Gabriel Skantze
VoXtream: Full-Stream Text-to-Speech with Extremely Low Latency
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:We present VoXtream, a fully autoregressive, zero-shot streaming text-to-speech (TTS) system for real-time use that begins speaking from the first word. VoXtream directly maps incoming phonemes to audio tokens using a monotonic alignment scheme and a dynamic look-ahead that does not delay onset. Built around an incremental phoneme transformer, a temporal transformer predicting semantic and duration tokens, and a depth transformer producing acoustic tokens, VoXtream achieves, to our knowledge, the lowest initial delay among publicly available streaming TTS: 102 ms on GPU. Despite being trained on a mid-scale 9k-hour corpus, it matches or surpasses larger baselines on several metrics, while delivering competitive quality in both output- and full-streaming settings. Demo and code are available at https://herimor.github.io/voxtream.
"Dyadosyncrasy", Idiosyncrasy and Demographic Factors in Turn-Taking
May 30, 2025Abstract:Turn-taking in dialogue follows universal constraints but also varies significantly. This study examines how demographic (sex, age, education) and individual factors shape turn-taking using a large dataset of US English conversations (Fisher). We analyze Transition Floor Offset (TFO) and find notable interspeaker variation. Sex and age have small but significant effects female speakers and older individuals exhibit slightly shorter offsets - while education shows no effect. Lighter topics correlate with shorter TFOs. However, individual differences have a greater impact, driven by a strong idiosyncratic and an even stronger "dyadosyncratic" component - speakers in a dyad resemble each other more than they resemble themselves in different dyads. This suggests that the dyadic relationship and joint activity are the strongest determinants of TFO, outweighing demographic influences.
Representation of perceived prosodic similarity of conversational feedback
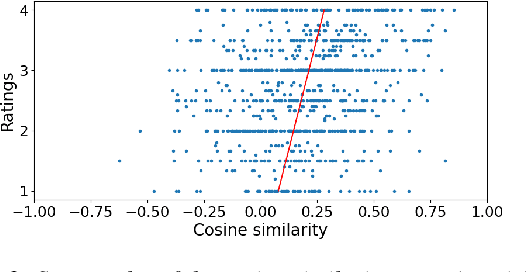
May 19, 2025Abstract:Vocal feedback (e.g., `mhm', `yeah', `okay') is an important component of spoken dialogue and is crucial to ensuring common ground in conversational systems. The exact meaning of such feedback is conveyed through both lexical and prosodic form. In this work, we investigate the perceived prosodic similarity of vocal feedback with the same lexical form, and to what extent existing speech representations reflect such similarities. A triadic comparison task with recruited participants is used to measure perceived similarity of feedback responses taken from two different datasets. We find that spectral and self-supervised speech representations encode prosody better than extracted pitch features, especially in the case of feedback from the same speaker. We also find that it is possible to further condense and align the representations to human perception through contrastive learning.
What Can You Say to a Robot? Capability Communication Leads to More Natural Conversations
Feb 03, 2025
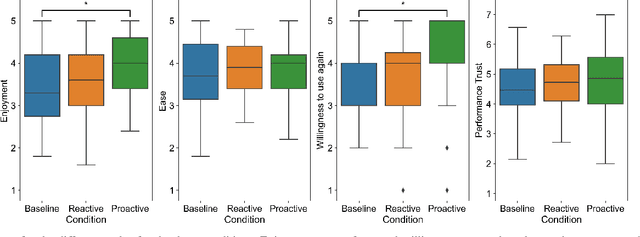
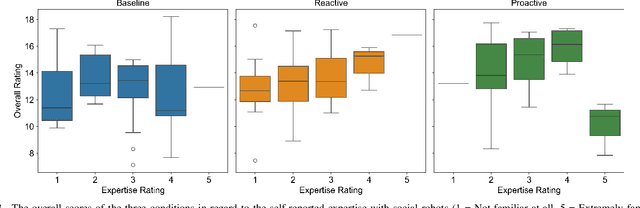
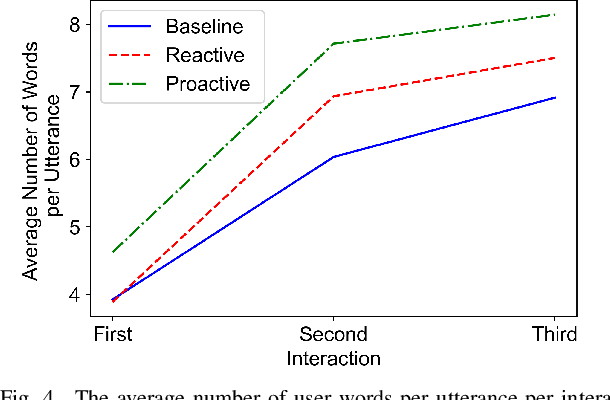
Abstract:When encountering a robot in the wild, it is not inherently clear to human users what the robot's capabilities are. When encountering misunderstandings or problems in spoken interaction, robots often just apologize and move on, without additional effort to make sure the user understands what happened. We set out to compare the effect of two speech based capability communication strategies (proactive, reactive) to a robot without such a strategy, in regard to the user's rating of and their behavior during the interaction. For this, we conducted an in-person user study with 120 participants who had three speech-based interactions with a social robot in a restaurant setting. Our results suggest that users preferred the robot communicating its capabilities proactively and adjusted their behavior in those interactions, using a more conversational interaction style while also enjoying the interaction more.
Applying General Turn-taking Models to Conversational Human-Robot Interaction
Jan 15, 2025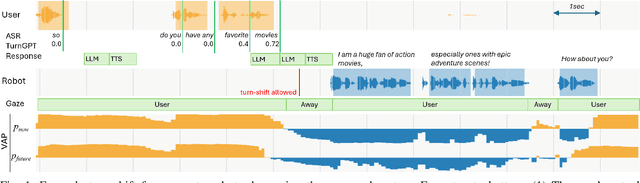
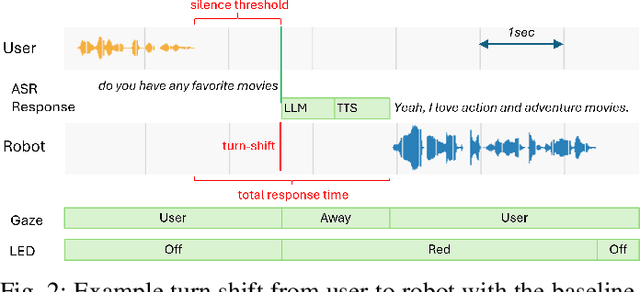
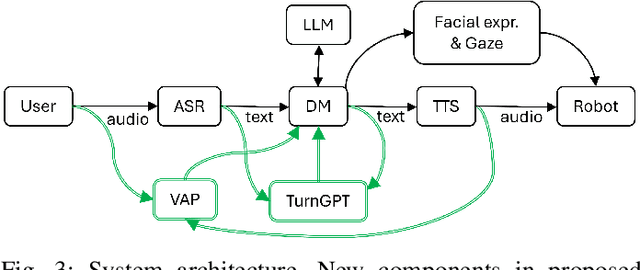

Abstract:Turn-taking is a fundamental aspect of conversation, but current Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) systems often rely on simplistic, silence-based models, leading to unnatural pauses and interruptions. This paper investigates, for the first time, the application of general turn-taking models, specifically TurnGPT and Voice Activity Projection (VAP), to improve conversational dynamics in HRI. These models are trained on human-human dialogue data using self-supervised learning objectives, without requiring domain-specific fine-tuning. We propose methods for using these models in tandem to predict when a robot should begin preparing responses, take turns, and handle potential interruptions. We evaluated the proposed system in a within-subject study against a traditional baseline system, using the Furhat robot with 39 adults in a conversational setting, in combination with a large language model for autonomous response generation. The results show that participants significantly prefer the proposed system, and it significantly reduces response delays and interruptions.
Yeah, Un, Oh: Continuous and Real-time Backchannel Prediction with Fine-tuning of Voice Activity Projection
Oct 21, 2024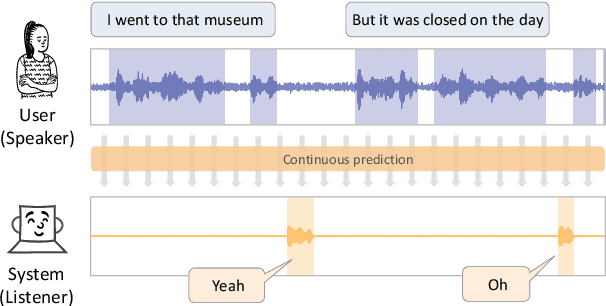
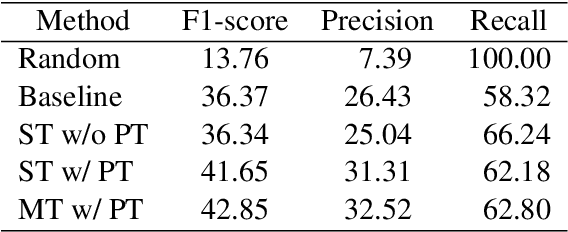

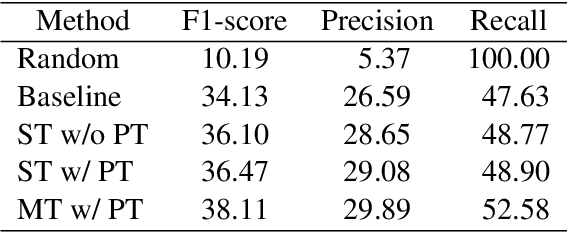
Abstract:In human conversations, short backchannel utterances such as "yeah" and "oh" play a crucial role in facilitating smooth and engaging dialogue. These backchannels signal attentiveness and understanding without interrupting the speaker, making their accurate prediction essential for creating more natural conversational agents. This paper proposes a novel method for real-time, continuous backchannel prediction using a fine-tuned Voice Activity Projection (VAP) model. While existing approaches have relied on turn-based or artificially balanced datasets, our approach predicts both the timing and type of backchannels in a continuous and frame-wise manner on unbalanced, real-world datasets. We first pre-train the VAP model on a general dialogue corpus to capture conversational dynamics and then fine-tune it on a specialized dataset focused on backchannel behavior. Experimental results demonstrate that our model outperforms baseline methods in both timing and type prediction tasks, achieving robust performance in real-time environments. This research offers a promising step toward more responsive and human-like dialogue systems, with implications for interactive spoken dialogue applications such as virtual assistants and robots.
Perception of Emotions in Human and Robot Faces: Is the Eye Region Enough?
Oct 18, 2024Abstract:The increased interest in developing next-gen social robots has raised questions about the factors affecting the perception of robot emotions. This study investigates the impact of robot appearances (humanlike, mechanical) and face regions (full-face, eye-region) on human perception of robot emotions. A between-subjects user study (N = 305) was conducted where participants were asked to identify the emotions being displayed in videos of robot faces, as well as a human baseline. Our findings reveal three important insights for effective social robot face design in Human-Robot Interaction (HRI): Firstly, robots equipped with a back-projected, fully animated face - regardless of whether they are more human-like or more mechanical-looking - demonstrate a capacity for emotional expression comparable to that of humans. Secondly, the recognition accuracy of emotional expressions in both humans and robots declines when only the eye region is visible. Lastly, within the constraint of only the eye region being visible, robots with more human-like features significantly enhance emotion recognition.
Referring Expression Generation in Visually Grounded Dialogue with Discourse-aware Comprehension Guiding
Sep 09, 2024
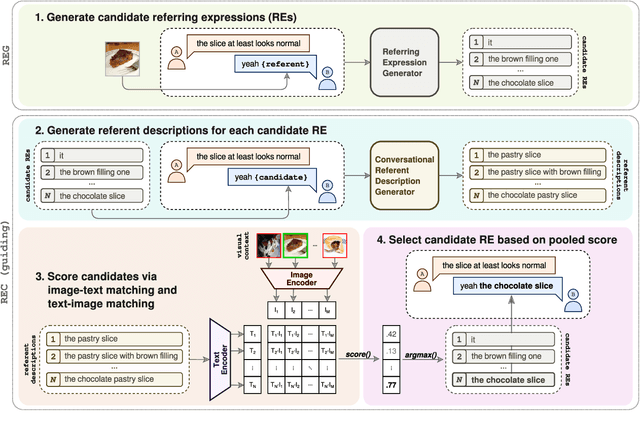
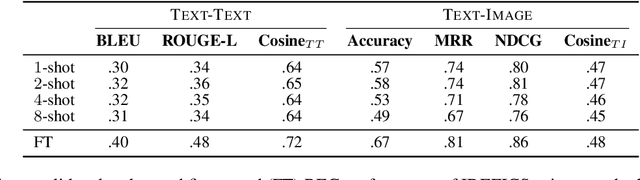
Abstract:We propose an approach to referring expression generation (REG) in visually grounded dialogue that is meant to produce referring expressions (REs) that are both discriminative and discourse-appropriate. Our method constitutes a two-stage process. First, we model REG as a text- and image-conditioned next-token prediction task. REs are autoregressively generated based on their preceding linguistic context and a visual representation of the referent. Second, we propose the use of discourse-aware comprehension guiding as part of a generate-and-rerank strategy through which candidate REs generated with our REG model are reranked based on their discourse-dependent discriminatory power. Results from our human evaluation indicate that our proposed two-stage approach is effective in producing discriminative REs, with higher performance in terms of text-image retrieval accuracy for reranked REs compared to those generated using greedy decoding.
Joint Learning of Context and Feedback Embeddings in Spoken Dialogue
Jun 11, 2024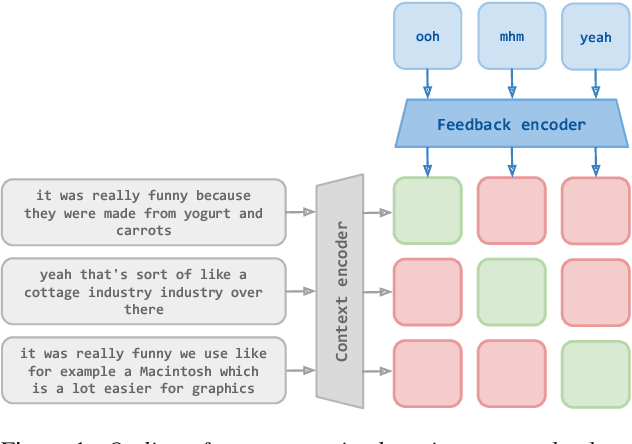


Abstract:Short feedback responses, such as backchannels, play an important role in spoken dialogue. So far, most of the modeling of feedback responses has focused on their timing, often neglecting how their lexical and prosodic form influence their contextual appropriateness and conversational function. In this paper, we investigate the possibility of embedding short dialogue contexts and feedback responses in the same representation space using a contrastive learning objective. In our evaluation, we primarily focus on how such embeddings can be used as a context-feedback appropriateness metric and thus for feedback response ranking in U.S. English dialogues. Our results show that the model outperforms humans given the same ranking task and that the learned embeddings carry information about the conversational function of feedback responses.
Human-Robot Interaction Conversational User Enjoyment Scale (HRI CUES)
May 02, 2024



Abstract:Understanding user enjoyment is crucial in human-robot interaction (HRI), as it can impact interaction quality and influence user acceptance and long-term engagement with robots, particularly in the context of conversations with social robots. However, current assessment methods rely solely on self-reported questionnaires, failing to capture interaction dynamics. This work introduces the Human-Robot Interaction Conversational User Enjoyment Scale (HRI CUES), a novel scale for assessing user enjoyment from an external perspective during conversations with a robot. Developed through rigorous evaluations and discussions of three annotators with relevant expertise, the scale provides a structured framework for assessing enjoyment in each conversation exchange (turn) alongside overall interaction levels. It aims to complement self-reported enjoyment from users and holds the potential for autonomously identifying user enjoyment in real-time HRI. The scale was validated on 25 older adults' open-domain dialogue with a companion robot that was powered by a large language model for conversations, corresponding to 174 minutes of data, showing moderate to good alignment. Additionally, the study offers insights into understanding the nuances and challenges of assessing user enjoyment in robot interactions, and provides guidelines on applying the scale to other domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge