Fred Callaway
Centaur: a foundation model of human cognition
Oct 26, 2024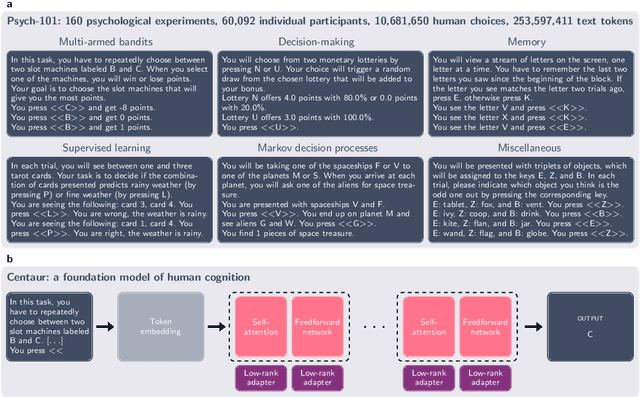

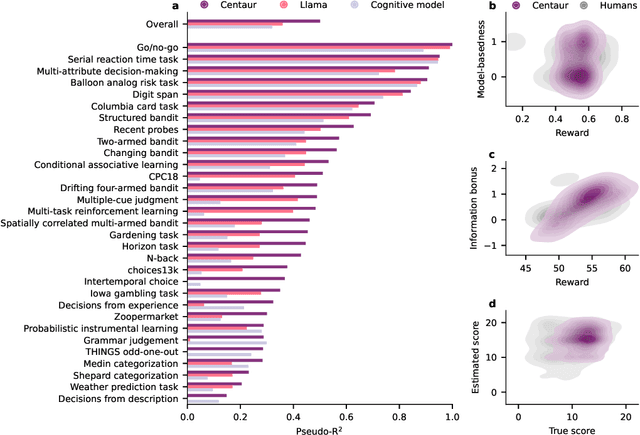
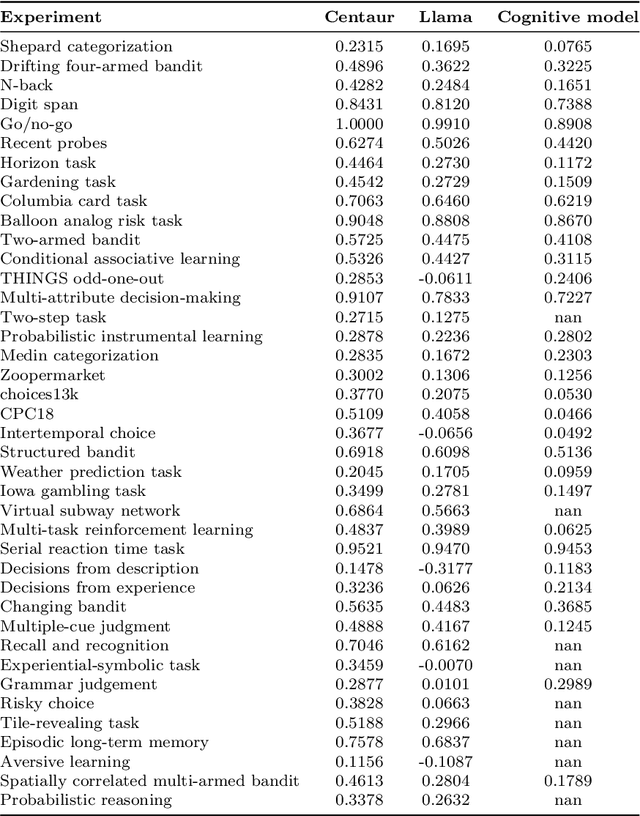
Abstract:Establishing a unified theory of cognition has been a major goal of psychology. While there have been previous attempts to instantiate such theories by building computational models, we currently do not have one model that captures the human mind in its entirety. Here we introduce Centaur, a computational model that can predict and simulate human behavior in any experiment expressible in natural language. We derived Centaur by finetuning a state-of-the-art language model on a novel, large-scale data set called Psych-101. Psych-101 reaches an unprecedented scale, covering trial-by-trial data from over 60,000 participants performing over 10,000,000 choices in 160 experiments. Centaur not only captures the behavior of held-out participants better than existing cognitive models, but also generalizes to new cover stories, structural task modifications, and entirely new domains. Furthermore, we find that the model's internal representations become more aligned with human neural activity after finetuning. Taken together, Centaur is the first real candidate for a unified model of human cognition. We anticipate that it will have a disruptive impact on the cognitive sciences, challenging the existing paradigm for developing computational models.
Resource-rational Task Decomposition to Minimize Planning Costs
Jul 27, 2020


Abstract:People often plan hierarchically. That is, rather than planning over a monolithic representation of a task, they decompose the task into simpler subtasks and then plan to accomplish those. Although much work explores how people decompose tasks, there is less analysis of why people decompose tasks in the way they do. Here, we address this question by formalizing task decomposition as a resource-rational representation problem. Specifically, we propose that people decompose tasks in a manner that facilitates efficient use of limited cognitive resources given the structure of the environment and their own planning algorithms. Using this model, we replicate several existing findings. Our account provides a normative explanation for how people identify subtasks as well as a framework for studying how people reason, plan, and act using resource-rational representations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge