Chang Gong
Pseudocode-Injection Magic: Enabling LLMs to Tackle Graph Computational Tasks
Jan 23, 2025Abstract:Graph computational tasks are inherently challenging and often demand the development of advanced algorithms for effective solutions. With the emergence of large language models (LLMs), researchers have begun investigating their potential to address these tasks. However, existing approaches are constrained by LLMs' limited capability to comprehend complex graph structures and their high inference costs, rendering them impractical for handling large-scale graphs. Inspired by human approaches to graph problems, we introduce a novel framework, PIE (Pseudocode-Injection-Enhanced LLM Reasoning for Graph Computational Tasks), which consists of three key steps: problem understanding, prompt design, and code generation. In this framework, LLMs are tasked with understanding the problem and extracting relevant information to generate correct code. The responsibility for analyzing the graph structure and executing the code is delegated to the interpreter. We inject task-related pseudocodes into the prompts to further assist the LLMs in generating efficient code. We also employ cost-effective trial-and-error techniques to ensure that the LLM-generated code executes correctly. Unlike other methods that require invoking LLMs for each individual test case, PIE only calls the LLM during the code generation phase, allowing the generated code to be reused and significantly reducing inference costs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PIE outperforms existing baselines in terms of both accuracy and computational efficiency.
CausalTAD: Causal Implicit Generative Model for Debiased Online Trajectory Anomaly Detection
Dec 25, 2024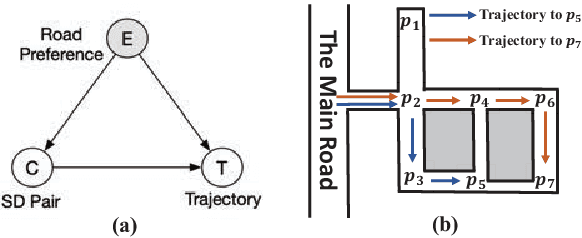
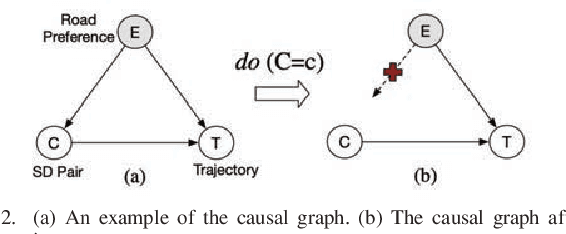
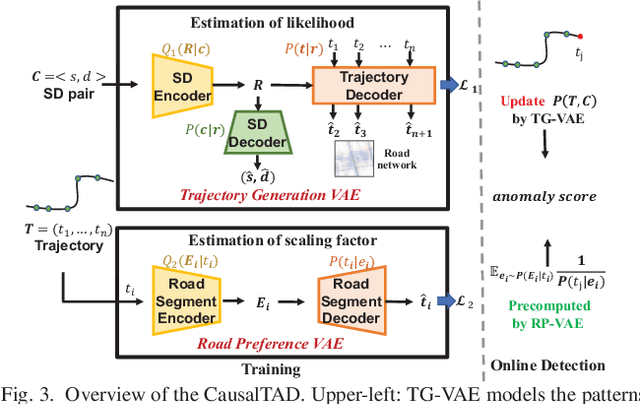
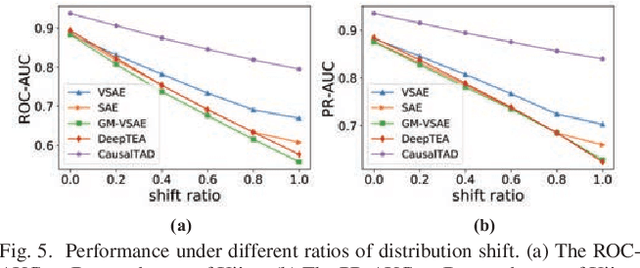
Abstract:Trajectory anomaly detection, aiming to estimate the anomaly risk of trajectories given the Source-Destination (SD) pairs, has become a critical problem for many real-world applications. Existing solutions directly train a generative model for observed trajectories and calculate the conditional generative probability $P({T}|{C})$ as the anomaly risk, where ${T}$ and ${C}$ represent the trajectory and SD pair respectively. However, we argue that the observed trajectories are confounded by road network preference which is a common cause of both SD distribution and trajectories. Existing methods ignore this issue limiting their generalization ability on out-of-distribution trajectories. In this paper, we define the debiased trajectory anomaly detection problem and propose a causal implicit generative model, namely CausalTAD, to solve it. CausalTAD adopts do-calculus to eliminate the confounding bias of road network preference and estimates $P({T}|do({C}))$ as the anomaly criterion. Extensive experiments show that CausalTAD can not only achieve superior performance on trained trajectories but also generally improve the performance of out-of-distribution data, with improvements of $2.1\% \sim 5.7\%$ and $10.6\% \sim 32.7\%$ respectively.
PORCA: Root Cause Analysis with Partially
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:Root Cause Analysis (RCA) aims at identifying the underlying causes of system faults by uncovering and analyzing the causal structure from complex systems. It has been widely used in many application domains. Reliable diagnostic conclusions are of great importance in mitigating system failures and financial losses. However, previous studies implicitly assume a full observation of the system, which neglect the effect of partial observation (i.e., missing nodes and latent malfunction). As a result, they fail in deriving reliable RCA results. In this paper, we unveil the issues of unobserved confounders and heterogeneity in partial observation and come up with a new problem of root cause analysis with partially observed data. To achieve this, we propose PORCA, a novel RCA framework which can explore reliable root causes under both unobserved confounders and unobserved heterogeneity. PORCA leverages magnified score-based causal discovery to efficiently optimize acyclic directed mixed graph under unobserved confounders. In addition, we also develop a heterogeneity-aware scheduling strategy to provide adaptive sample weights. Extensive experimental results on one synthetic and two real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed framework.
STBench: Assessing the Ability of Large Language Models in Spatio-Temporal Analysis
Jun 27, 2024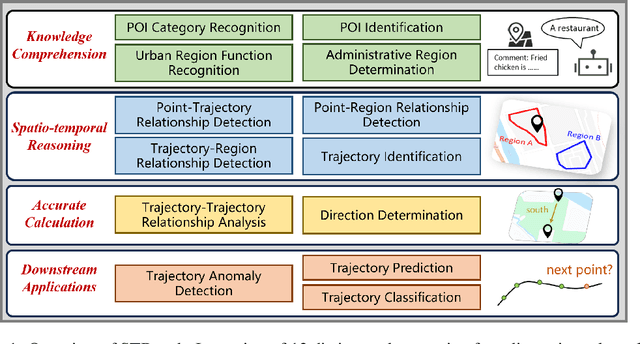

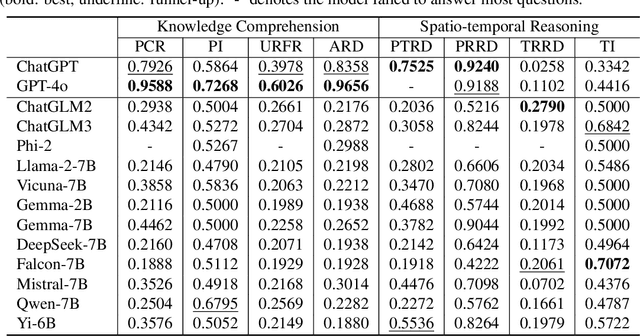
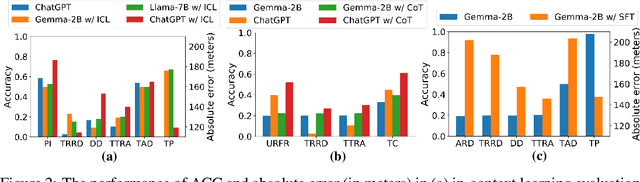
Abstract:The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) holds promise for reforming the methodology of spatio-temporal data mining. However, current works for evaluating the spatio-temporal understanding capability of LLMs are somewhat limited and biased. These works either fail to incorporate the latest language models or only focus on assessing the memorized spatio-temporal knowledge. To address this gap, this paper dissects LLMs' capability of spatio-temporal data into four distinct dimensions: knowledge comprehension, spatio-temporal reasoning, accurate computation, and downstream applications. We curate several natural language question-answer tasks for each category and build the benchmark dataset, namely STBench, containing 13 distinct tasks and over 60,000 QA pairs. Moreover, we have assessed the capabilities of 13 LLMs, such as GPT-4o, Gemma and Mistral. Experimental results reveal that existing LLMs show remarkable performance on knowledge comprehension and spatio-temporal reasoning tasks, with potential for further enhancement on other tasks through in-context learning, chain-of-though prompting, and fine-tuning. The code and datasets of STBench are released on https://github.com/LwbXc/STBench.
CausalMMM: Learning Causal Structure for Marketing Mix Modeling
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:In online advertising, marketing mix modeling (MMM) is employed to predict the gross merchandise volume (GMV) of brand shops and help decision-makers to adjust the budget allocation of various advertising channels. Traditional MMM methods leveraging regression techniques can fail in handling the complexity of marketing. Although some efforts try to encode the causal structures for better prediction, they have the strict restriction that causal structures are prior-known and unchangeable. In this paper, we define a new causal MMM problem that automatically discovers the interpretable causal structures from data and yields better GMV predictions. To achieve causal MMM, two essential challenges should be addressed: (1) Causal Heterogeneity. The causal structures of different kinds of shops vary a lot. (2) Marketing Response Patterns. Various marketing response patterns i.e., carryover effect and shape effect, have been validated in practice. We argue that causal MMM needs dynamically discover specific causal structures for different shops and the predictions should comply with the prior known marketing response patterns. Thus, we propose CausalMMM that integrates Granger causality in a variational inference framework to measure the causal relationships between different channels and predict the GMV with the regularization of both temporal and saturation marketing response patterns. Extensive experiments show that CausalMMM can not only achieve superior performance of causal structure learning on synthetic datasets with improvements of 5.7%\sim 7.1%, but also enhance the GMV prediction results on a representative E-commerce platform.
Causal Discovery from Temporal Data: An Overview and New Perspectives
Mar 17, 2023



Abstract:Temporal data, representing chronological observations of complex systems, has always been a typical data structure that can be widely generated by many domains, such as industry, medicine and finance. Analyzing this type of data is extremely valuable for various applications. Thus, different temporal data analysis tasks, eg, classification, clustering and prediction, have been proposed in the past decades. Among them, causal discovery, learning the causal relations from temporal data, is considered an interesting yet critical task and has attracted much research attention. Existing casual discovery works can be divided into two highly correlated categories according to whether the temporal data is calibrated, ie, multivariate time series casual discovery, and event sequence casual discovery. However, most previous surveys are only focused on the time series casual discovery and ignore the second category. In this paper, we specify the correlation between the two categories and provide a systematical overview of existing solutions. Furthermore, we provide public datasets, evaluation metrics and new perspectives for temporal data casual discovery.
CausalMTA: Eliminating the User Confounding Bias for Causal Multi-touch Attribution
Dec 21, 2021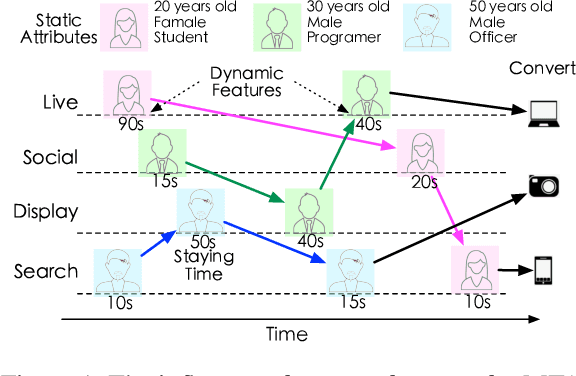
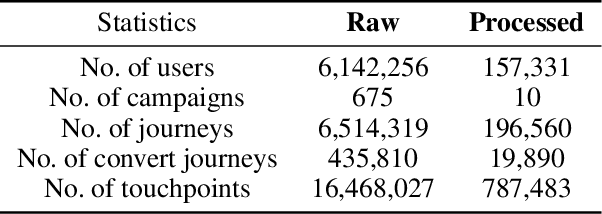
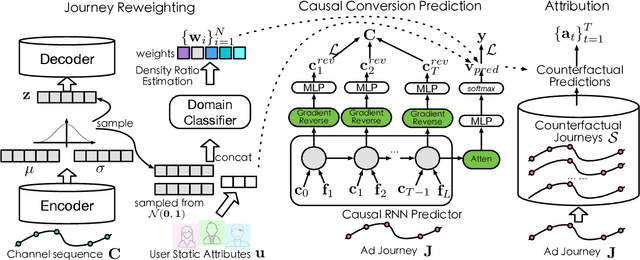
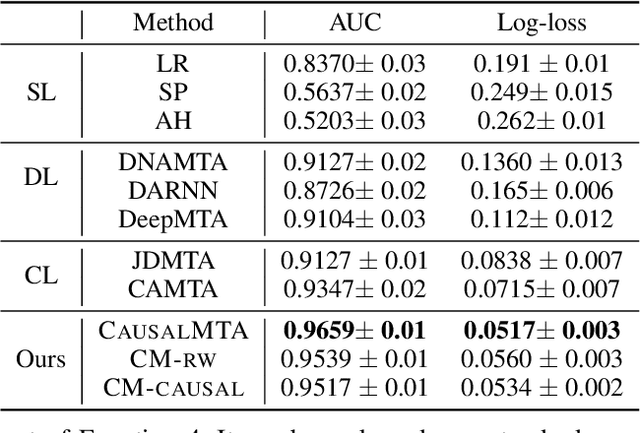
Abstract:Multi-touch attribution (MTA), aiming to estimate the contribution of each advertisement touchpoint in conversion journeys, is essential for budget allocation and automatically advertising. Existing methods first train a model to predict the conversion probability of the advertisement journeys with historical data and calculate the attribution of each touchpoint using counterfactual predictions. An assumption of these works is the conversion prediction model is unbiased, i.e., it can give accurate predictions on any randomly assigned journey, including both the factual and counterfactual ones. Nevertheless, this assumption does not always hold as the exposed advertisements are recommended according to user preferences. This confounding bias of users would lead to an out-of-distribution (OOD) problem in the counterfactual prediction and cause concept drift in attribution. In this paper, we define the causal MTA task and propose CausalMTA to eliminate the influence of user preferences. It systemically eliminates the confounding bias from both static and dynamic preferences to learn the conversion prediction model using historical data. We also provide a theoretical analysis to prove CausalMTA can learn an unbiased prediction model with sufficient data. Extensive experiments on both public datasets and the impression data in an e-commerce company show that CausalMTA not only achieves better prediction performance than the state-of-the-art method but also generates meaningful attribution credits across different advertising channels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge