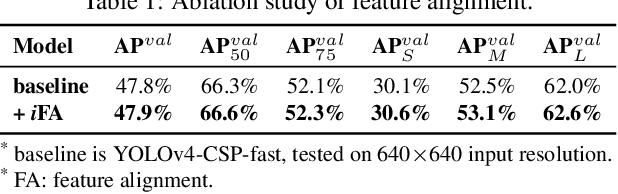
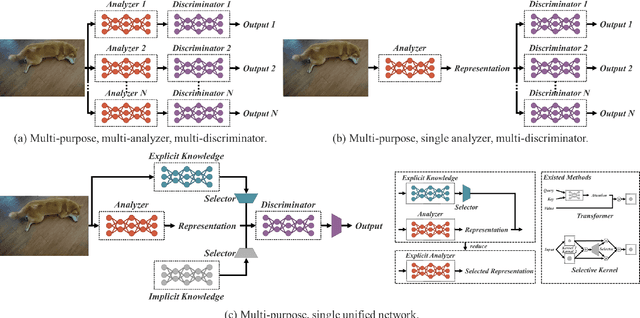
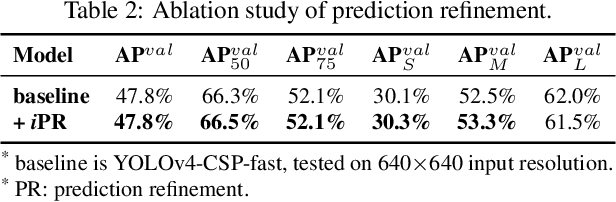
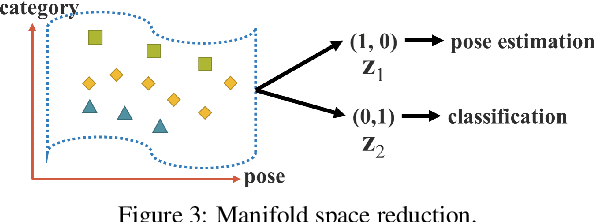
Abstract:People ``understand'' the world via vision, hearing, tactile, and also the past experience. Human experience can be learned through normal learning (we call it explicit knowledge), or subconsciously (we call it implicit knowledge). These experiences learned through normal learning or subconsciously will be encoded and stored in the brain. Using these abundant experience as a huge database, human beings can effectively process data, even they were unseen beforehand. In this paper, we propose a unified network to encode implicit knowledge and explicit knowledge together, just like the human brain can learn knowledge from normal learning as well as subconsciousness learning. The unified network can generate a unified representation to simultaneously serve various tasks. We can perform kernel space alignment, prediction refinement, and multi-task learning in a convolutional neural network. The results demonstrate that when implicit knowledge is introduced into the neural network, it benefits the performance of all tasks. We further analyze the implicit representation learnt from the proposed unified network, and it shows great capability on catching the physical meaning of different tasks. The source code of this work is at : https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge