Beatrice Knudsen
ImplicitStainer: Data-Efficient Medical Image Translation for Virtual Antibody-based Tissue Staining Using Local Implicit Functions
May 14, 2025Abstract:Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is a gold standard for microscopic diagnosis in pathology. However, H&E staining does not capture all the diagnostic information that may be needed. To obtain additional molecular information, immunohistochemical (IHC) stains highlight proteins that mark specific cell types, such as CD3 for T-cells or CK8/18 for epithelial cells. While IHC stains are vital for prognosis and treatment guidance, they are typically only available at specialized centers and time consuming to acquire, leading to treatment delays for patients. Virtual staining, enabled by deep learning-based image translation models, provides a promising alternative by computationally generating IHC stains from H&E stained images. Although many GAN and diffusion based image to image (I2I) translation methods have been used for virtual staining, these models treat image patches as independent data points, which results in increased and more diverse data requirements for effective generation. We present ImplicitStainer, a novel approach that leverages local implicit functions to improve image translation, specifically virtual staining performance, by focusing on pixel-level predictions. This method enhances robustness to variations in dataset sizes, delivering high-quality results even with limited data. We validate our approach on two datasets using a comprehensive set of metrics and benchmark it against over fifteen state-of-the-art GAN- and diffusion based models. Full Code and models trained will be released publicly via Github upon acceptance.
VIMs: Virtual Immunohistochemistry Multiplex staining via Text-to-Stain Diffusion Trained on Uniplex Stains
Jul 26, 2024

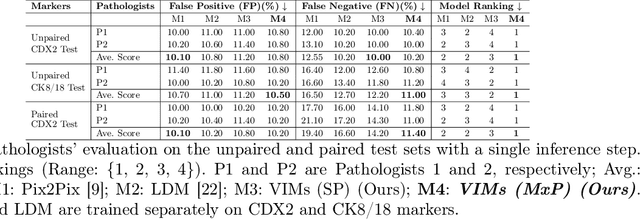
Abstract:This paper introduces a Virtual Immunohistochemistry Multiplex staining (VIMs) model designed to generate multiple immunohistochemistry (IHC) stains from a single hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained tissue section. IHC stains are crucial in pathology practice for resolving complex diagnostic questions and guiding patient treatment decisions. While commercial laboratories offer a wide array of up to 400 different antibody-based IHC stains, small biopsies often lack sufficient tissue for multiple stains while preserving material for subsequent molecular testing. This highlights the need for virtual IHC staining. Notably, VIMs is the first model to address this need, leveraging a large vision-language single-step diffusion model for virtual IHC multiplexing through text prompts for each IHC marker. VIMs is trained on uniplex paired H&E and IHC images, employing an adversarial training module. Testing of VIMs includes both paired and unpaired image sets. To enhance computational efficiency, VIMs utilizes a pre-trained large latent diffusion model fine-tuned with small, trainable weights through the Low-Rank Adapter (LoRA) approach. Experiments on nuclear and cytoplasmic IHC markers demonstrate that VIMs outperforms the base diffusion model and achieves performance comparable to Pix2Pix, a standard generative model for paired image translation. Multiple evaluation methods, including assessments by two pathologists, are used to determine the performance of VIMs. Additionally, experiments with different prompts highlight the impact of text conditioning. This paper represents the first attempt to accelerate histopathology research by demonstrating the generation of multiple IHC stains from a single H&E input using a single model trained solely on uniplex data.
F2FLDM: Latent Diffusion Models with Histopathology Pre-Trained Embeddings for Unpaired Frozen Section to FFPE Translation
Apr 19, 2024



Abstract:The Frozen Section (FS) technique is a rapid and efficient method, taking only 15-30 minutes to prepare slides for pathologists' evaluation during surgery, enabling immediate decisions on further surgical interventions. However, FS process often introduces artifacts and distortions like folds and ice-crystal effects. In contrast, these artifacts and distortions are absent in the higher-quality formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) slides, which require 2-3 days to prepare. While Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based methods have been used to translate FS to FFPE images (F2F), they may leave morphological inaccuracies with remaining FS artifacts or introduce new artifacts, reducing the quality of these translations for clinical assessments. In this study, we benchmark recent generative models, focusing on GANs and Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs), to overcome these limitations. We introduce a novel approach that combines LDMs with Histopathology Pre-Trained Embeddings to enhance restoration of FS images. Our framework leverages LDMs conditioned by both text and pre-trained embeddings to learn meaningful features of FS and FFPE histopathology images. Through diffusion and denoising techniques, our approach not only preserves essential diagnostic attributes like color staining and tissue morphology but also proposes an embedding translation mechanism to better predict the targeted FFPE representation of input FS images. As a result, this work achieves a significant improvement in classification performance, with the Area Under the Curve rising from 81.99% to 94.64%, accompanied by an advantageous CaseFD. This work establishes a new benchmark for FS to FFPE image translation quality, promising enhanced reliability and accuracy in histopathology FS image analysis. Our work is available at https://minhmanho.github.io/f2f_ldm/.
DISC: Latent Diffusion Models with Self-Distillation from Separated Conditions for Prostate Cancer Grading
Apr 19, 2024Abstract:Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) can generate high-fidelity images from noise, offering a promising approach for augmenting histopathology images for training cancer grading models. While previous works successfully generated high-fidelity histopathology images using LDMs, the generation of image tiles to improve prostate cancer grading has not yet been explored. Additionally, LDMs face challenges in accurately generating admixtures of multiple cancer grades in a tile when conditioned by a tile mask. In this study, we train specific LDMs to generate synthetic tiles that contain multiple Gleason Grades (GGs) by leveraging pixel-wise annotations in input tiles. We introduce a novel framework named Self-Distillation from Separated Conditions (DISC) that generates GG patterns guided by GG masks. Finally, we deploy a training framework for pixel-level and slide-level prostate cancer grading, where synthetic tiles are effectively utilized to improve the cancer grading performance of existing models. As a result, this work surpasses previous works in two domains: 1) our LDMs enhanced with DISC produce more accurate tiles in terms of GG patterns, and 2) our training scheme, incorporating synthetic data, significantly improves the generalization of the baseline model for prostate cancer grading, particularly in challenging cases of rare GG5, demonstrating the potential of generative models to enhance cancer grading when data is limited.
StainDiffuser: MultiTask Dual Diffusion Model for Virtual Staining
Mar 17, 2024Abstract:Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining is the most commonly used for disease diagnosis and tumor recurrence tracking. Hematoxylin excels at highlighting nuclei, whereas eosin stains the cytoplasm. However, H&E stain lacks details for differentiating different types of cells relevant to identifying the grade of the disease or response to specific treatment variations. Pathologists require special immunohistochemical (IHC) stains that highlight different cell types. These stains help in accurately identifying different regions of disease growth and their interactions with the cell's microenvironment. The advent of deep learning models has made Image-to-Image (I2I) translation a key research area, reducing the need for expensive physical staining processes. Pix2Pix and CycleGAN are still the most commonly used methods for virtual staining applications. However, both suffer from hallucinations or staining irregularities when H&E stain has less discriminate information about the underlying cells IHC needs to highlight (e.g.,CD3 lymphocytes). Diffusion models are currently the state-of-the-art models for image generation and conditional generation tasks. However, they require extensive and diverse datasets (millions of samples) to converge, which is less feasible for virtual staining applications.Inspired by the success of multitask deep learning models for limited dataset size, we propose StainDiffuser, a novel multitask dual diffusion architecture for virtual staining that converges under a limited training budget. StainDiffuser trains two diffusion processes simultaneously: (a) generation of cell-specific IHC stain from H&E and (b) H&E-based cell segmentation using coarse segmentation only during training. Our results show that StainDiffuser produces high-quality results for easier (CK8/18,epithelial marker) and difficult stains(CD3, Lymphocytes).
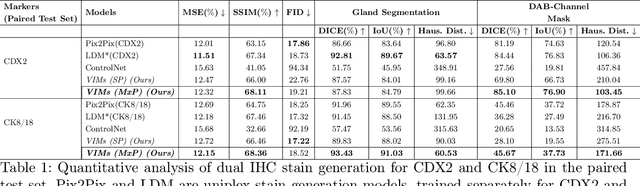
Structural Cycle GAN for Virtual Immunohistochemistry Staining of Gland Markers in the Colon
Aug 25, 2023



Abstract:With the advent of digital scanners and deep learning, diagnostic operations may move from a microscope to a desktop. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining is one of the most frequently used stains for disease analysis, diagnosis, and grading, but pathologists do need different immunohistochemical (IHC) stains to analyze specific structures or cells. Obtaining all of these stains (H&E and different IHCs) on a single specimen is a tedious and time-consuming task. Consequently, virtual staining has emerged as an essential research direction. Here, we propose a novel generative model, Structural Cycle-GAN (SC-GAN), for synthesizing IHC stains from H&E images, and vice versa. Our method expressly incorporates structural information in the form of edges (in addition to color data) and employs attention modules exclusively in the decoder of the proposed generator model. This integration enhances feature localization and preserves contextual information during the generation process. In addition, a structural loss is incorporated to ensure accurate structure alignment between the generated and input markers. To demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed model, experiments are conducted with two IHC markers emphasizing distinct structures of glands in the colon: the nucleus of epithelial cells (CDX2) and the cytoplasm (CK818). Quantitative metrics such as FID and SSIM are frequently used for the analysis of generative models, but they do not correlate explicitly with higher-quality virtual staining results. Therefore, we propose two new quantitative metrics that correlate directly with the virtual staining specificity of IHC markers.
To pretrain or not to pretrain? A case study of domain-specific pretraining for semantic segmentation in histopathology
Jul 06, 2023Abstract:Annotating medical imaging datasets is costly, so fine-tuning (or transfer learning) is the most effective method for digital pathology vision applications such as disease classification and semantic segmentation. However, due to texture bias in models trained on real-world images, transfer learning for histopathology applications might result in underperforming models, which necessitates the need for using unlabeled histopathology data and self-supervised methods to discover domain-specific characteristics. Here, we tested the premise that histopathology-specific pretrained models provide better initializations for pathology vision tasks, i.e., gland and cell segmentation. In this study, we compare the performance of gland and cell segmentation tasks with domain-specific and non-domain-specific pretrained weights. Moreover, we investigate the data size at which domain-specific pretraining produces a statistically significant difference in performance. In addition, we investigated whether domain-specific initialization improves the effectiveness of out-of-domain testing on distinct datasets but the same task. The results indicate that performance gain using domain-specific pretraining depends on both the task and the size of the training dataset. In instances with limited dataset sizes, a significant improvement in gland segmentation performance was also observed, whereas models trained on cell segmentation datasets exhibit no improvement.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation via Feature-space Density Matching
May 09, 2023Abstract:Semantic segmentation is a critical step in automated image interpretation and analysis where pixels are classified into one or more predefined semantically meaningful classes. Deep learning approaches for semantic segmentation rely on harnessing the power of annotated images to learn features indicative of these semantic classes. Nonetheless, they often fail to generalize when there is a significant domain (i.e., distributional) shift between the training (i.e., source) data and the dataset(s) encountered when deployed (i.e., target), necessitating manual annotations for the target data to achieve acceptable performance. This is especially important in medical imaging because different image modalities have significant intra- and inter-site variations due to protocol and vendor variability. Current techniques are sensitive to hyperparameter tuning and target dataset size. This paper presents an unsupervised domain adaptation approach for semantic segmentation that alleviates the need for annotating target data. Using kernel density estimation, we match the target data distribution to the source data in the feature space. We demonstrate that our results are comparable or superior on multiple-site prostate MRI and histopathology images, which mitigates the need for annotating target data.
A Pathologist-Informed Workflow for Classification of Prostate Glands in Histopathology
Sep 27, 2022Abstract:Pathologists diagnose and grade prostate cancer by examining tissue from needle biopsies on glass slides. The cancer's severity and risk of metastasis are determined by the Gleason grade, a score based on the organization and morphology of prostate cancer glands. For diagnostic work-up, pathologists first locate glands in the whole biopsy core, and -- if they detect cancer -- they assign a Gleason grade. This time-consuming process is subject to errors and significant inter-observer variability, despite strict diagnostic criteria. This paper proposes an automated workflow that follows pathologists' \textit{modus operandi}, isolating and classifying multi-scale patches of individual glands in whole slide images (WSI) of biopsy tissues using distinct steps: (1) two fully convolutional networks segment epithelium versus stroma and gland boundaries, respectively; (2) a classifier network separates benign from cancer glands at high magnification; and (3) an additional classifier predicts the grade of each cancer gland at low magnification. Altogether, this process provides a gland-specific approach for prostate cancer grading that we compare against other machine-learning-based grading methods.
* Published as a workshop paper at MICCAI MOVI 2022
Stain based contrastive co-training for histopathological image analysis
Jun 24, 2022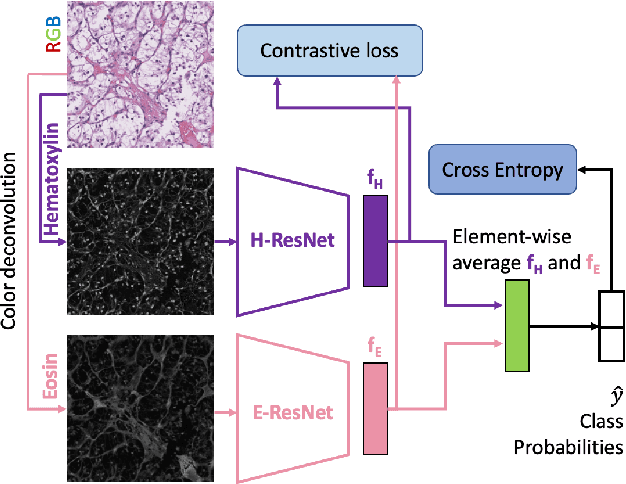
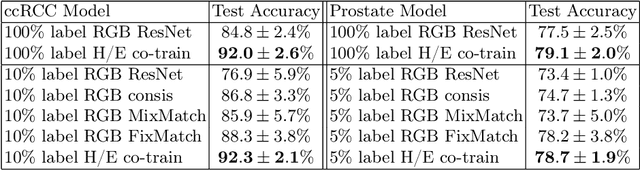
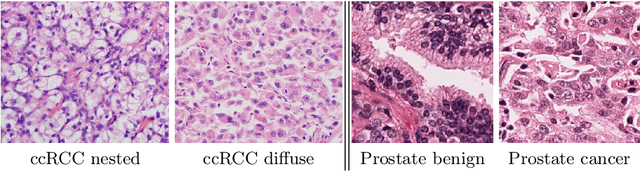

Abstract:We propose a novel semi-supervised learning approach for classification of histopathology images. We employ strong supervision with patch-level annotations combined with a novel co-training loss to create a semi-supervised learning framework. Co-training relies on multiple conditionally independent and sufficient views of the data. We separate the hematoxylin and eosin channels in pathology images using color deconvolution to create two views of each slide that can partially fulfill these requirements. Two separate CNNs are used to embed the two views into a joint feature space. We use a contrastive loss between the views in this feature space to implement co-training. We evaluate our approach in clear cell renal cell and prostate carcinomas, and demonstrate improvement over state-of-the-art semi-supervised learning methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge