Anqi Wang
Discriminative Pedestrian Features and Gated Channel Attention for Clothes-Changing Person Re-Identification
Oct 29, 2024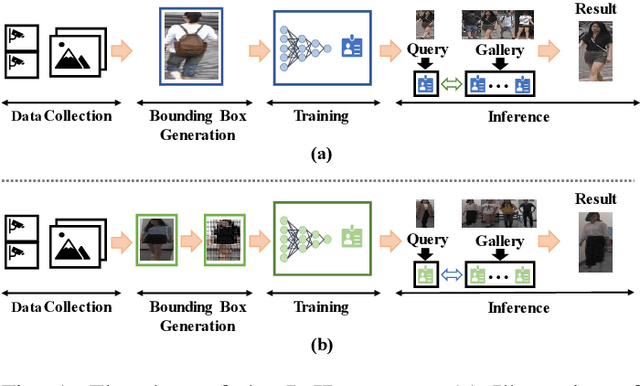
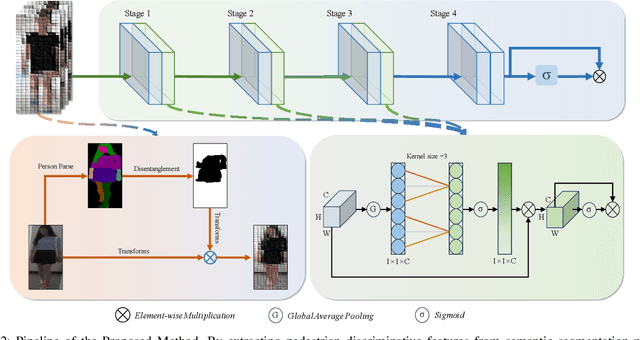
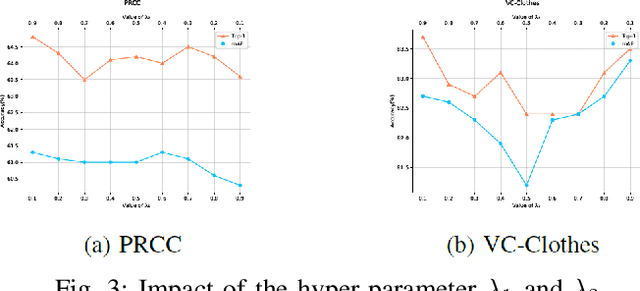
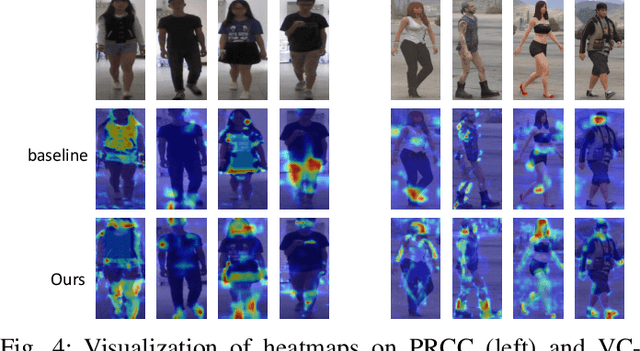
Abstract:In public safety and social life, the task of Clothes-Changing Person Re-Identification (CC-ReID) has become increasingly significant. However, this task faces considerable challenges due to appearance changes caused by clothing alterations. Addressing this issue, this paper proposes an innovative method for disentangled feature extraction, effectively extracting discriminative features from pedestrian images that are invariant to clothing. This method leverages pedestrian parsing techniques to identify and retain features closely associated with individual identity while disregarding the variable nature of clothing attributes. Furthermore, this study introduces a gated channel attention mechanism, which, by adjusting the network's focus, aids the model in more effectively learning and emphasizing features critical for pedestrian identity recognition. Extensive experiments conducted on two standard CC-ReID datasets validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, with performance surpassing current leading solutions. The Top-1 accuracy under clothing change scenarios on the PRCC and VC-Clothes datasets reached 64.8% and 83.7%, respectively.
Exploring the Potential of Large Language Models in Artistic Creation: Collaboration and Reflection on Creative Programming
Feb 15, 2024



Abstract:Recently, the potential of large language models (LLMs) has been widely used in assisting programming. However, current research does not explore the artist potential of LLMs in creative coding within artist and AI collaboration. Our work probes the reflection type of artists in the creation process with such collaboration. We compare two common collaboration approaches: invoking the entire program and multiple subtasks. Our findings exhibit artists' different stimulated reflections in two different methods. Our finding also shows the correlation of reflection type with user performance, user satisfaction, and subjective experience in two collaborations through conducting two methods, including experimental data and qualitative interviews. In this sense, our work reveals the artistic potential of LLM in creative coding. Meanwhile, we provide a critical lens of human-AI collaboration from the artists' perspective and expound design suggestions for future work of AI-assisted creative tasks.
VR PreM+ : An Immersive Pre-learning Branching Visualization System for Museum Tours
Nov 01, 2023
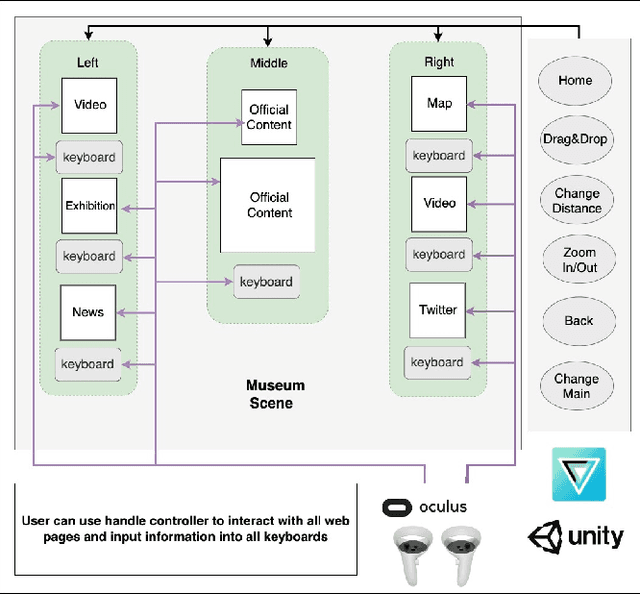

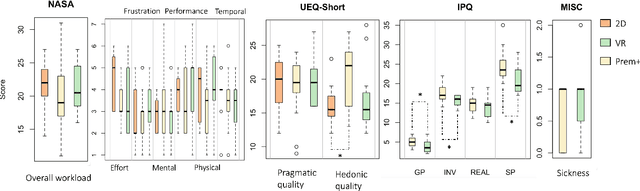
Abstract:We present VR PreM+, an innovative VR system designed to enhance web exploration beyond traditional computer screens. Unlike static 2D displays, VR PreM+ leverages 3D environments to create an immersive pre-learning experience. Using keyword-based information retrieval allows users to manage and connect various content sources in a dynamic 3D space, improving communication and data comparison. We conducted preliminary and user studies that demonstrated efficient information retrieval, increased user engagement, and a greater sense of presence. These findings yielded three design guidelines for future VR information systems: display, interaction, and user-centric design. VR PreM+ bridges the gap between traditional web browsing and immersive VR, offering an interactive and comprehensive approach to information acquisition. It holds promise for research, education, and beyond.
Towards Computational Architecture of Liberty: A Comprehensive Survey on Deep Learning for Generating Virtual Architecture in the Metaverse
Apr 30, 2023



Abstract:3D shape generation techniques utilizing deep learning are increasing attention from both computer vision and architectural design. This survey focuses on investigating and comparing the current latest approaches to 3D object generation with deep generative models (DGMs), including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), 3D-aware images, and diffusion models. We discuss 187 articles (80.7% of articles published between 2018-2022) to review the field of generated possibilities of architecture in virtual environments, limited to the architecture form. We provide an overview of architectural research, virtual environment, and related technical approaches, followed by a review of recent trends in discrete voxel generation, 3D models generated from 2D images, and conditional parameters. We highlight under-explored issues in 3D generation and parameterized control that is worth further investigation. Moreover, we speculate that four research agendas including data limitation, editability, evaluation metrics, and human-computer interaction are important enablers of ubiquitous interaction with immersive systems in architecture for computer-aided design Our work contributes to researchers' understanding of the current potential and future needs of deep learnings in generating virtual architecture.
Infrared and visible image fusion based on Multi-State Contextual Hidden Markov Model
Jan 26, 2022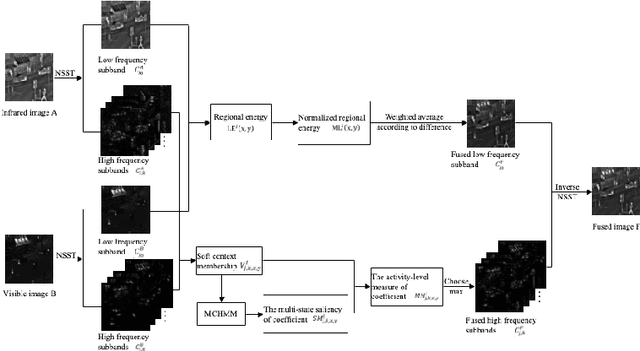
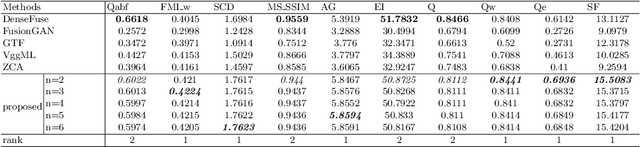
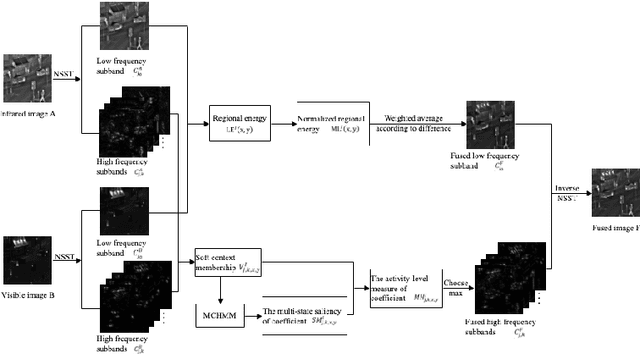
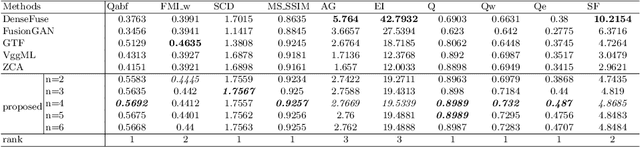
Abstract:The traditional two-state hidden Markov model divides the high frequency coefficients only into two states (large and small states). Such scheme is prone to produce an inaccurate statistical model for the high frequency subband and reduces the quality of fusion result. In this paper, a fine-grained multi-state contextual hidden Markov model (MCHMM) is proposed for infrared and visible image fusion in the non-subsampled Shearlet domain, which takes full consideration of the strong correlations and level of details of NSST coefficients. To this end, an accurate soft context variable is designed correspondingly from the perspective of context correlation. Then, the statistical features provided by MCHMM are utilized for the fusion of high frequency subbands. To ensure the visual quality, a fusion strategy based on the difference in regional energy is proposed as well for lowfrequency subbands. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve a superior performance compared with other fusion methods in both subjective and objective aspects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge