Catharine Oertel
What Can You Say to a Robot? Capability Communication Leads to More Natural Conversations
Feb 03, 2025
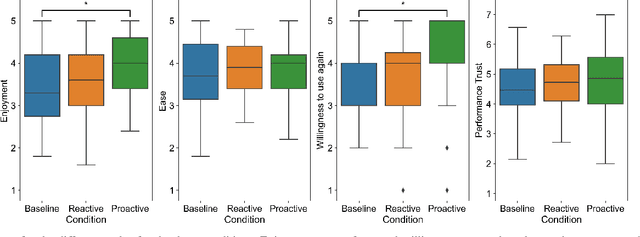
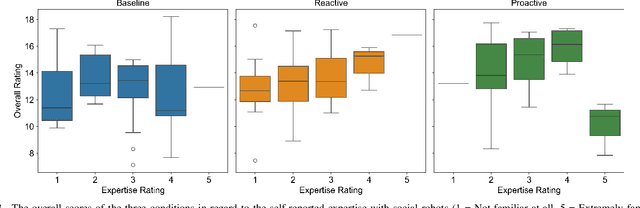
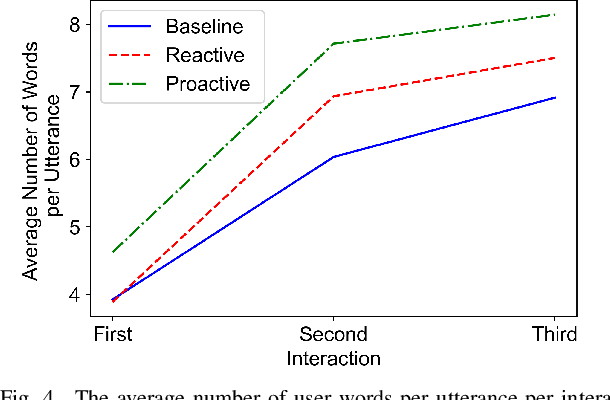
Abstract:When encountering a robot in the wild, it is not inherently clear to human users what the robot's capabilities are. When encountering misunderstandings or problems in spoken interaction, robots often just apologize and move on, without additional effort to make sure the user understands what happened. We set out to compare the effect of two speech based capability communication strategies (proactive, reactive) to a robot without such a strategy, in regard to the user's rating of and their behavior during the interaction. For this, we conducted an in-person user study with 120 participants who had three speech-based interactions with a social robot in a restaurant setting. Our results suggest that users preferred the robot communicating its capabilities proactively and adjusted their behavior in those interactions, using a more conversational interaction style while also enjoying the interaction more.
Dynamics of Collective Group Affect: Group-level Annotations and the Multimodal Modeling of Convergence and Divergence
Sep 13, 2024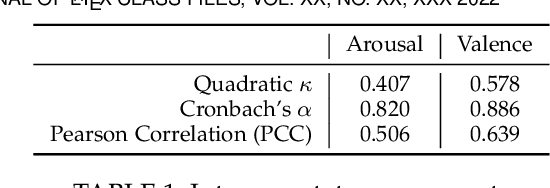
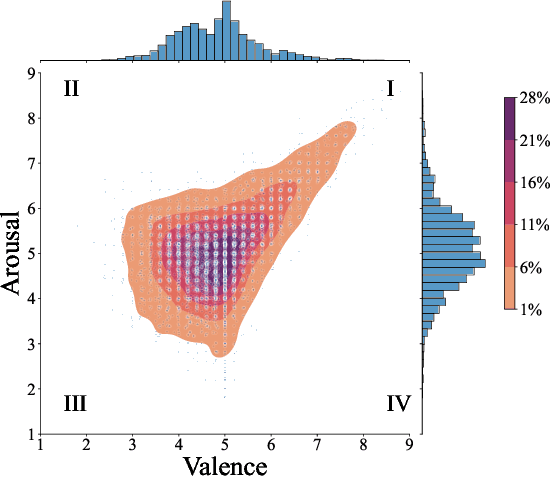

Abstract:Collaborating in a group, whether face-to-face or virtually, involves continuously expressing emotions and interpreting those of other group members. Therefore, understanding group affect is essential to comprehending how groups interact and succeed in collaborative efforts. In this study, we move beyond individual-level affect and investigate group-level affect -- a collective phenomenon that reflects the shared mood or emotions among group members at a particular moment. As the first in literature, we gather annotations for group-level affective expressions using a fine-grained temporal approach (15 second windows) that also captures the inherent dynamics of the collective construct. To this end, we use trained annotators and an annotation procedure specifically tuned to capture the entire scope of the group interaction. In addition, we model group affect dynamics over time. One way to study the ebb and flow of group affect in group interactions is to model the underlying convergence (driven by emotional contagion) and divergence (resulting from emotional reactivity) of affective expressions amongst group members. To capture these interpersonal dynamics, we extract synchrony based features from both audio and visual social signal cues. An analysis of these features reveals that interacting groups tend to diverge in terms of their social signals along neutral levels of group affect, and converge along extreme levels of affect expression. We further present results on the predictive modeling of dynamic group affect which underscores the importance of using synchrony-based features in the modeling process, as well as the multimodal nature of group affect. We anticipate that the presented models will serve as the baselines of future research on the automatic recognition of dynamic group affect.
A Survey on Dialogue Management in Human-Robot Interaction
Jul 20, 2023



Abstract:As social robots see increasing deployment within the general public, improving the interaction with those robots is essential. Spoken language offers an intuitive interface for the human-robot interaction (HRI), with dialogue management (DM) being a key component in those interactive systems. Yet, to overcome current challenges and manage smooth, informative and engaging interaction a more structural approach to combining HRI and DM is needed. In this systematic review, we analyse the current use of DM in HRI and focus on the type of dialogue manager used, its capabilities, evaluation methods and the challenges specific to DM in HRI. We identify the challenges and current scientific frontier related to the DM approach, interaction domain, robot appearance, physical situatedness and multimodality.
Perceived personality state estimation in dyadic and small group interaction with deep learning methods
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Dyadic and small group collaboration is an evolutionary advantageous behaviour and the need for such collaboration is a regular occurrence in day to day life. In this paper we estimate the perceived personality traits of individuals in dyadic and small groups over thin-slices of interaction on four multimodal datasets. We find that our transformer based predictive model performs similarly to human annotators tasked with predicting the perceived big-five personality traits of participants. Using this model we analyse the estimated perceived personality traits of individuals performing tasks in small groups and dyads. Permutation analysis shows that in the case of small groups undergoing collaborative tasks, the perceived personality of group members clusters, this is also observed for dyads in a collaborative problem solving task, but not in dyads under non-collaborative task settings. Additionally, we find that the group level average perceived personality traits provide a better predictor of group performance than the group level average self-reported personality traits.
Impact of annotation modality on label quality and model performance in the automatic assessment of laughter in-the-wild
Nov 02, 2022
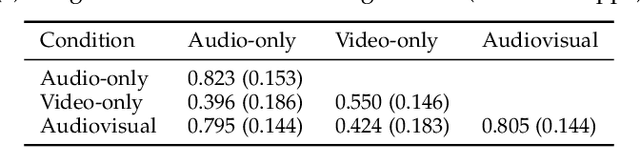
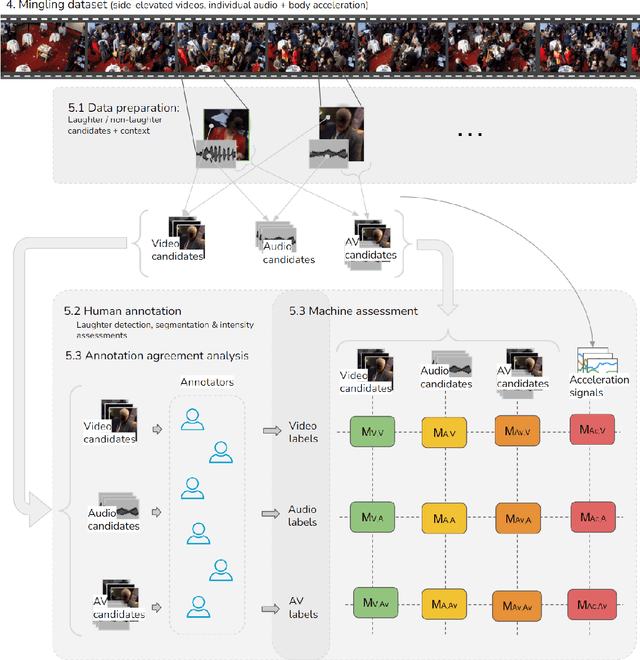
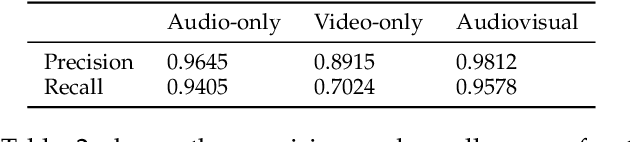
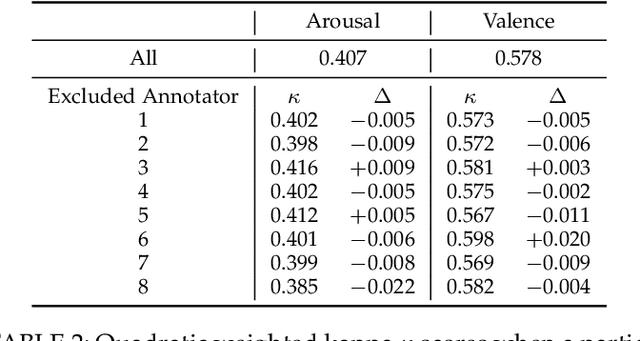
Abstract:Laughter is considered one of the most overt signals of joy. Laughter is well-recognized as a multimodal phenomenon but is most commonly detected by sensing the sound of laughter. It is unclear how perception and annotation of laughter differ when annotated from other modalities like video, via the body movements of laughter. In this paper we take a first step in this direction by asking if and how well laughter can be annotated when only audio, only video (containing full body movement information) or audiovisual modalities are available to annotators. We ask whether annotations of laughter are congruent across modalities, and compare the effect that labeling modality has on machine learning model performance. We compare annotations and models for laughter detection, intensity estimation, and segmentation, three tasks common in previous studies of laughter. Our analysis of more than 4000 annotations acquired from 48 annotators revealed evidence for incongruity in the perception of laughter, and its intensity between modalities. Further analysis of annotations against consolidated audiovisual reference annotations revealed that recall was lower on average for video when compared to the audio condition, but tended to increase with the intensity of the laughter samples. Our machine learning experiments compared the performance of state-of-the-art unimodal (audio-based, video-based and acceleration-based) and multi-modal models for different combinations of input modalities, training label modality, and testing label modality. Models with video and acceleration inputs had similar performance regardless of training label modality, suggesting that it may be entirely appropriate to train models for laughter detection from body movements using video-acquired labels, despite their lower inter-rater agreement.
Towards a Real-time Measure of the Perception of Anthropomorphism in Human-robot Interaction
Jan 24, 2022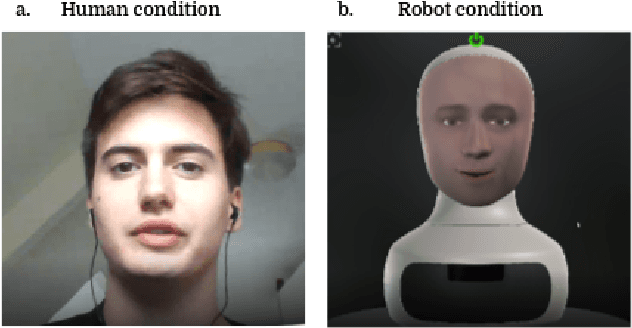
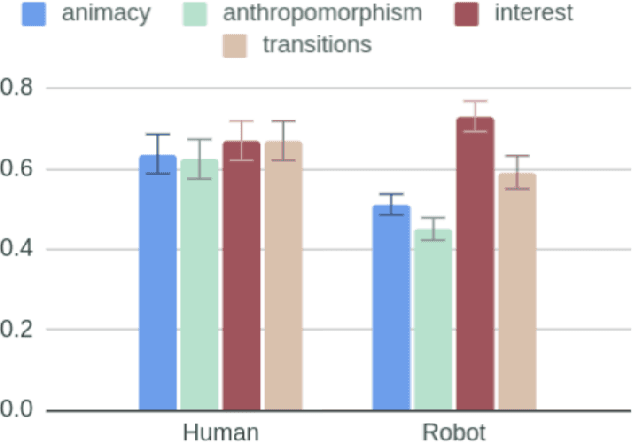
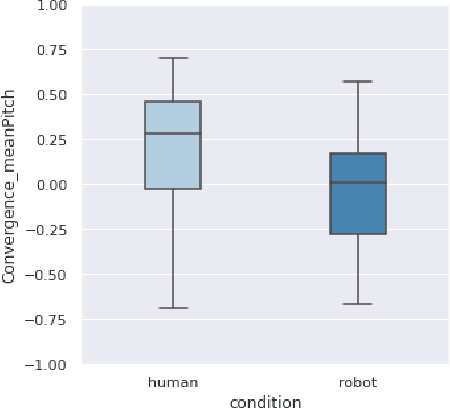
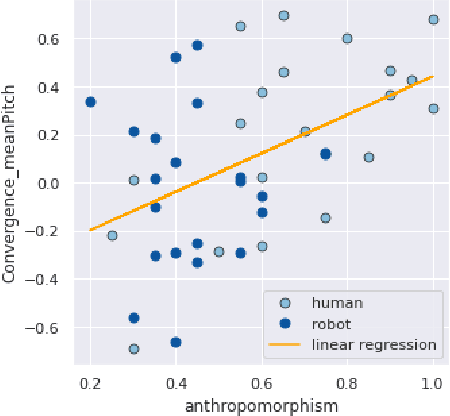
Abstract:How human-like do conversational robots need to look to enable long-term human-robot conversation? One essential aspect of long-term interaction is a human's ability to adapt to the varying degrees of a conversational partner's engagement and emotions. Prosodically, this can be achieved through (dis)entrainment. While speech-synthesis has been a limiting factor for many years, restrictions in this regard are increasingly mitigated. These advancements now emphasise the importance of studying the effect of robot embodiment on human entrainment. In this study, we conducted a between-subjects online human-robot interaction experiment in an educational use-case scenario where a tutor was either embodied through a human or a robot face. 43 English-speaking participants took part in the study for whom we analysed the degree of acoustic-prosodic entrainment to the human or robot face, respectively. We found that the degree of subjective and objective perception of anthropomorphism positively correlates with acoustic-prosodic entrainment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge