Joint Learning of Context and Feedback Embeddings in Spoken Dialogue
Paper and Code
Jun 11, 2024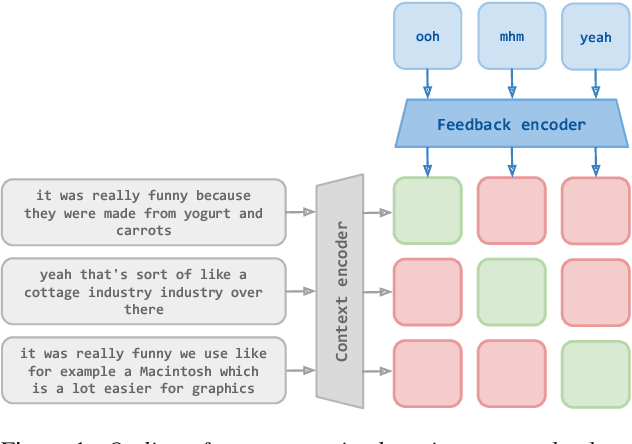


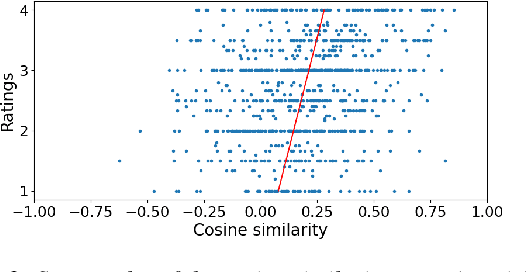
Short feedback responses, such as backchannels, play an important role in spoken dialogue. So far, most of the modeling of feedback responses has focused on their timing, often neglecting how their lexical and prosodic form influence their contextual appropriateness and conversational function. In this paper, we investigate the possibility of embedding short dialogue contexts and feedback responses in the same representation space using a contrastive learning objective. In our evaluation, we primarily focus on how such embeddings can be used as a context-feedback appropriateness metric and thus for feedback response ranking in U.S. English dialogues. Our results show that the model outperforms humans given the same ranking task and that the learned embeddings carry information about the conversational function of feedback responses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge