Benoit Dumoulin
Position: Agentic Evolution is the Path to Evolving LLMs
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) move from curated training sets into open-ended real-world environments, a fundamental limitation emerges: static training cannot keep pace with continual deployment environment change. Scaling training-time and inference-time compute improves static capability but does not close this train-deploy gap. We argue that addressing this limitation requires a new scaling axis-evolution. Existing deployment-time adaptation methods, whether parametric fine-tuning or heuristic memory accumulation, lack the strategic agency needed to diagnose failures and produce durable improvements. Our position is that agentic evolution represents the inevitable future of LLM adaptation, elevating evolution itself from a fixed pipeline to an autonomous evolver agent. We instantiate this vision in a general framework, A-Evolve, which treats deployment-time improvement as a deliberate, goal-directed optimization process over persistent system state. We further propose the evolution-scaling hypothesis: the capacity for adaptation scales with the compute allocated to evolution, positioning agentic evolution as a scalable path toward sustained, open-ended adaptation in the real world.
TRAJECT-Bench:A Trajectory-Aware Benchmark for Evaluating Agentic Tool Use
Oct 06, 2025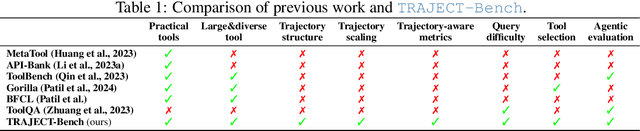

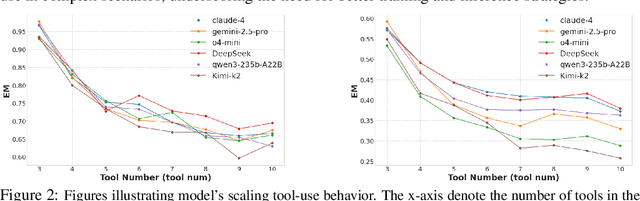
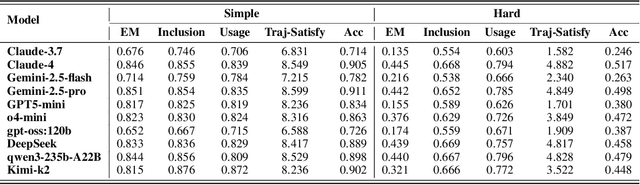
Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based agents increasingly rely on tool use to complete real-world tasks. While existing works evaluate the LLMs' tool use capability, they largely focus on the final answers yet overlook the detailed tool usage trajectory, i.e., whether tools are selected, parameterized, and ordered correctly. We introduce TRAJECT-Bench, a trajectory-aware benchmark to comprehensively evaluate LLMs' tool use capability through diverse tasks with fine-grained evaluation metrics. TRAJECT-Bench pairs high-fidelity, executable tools across practical domains with tasks grounded in production-style APIs, and synthesizes trajectories that vary in breadth (parallel calls) and depth (interdependent chains). Besides final accuracy, TRAJECT-Bench also reports trajectory-level diagnostics, including tool selection and argument correctness, and dependency/order satisfaction. Analyses reveal failure modes such as similar tool confusion and parameter-blind selection, and scaling behavior with tool diversity and trajectory length where the bottleneck of transiting from short to mid-length trajectories is revealed, offering actionable guidance for LLMs' tool use.
Explore-Exploit: A Framework for Interactive and Online Learning
Dec 01, 2018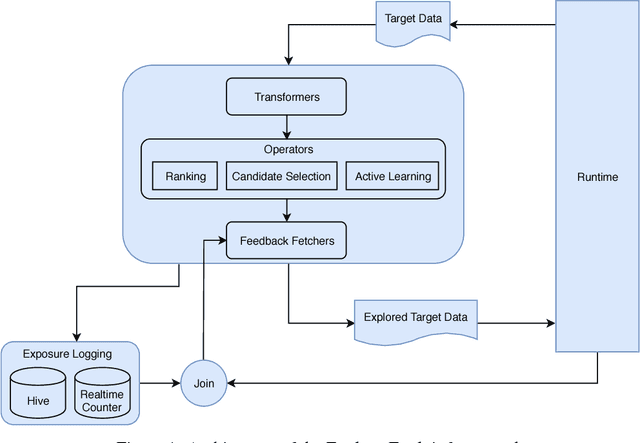
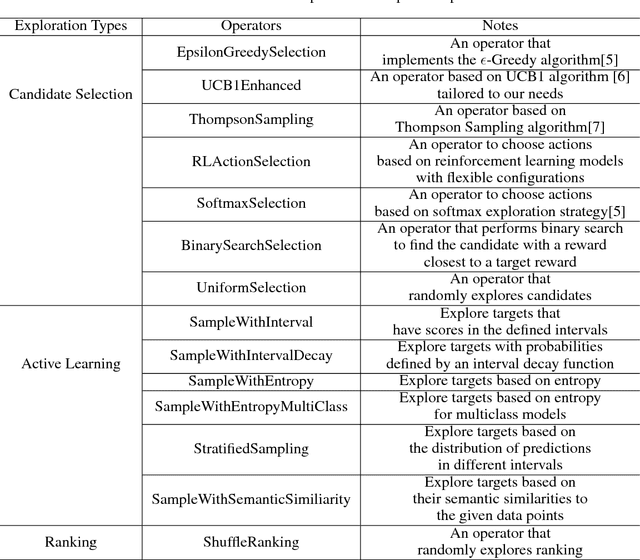
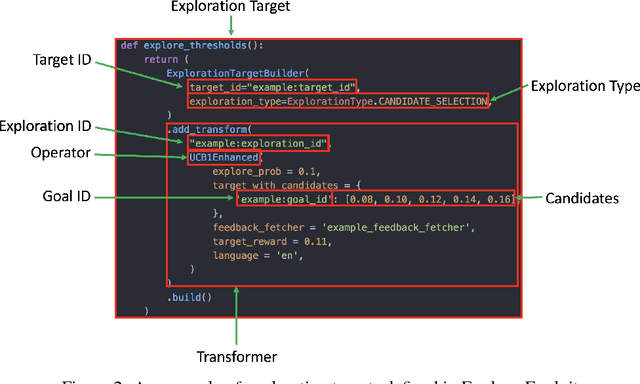
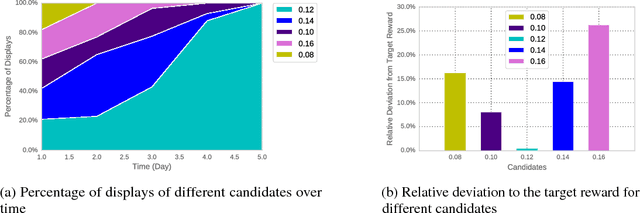
Abstract:Interactive user interfaces need to continuously evolve based on the interactions that a user has (or does not have) with the system. This may require constant exploration of various options that the system may have for the user and obtaining signals of user preferences on those. However, such an exploration, especially when the set of available options itself can change frequently, can lead to sub-optimal user experiences. We present Explore-Exploit: a framework designed to collect and utilize user feedback in an interactive and online setting that minimizes regressions in end-user experience. This framework provides a suite of online learning operators for various tasks such as personalization ranking, candidate selection and active learning. We demonstrate how to integrate this framework with run-time services to leverage online and interactive machine learning out-of-the-box. We also present results demonstrating the efficiencies that can be achieved using the Explore-Exploit framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge