Mu-Yi Shen
LTCXNet: Advancing Chest X-Ray Analysis with Solutions for Long-Tailed Multi-Label Classification and Fairness Challenges
Nov 16, 2024Abstract:Chest X-rays (CXRs) often display various diseases with disparate class frequencies, leading to a long-tailed, multi-label data distribution. In response to this challenge, we explore the Pruned MIMIC-CXR-LT dataset, a curated collection derived from the MIMIC-CXR dataset, specifically designed to represent a long-tailed and multi-label data scenario. We introduce LTCXNet, a novel framework that integrates the ConvNeXt model, ML-Decoder, and strategic data augmentation, further enhanced by an ensemble approach. We demonstrate that LTCXNet improves the performance of CXR interpretation across all classes, especially enhancing detection in rarer classes like `Pneumoperitoneum' and `Pneumomediastinum' by 79\% and 48\%, respectively. Beyond performance metrics, our research extends into evaluating fairness, highlighting that some methods, while improving model accuracy, could inadvertently affect fairness across different demographic groups negatively. This work contributes to advancing the understanding and management of long-tailed, multi-label data distributions in medical imaging, paving the way for more equitable and effective diagnostic tools.
DriveEnv-NeRF: Exploration of A NeRF-Based Autonomous Driving Environment for Real-World Performance Validation
Mar 23, 2024Abstract:In this study, we introduce the DriveEnv-NeRF framework, which leverages Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) to enable the validation and faithful forecasting of the efficacy of autonomous driving agents in a targeted real-world scene. Standard simulator-based rendering often fails to accurately reflect real-world performance due to the sim-to-real gap, which represents the disparity between virtual simulations and real-world conditions. To mitigate this gap, we propose a workflow for building a high-fidelity simulation environment of the targeted real-world scene using NeRF. This approach is capable of rendering realistic images from novel viewpoints and constructing 3D meshes for emulating collisions. The validation of these capabilities through the comparison of success rates in both simulated and real environments demonstrates the benefits of using DriveEnv-NeRF as a real-world performance indicator. Furthermore, the DriveEnv-NeRF framework can serve as a training environment for autonomous driving agents under various lighting conditions. This approach enhances the robustness of the agents and reduces performance degradation when deployed to the target real scene, compared to agents fully trained using the standard simulator rendering pipeline.
MVA2023 Small Object Detection Challenge for Spotting Birds: Dataset, Methods, and Results
Jul 18, 2023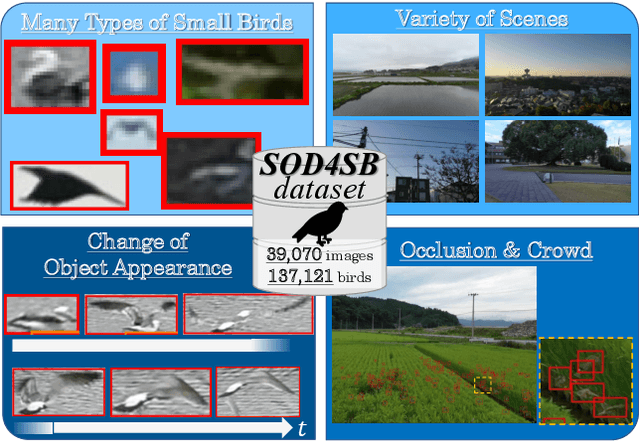
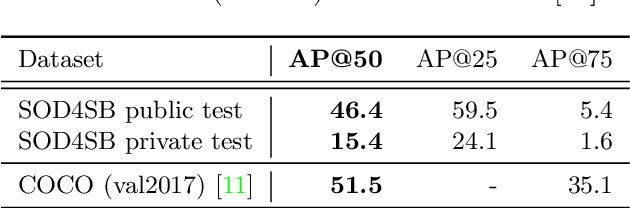
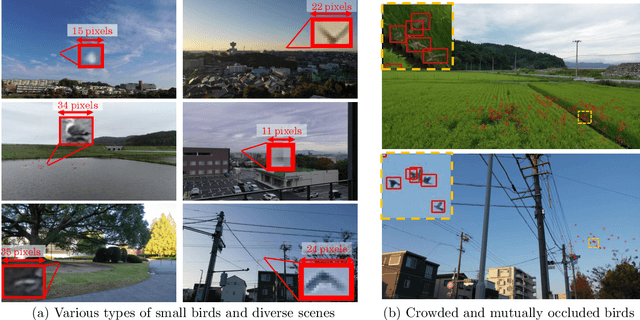
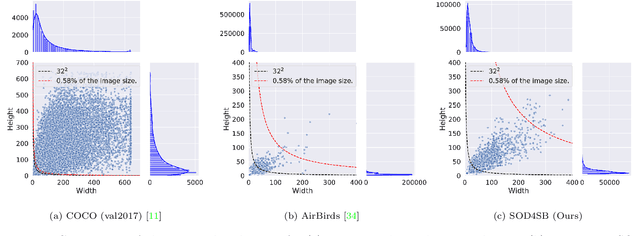
Abstract:Small Object Detection (SOD) is an important machine vision topic because (i) a variety of real-world applications require object detection for distant objects and (ii) SOD is a challenging task due to the noisy, blurred, and less-informative image appearances of small objects. This paper proposes a new SOD dataset consisting of 39,070 images including 137,121 bird instances, which is called the Small Object Detection for Spotting Birds (SOD4SB) dataset. The detail of the challenge with the SOD4SB dataset is introduced in this paper. In total, 223 participants joined this challenge. This paper briefly introduces the award-winning methods. The dataset, the baseline code, and the website for evaluation on the public testset are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge