Bahar Irfan
Applying General Turn-taking Models to Conversational Human-Robot Interaction
Jan 15, 2025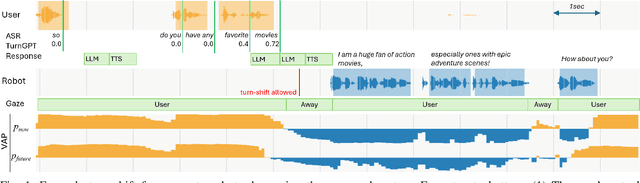
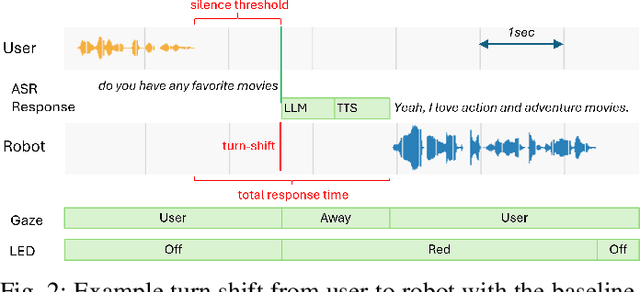
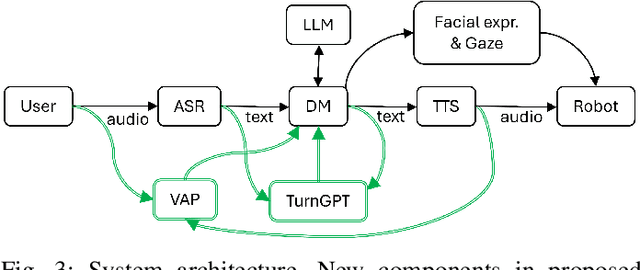

Abstract:Turn-taking is a fundamental aspect of conversation, but current Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) systems often rely on simplistic, silence-based models, leading to unnatural pauses and interruptions. This paper investigates, for the first time, the application of general turn-taking models, specifically TurnGPT and Voice Activity Projection (VAP), to improve conversational dynamics in HRI. These models are trained on human-human dialogue data using self-supervised learning objectives, without requiring domain-specific fine-tuning. We propose methods for using these models in tandem to predict when a robot should begin preparing responses, take turns, and handle potential interruptions. We evaluated the proposed system in a within-subject study against a traditional baseline system, using the Furhat robot with 39 adults in a conversational setting, in combination with a large language model for autonomous response generation. The results show that participants significantly prefer the proposed system, and it significantly reduces response delays and interruptions.
Human-Robot Interaction Conversational User Enjoyment Scale (HRI CUES)
May 02, 2024



Abstract:Understanding user enjoyment is crucial in human-robot interaction (HRI), as it can impact interaction quality and influence user acceptance and long-term engagement with robots, particularly in the context of conversations with social robots. However, current assessment methods rely solely on self-reported questionnaires, failing to capture interaction dynamics. This work introduces the Human-Robot Interaction Conversational User Enjoyment Scale (HRI CUES), a novel scale for assessing user enjoyment from an external perspective during conversations with a robot. Developed through rigorous evaluations and discussions of three annotators with relevant expertise, the scale provides a structured framework for assessing enjoyment in each conversation exchange (turn) alongside overall interaction levels. It aims to complement self-reported enjoyment from users and holds the potential for autonomously identifying user enjoyment in real-time HRI. The scale was validated on 25 older adults' open-domain dialogue with a companion robot that was powered by a large language model for conversations, corresponding to 174 minutes of data, showing moderate to good alignment. Additionally, the study offers insights into understanding the nuances and challenges of assessing user enjoyment in robot interactions, and provides guidelines on applying the scale to other domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge