Artem Bazhenov
Echo: An Open-Source, Low-Cost Teleoperation System with Force Feedback for Dataset Collection in Robot Learning
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:In this article, we propose Echo, a novel joint-matching teleoperation system designed to enhance the collection of datasets for manual and bimanual tasks. Our system is specifically tailored for controlling the UR manipulator and features a custom controller with force feedback and adjustable sensitivity modes, enabling precise and intuitive operation. Additionally, Echo integrates a user-friendly dataset recording interface, simplifying the process of collecting high-quality training data for imitation learning. The system is designed to be reliable, cost-effective, and easily reproducible, making it an accessible tool for researchers, laboratories, and startups passionate about advancing robotics through imitation learning. Although the current implementation focuses on the UR manipulator, Echo architecture is reconfigurable and can be adapted to other manipulators and humanoid systems. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Echo through a series of experiments, showcasing its ability to perform complex bimanual tasks and its potential to accelerate research in the field. We provide assembly instructions, a hardware description, and code at https://eterwait.github.io/Echo/.
MissionGPT: Mission Planner for Mobile Robot based on Robotics Transformer Model
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach to building mission planners based on neural networks with Transformer architecture and Large Language Models (LLMs). This approach demonstrates the possibility of setting a task for a mobile robot and its successful execution without the use of perception algorithms, based only on the data coming from the camera. In this work, a success rate of more than 50\% was obtained for one of the basic actions for mobile robots. The proposed approach is of practical importance in the field of warehouse logistics robots, as in the future it may allow to eliminate the use of markings, LiDARs, beacons and other tools for robot orientation in space. In conclusion, this approach can be scaled for any type of robot and for any number of robots.
HyperSurf: Quadruped Robot Leg Capable of Surface Recognition with GRU and Real-to-Sim Transferring
Jul 22, 2024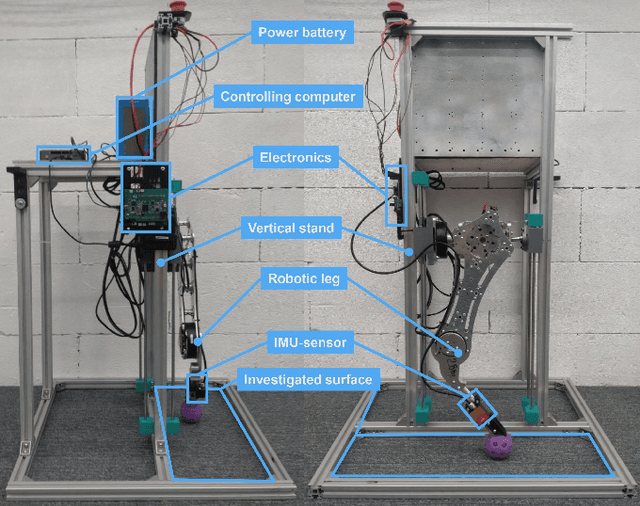
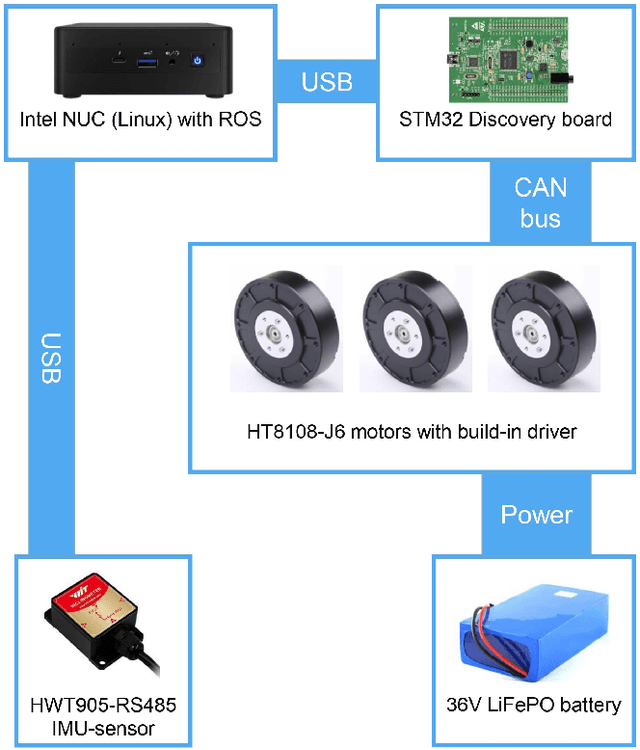
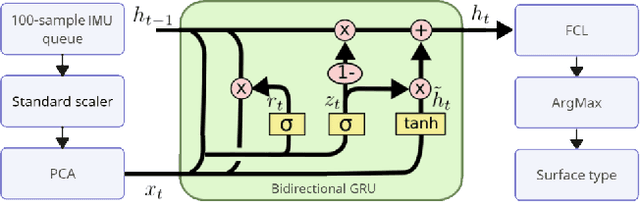
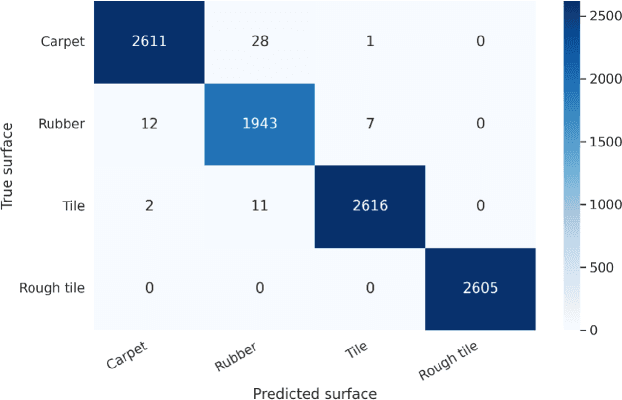
Abstract:This paper introduces a system of data collection acceleration and real-to-sim transferring for surface recognition on a quadruped robot. The system features a mechanical single-leg setup capable of stepping on various easily interchangeable surfaces. Additionally, it incorporates a GRU-based Surface Recognition System, inspired by the system detailed in the Dog-Surf paper. This setup facilitates the expansion of dataset collection for model training, enabling data acquisition from hard-to-reach surfaces in laboratory conditions. Furthermore, it opens avenues for transferring surface properties from reality to simulation, thereby allowing the training of optimal gaits for legged robots in simulation environments using a pre-prepared library of digital twins of surfaces. Moreover, enhancements have been made to the GRU-based Surface Recognition System, allowing for the integration of data from both the quadruped robot and the single-leg setup. The dataset and code have been made publicly available.
DogSurf: Quadruped Robot Capable of GRU-based Surface Recognition for Blind Person Navigation
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces DogSurf - a newapproach of using quadruped robots to help visually impaired people navigate in real world. The presented method allows the quadruped robot to detect slippery surfaces, and to use audio and haptic feedback to inform the user when to stop. A state-of-the-art GRU-based neural network architecture with mean accuracy of 99.925% was proposed for the task of multiclass surface classification for quadruped robots. A dataset was collected on a Unitree Go1 Edu robot. The dataset and code have been posted to the public domain.
CognitiveDog: Large Multimodal Model Based System to Translate Vision and Language into Action of Quadruped Robot
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces CognitiveDog, a pioneering development of quadruped robot with Large Multi-modal Model (LMM) that is capable of not only communicating with humans verbally but also physically interacting with the environment through object manipulation. The system was realized on Unitree Go1 robot-dog equipped with a custom gripper and demonstrated autonomous decision-making capabilities, independently determining the most appropriate actions and interactions with various objects to fulfill user-defined tasks. These tasks do not necessarily include direct instructions, challenging the robot to comprehend and execute them based on natural language input and environmental cues. The paper delves into the intricacies of this system, dataset characteristics, and the software architecture. Key to this development is the robot's proficiency in navigating space using Visual-SLAM, effectively manipulating and transporting objects, and providing insightful natural language commentary during task execution. Experimental results highlight the robot's advanced task comprehension and adaptability, underscoring its potential in real-world applications. The dataset used to fine-tune the robot-dog behavior generation model is provided at the following link: huggingface.co/datasets/ArtemLykov/CognitiveDog_dataset
LLM-MARS: Large Language Model for Behavior Tree Generation and NLP-enhanced Dialogue in Multi-Agent Robot Systems
Dec 14, 2023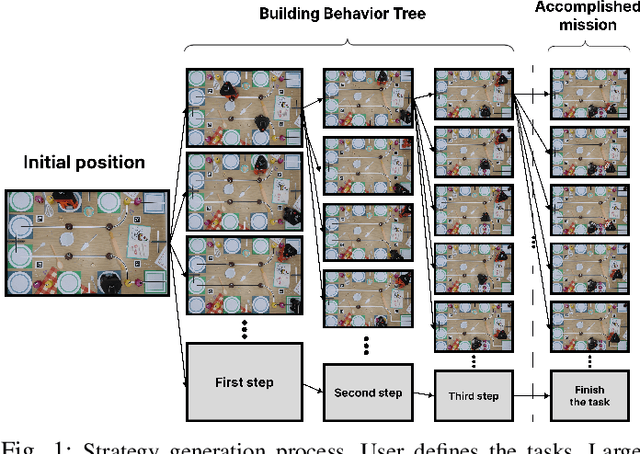
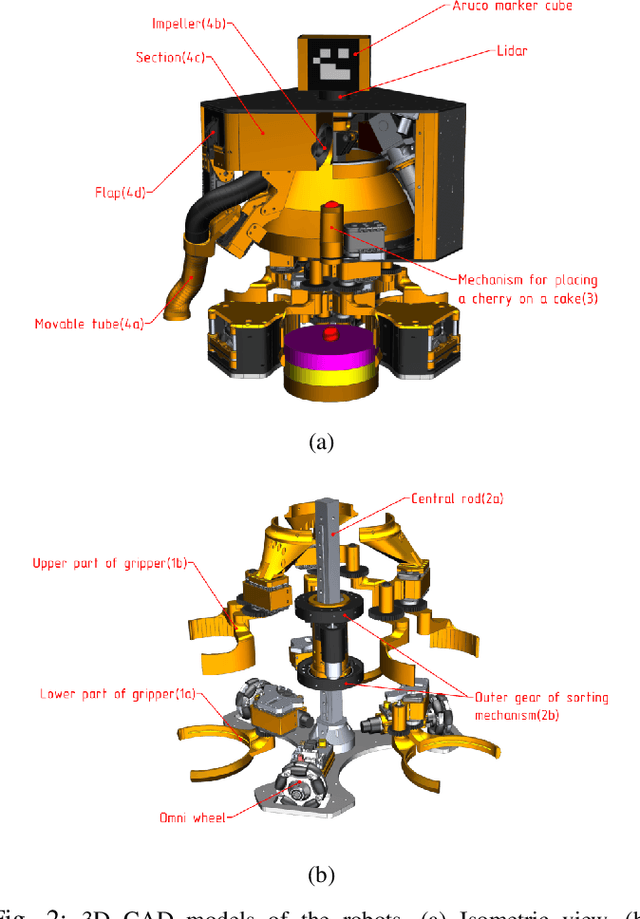
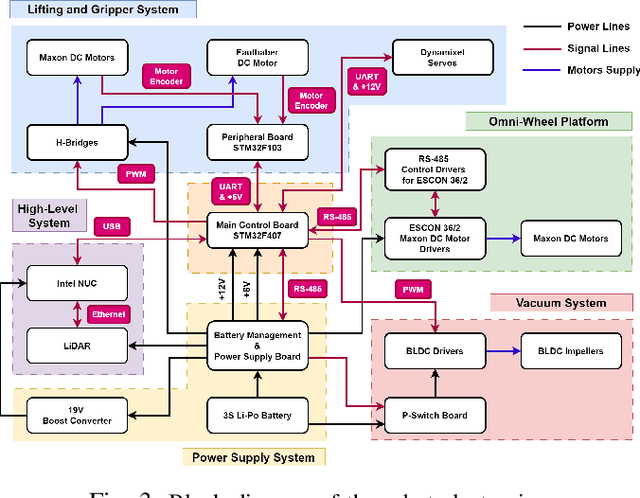

Abstract:This paper introduces LLM-MARS, first technology that utilizes a Large Language Model based Artificial Intelligence for Multi-Agent Robot Systems. LLM-MARS enables dynamic dialogues between humans and robots, allowing the latter to generate behavior based on operator commands and provide informative answers to questions about their actions. LLM-MARS is built on a transformer-based Large Language Model, fine-tuned from the Falcon 7B model. We employ a multimodal approach using LoRa adapters for different tasks. The first LoRa adapter was developed by fine-tuning the base model on examples of Behavior Trees and their corresponding commands. The second LoRa adapter was developed by fine-tuning on question-answering examples. Practical trials on a multi-agent system of two robots within the Eurobot 2023 game rules demonstrate promising results. The robots achieve an average task execution accuracy of 79.28% in compound commands. With commands containing up to two tasks accuracy exceeded 90%. Evaluation confirms the system's answers on operators questions exhibit high accuracy, relevance, and informativeness. LLM-MARS and similar multi-agent robotic systems hold significant potential to revolutionize logistics, enabling autonomous exploration missions and advancing Industry 5.0.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge