Baole Wei
ToolWeaver: Weaving Collaborative Semantics for Scalable Tool Use in Large Language Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Prevalent retrieval-based tool-use pipelines struggle with a dual semantic challenge: their retrievers often employ encoders that fail to capture complex semantics, while the Large Language Model (LLM) itself lacks intrinsic tool knowledge from its natural language pretraining. Generative methods offer a powerful alternative by unifying selection and execution, tasking the LLM to directly learn and generate tool identifiers. However, the common practice of mapping each tool to a unique new token introduces substantial limitations: it creates a scalability and generalization crisis, as the vocabulary size explodes and each tool is assigned a semantically isolated token. This approach also creates a semantic bottleneck that hinders the learning of collaborative tool relationships, as the model must infer them from sparse co-occurrences of monolithic tool IDs within a vast library. To address these limitations, we propose ToolWeaver, a novel generative tool learning framework that encodes tools into hierarchical sequences. This approach makes vocabulary expansion logarithmic to the number of tools. Crucially, it enables the model to learn collaborative patterns from the dense co-occurrence of shared codes, rather than the sparse co-occurrence of monolithic tool IDs. We generate these structured codes through a novel tokenization process designed to weave together a tool's intrinsic semantics with its extrinsic co-usage patterns. These structured codes are then integrated into the LLM through a generative alignment stage, where the model is fine-tuned to produce the hierarchical code sequences. Evaluation results with nearly 47,000 tools show that ToolWeaver significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, establishing a more scalable, generalizable, and semantically-aware foundation for advanced tool-augmented agents.
Uni-MuMER: Unified Multi-Task Fine-Tuning of Vision-Language Model for Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition
May 29, 2025Abstract:Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition (HMER) remains a persistent challenge in Optical Character Recognition (OCR) due to the inherent freedom of symbol layout and variability in handwriting styles. Prior methods have faced performance bottlenecks, proposing isolated architectural modifications that are difficult to integrate coherently into a unified framework. Meanwhile, recent advances in pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated strong cross-task generalization, offering a promising foundation for developing unified solutions. In this paper, we introduce Uni-MuMER, which fully fine-tunes a VLM for the HMER task without modifying its architecture, effectively injecting domain-specific knowledge into a generalist framework. Our method integrates three data-driven tasks: Tree-Aware Chain-of-Thought (Tree-CoT) for structured spatial reasoning, Error-Driven Learning (EDL) for reducing confusion among visually similar characters, and Symbol Counting (SC) for improving recognition consistency in long expressions. Experiments on the CROHME and HME100K datasets show that Uni-MuMER achieves new state-of-the-art performance, surpassing the best lightweight specialized model SSAN by 16.31% and the top-performing VLM Gemini2.5-flash by 24.42% in the zero-shot setting. Our datasets, models, and code are open-sourced at: https://github.com/BFlameSwift/Uni-MuMER
Vote&Mix: Plug-and-Play Token Reduction for Efficient Vision Transformer
Aug 30, 2024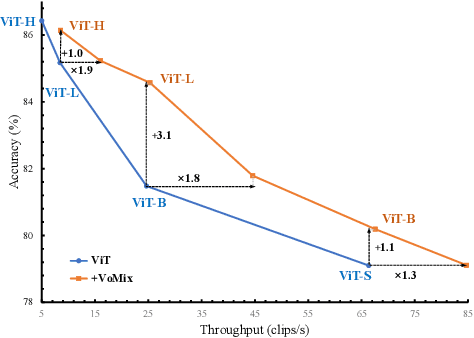
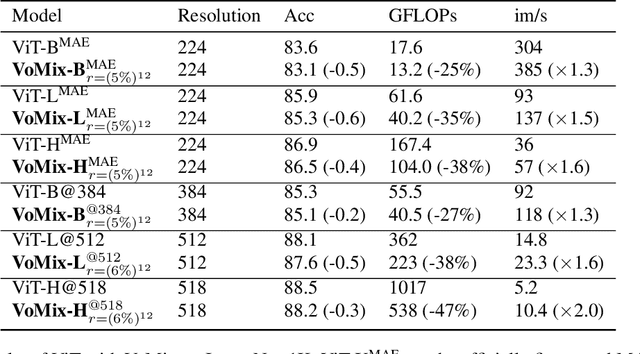
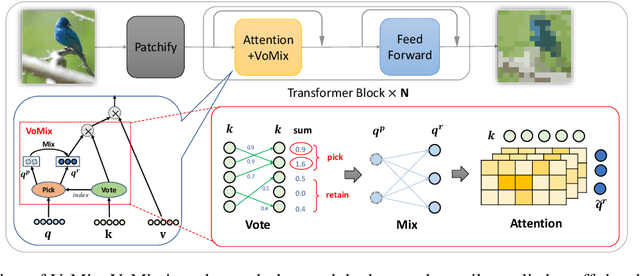
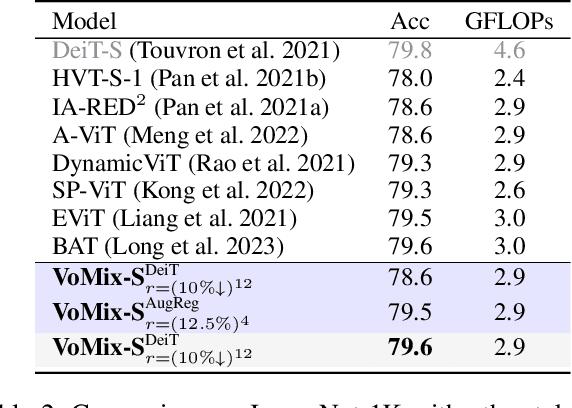
Abstract:Despite the remarkable success of Vision Transformers (ViTs) in various visual tasks, they are often hindered by substantial computational cost. In this work, we introduce Vote\&Mix (\textbf{VoMix}), a plug-and-play and parameter-free token reduction method, which can be readily applied to off-the-shelf ViT models \textit{without any training}. VoMix tackles the computational redundancy of ViTs by identifying tokens with high homogeneity through a layer-wise token similarity voting mechanism. Subsequently, the selected tokens are mixed into the retained set, thereby preserving visual information. Experiments demonstrate VoMix significantly improves the speed-accuracy tradeoff of ViTs on both images and videos. Without any training, VoMix achieves a 2$\times$ increase in throughput of existing ViT-H on ImageNet-1K and a 2.4$\times$ increase in throughput of existing ViT-L on Kinetics-400 video dataset, with a mere 0.3\% drop in top-1 accuracy.
SegHist: A General Segmentation-based Framework for Chinese Historical Document Text Line Detection
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Text line detection is a key task in historical document analysis facing many challenges of arbitrary-shaped text lines, dense texts, and text lines with high aspect ratios, etc. In this paper, we propose a general framework for historical document text detection (SegHist), enabling existing segmentation-based text detection methods to effectively address the challenges, especially text lines with high aspect ratios. Integrating the SegHist framework with the commonly used method DB++, we develop DB-SegHist. This approach achieves SOTA on the CHDAC, MTHv2, and competitive results on HDRC datasets, with a significant improvement of 1.19% on the most challenging CHDAC dataset which features more text lines with high aspect ratios. Moreover, our method attains SOTA on rotated MTHv2 and rotated HDRC, demonstrating its rotational robustness. The code is available at https://github.com/LumionHXJ/SegHist.
Recognition-Guided Diffusion Model for Scene Text Image Super-Resolution
Nov 22, 2023Abstract:Scene Text Image Super-Resolution (STISR) aims to enhance the resolution and legibility of text within low-resolution (LR) images, consequently elevating recognition accuracy in Scene Text Recognition (STR). Previous methods predominantly employ discriminative Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) augmented with diverse forms of text guidance to address this issue. Nevertheless, they remain deficient when confronted with severely blurred images, due to their insufficient generation capability when little structural or semantic information can be extracted from original images. Therefore, we introduce RGDiffSR, a Recognition-Guided Diffusion model for scene text image Super-Resolution, which exhibits great generative diversity and fidelity even in challenging scenarios. Moreover, we propose a Recognition-Guided Denoising Network, to guide the diffusion model generating LR-consistent results through succinct semantic guidance. Experiments on the TextZoom dataset demonstrate the superiority of RGDiffSR over prior state-of-the-art methods in both text recognition accuracy and image fidelity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge