Carlos G. Correa
Program-Based Strategy Induction for Reinforcement Learning
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:Typical models of learning assume incremental estimation of continuously-varying decision variables like expected rewards. However, this class of models fails to capture more idiosyncratic, discrete heuristics and strategies that people and animals appear to exhibit. Despite recent advances in strategy discovery using tools like recurrent networks that generalize the classic models, the resulting strategies are often onerous to interpret, making connections to cognition difficult to establish. We use Bayesian program induction to discover strategies implemented by programs, letting the simplicity of strategies trade off against their effectiveness. Focusing on bandit tasks, we find strategies that are difficult or unexpected with classical incremental learning, like asymmetric learning from rewarded and unrewarded trials, adaptive horizon-dependent random exploration, and discrete state switching.
Exploring the hierarchical structure of human plans via program generation
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:Human behavior is inherently hierarchical, resulting from the decomposition of a task into subtasks or an abstract action into concrete actions. However, behavior is typically measured as a sequence of actions, which makes it difficult to infer its hierarchical structure. In this paper, we explore how people form hierarchically-structured plans, using an experimental paradigm that makes hierarchical representations observable: participants create programs that produce sequences of actions in a language with explicit hierarchical structure. This task lets us test two well-established principles of human behavior: utility maximization (i.e. using fewer actions) and minimum description length (MDL; i.e. having a shorter program). We find that humans are sensitive to both metrics, but that both accounts fail to predict a qualitative feature of human-created programs, namely that people prefer programs with reuse over and above the predictions of MDL. We formalize this preference for reuse by extending the MDL account into a generative model over programs, modeling hierarchy choice as the induction of a grammar over actions. Our account can explain the preference for reuse and provides the best prediction of human behavior, going beyond simple accounts of compressibility to highlight a principle that guides hierarchical planning.
Structurally guided task decomposition in spatial navigation tasks
Oct 03, 2023

Abstract:How are people able to plan so efficiently despite limited cognitive resources? We aimed to answer this question by extending an existing model of human task decomposition that can explain a wide range of simple planning problems by adding structure information to the task to facilitate planning in more complex tasks. The extended model was then applied to a more complex planning domain of spatial navigation. Our results suggest that our framework can correctly predict the navigation strategies of the majority of the participants in an online experiment.
Humans decompose tasks by trading off utility and computational cost
Nov 07, 2022



Abstract:Human behavior emerges from planning over elaborate decompositions of tasks into goals, subgoals, and low-level actions. How are these decompositions created and used? Here, we propose and evaluate a normative framework for task decomposition based on the simple idea that people decompose tasks to reduce the overall cost of planning while maintaining task performance. Analyzing 11,117 distinct graph-structured planning tasks, we find that our framework justifies several existing heuristics for task decomposition and makes predictions that can be distinguished from two alternative normative accounts. We report a behavioral study of task decomposition ($N=806$) that uses 30 randomly sampled graphs, a larger and more diverse set than that of any previous behavioral study on this topic. We find that human responses are more consistent with our framework for task decomposition than alternative normative accounts and are most consistent with a heuristic -- betweenness centrality -- that is justified by our approach. Taken together, our results provide new theoretical insight into the computational principles underlying the intelligent structuring of goal-directed behavior.
Using Natural Language and Program Abstractions to Instill Human Inductive Biases in Machines
May 23, 2022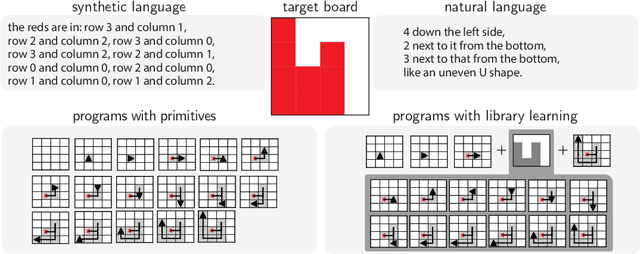
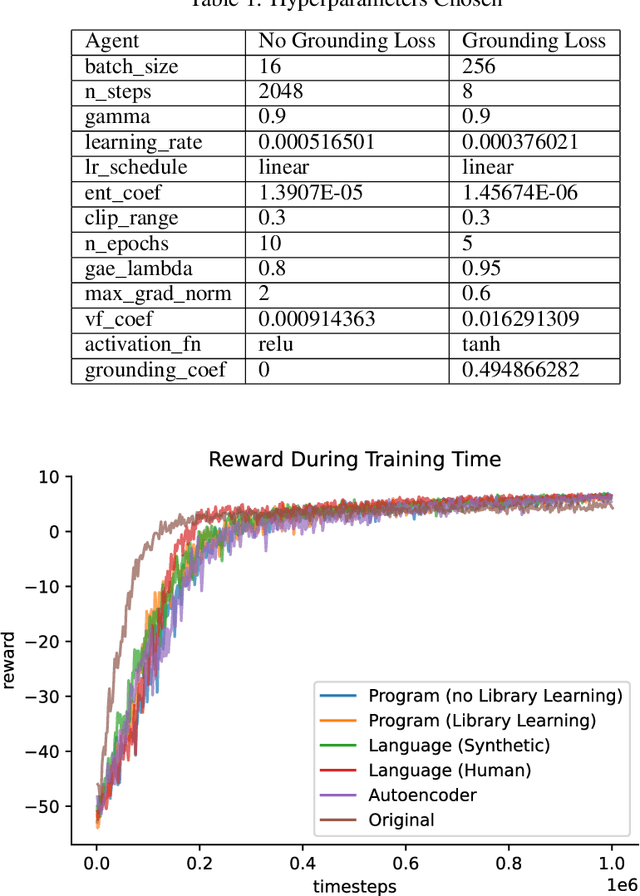
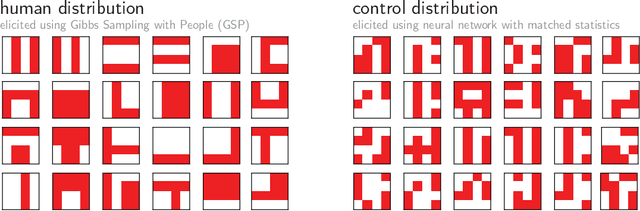
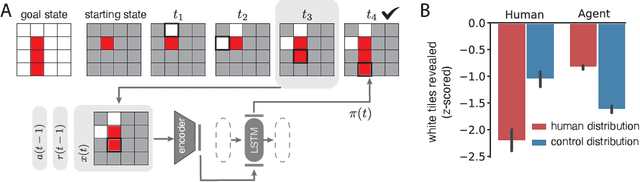
Abstract:Strong inductive biases are a key component of human intelligence, allowing people to quickly learn a variety of tasks. Although meta-learning has emerged as an approach for endowing neural networks with useful inductive biases, agents trained by meta-learning may acquire very different strategies from humans. We show that co-training these agents on predicting representations from natural language task descriptions and from programs induced to generate such tasks guides them toward human-like inductive biases. Human-generated language descriptions and program induction with library learning both result in more human-like behavior in downstream meta-reinforcement learning agents than less abstract controls (synthetic language descriptions, program induction without library learning), suggesting that the abstraction supported by these representations is key.
Control of mental representations in human planning
May 14, 2021


Abstract:One of the most striking features of human cognition is the capacity to plan. Two aspects of human planning stand out: its efficiency, even in complex environments, and its flexibility, even in changing environments. Efficiency is especially impressive because directly computing an optimal plan is intractable, even for modestly complex tasks, and yet people successfully solve myriad everyday problems despite limited cognitive resources. Standard accounts in psychology, economics, and artificial intelligence have suggested this is because people have a mental representation of a task and then use heuristics to plan in that representation. However, this approach generally assumes that mental representations are fixed. Here, we propose that mental representations can be controlled and that this provides opportunities to adaptively simplify problems so they can be more easily reasoned about -- a process we refer to as construal. We construct a formal model of this process and, in a series of large, pre-registered behavioral experiments, show both that construal is subject to online cognitive control and that people form value-guided construals that optimally balance the complexity of a representation and its utility for planning and acting. These results demonstrate how strategically perceiving and conceiving problems facilitates the effective use of limited cognitive resources.
Resource-rational Task Decomposition to Minimize Planning Costs
Jul 27, 2020


Abstract:People often plan hierarchically. That is, rather than planning over a monolithic representation of a task, they decompose the task into simpler subtasks and then plan to accomplish those. Although much work explores how people decompose tasks, there is less analysis of why people decompose tasks in the way they do. Here, we address this question by formalizing task decomposition as a resource-rational representation problem. Specifically, we propose that people decompose tasks in a manner that facilitates efficient use of limited cognitive resources given the structure of the environment and their own planning algorithms. Using this model, we replicate several existing findings. Our account provides a normative explanation for how people identify subtasks as well as a framework for studying how people reason, plan, and act using resource-rational representations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge