Angela Tong
Deep Learning-based Unsupervised Domain Adaptation via a Unified Model for Prostate Lesion Detection Using Multisite Bi-parametric MRI Datasets
Aug 08, 2024


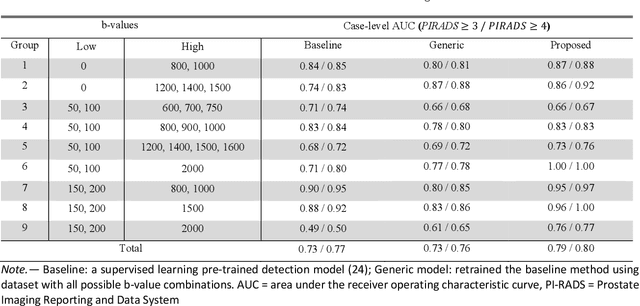
Abstract:Our hypothesis is that UDA using diffusion-weighted images, generated with a unified model, offers a promising and reliable strategy for enhancing the performance of supervised learning models in multi-site prostate lesion detection, especially when various b-values are present. This retrospective study included data from 5,150 patients (14,191 samples) collected across nine different imaging centers. A novel UDA method using a unified generative model was developed for multi-site PCa detection. This method translates diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) acquisitions, including apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and individual DW images acquired using various b-values, to align with the style of images acquired using b-values recommended by Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) guidelines. The generated ADC and DW images replace the original images for PCa detection. An independent set of 1,692 test cases (2,393 samples) was used for evaluation. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was used as the primary metric, and statistical analysis was performed via bootstrapping. For all test cases, the AUC values for baseline SL and UDA methods were 0.73 and 0.79 (p<.001), respectively, for PI-RADS>=3, and 0.77 and 0.80 (p<.001) for PI-RADS>=4 PCa lesions. In the 361 test cases under the most unfavorable image acquisition setting, the AUC values for baseline SL and UDA were 0.49 and 0.76 (p<.001) for PI-RADS>=3, and 0.50 and 0.77 (p<.001) for PI-RADS>=4 PCa lesions. The results indicate the proposed UDA with generated images improved the performance of SL methods in multi-site PCa lesion detection across datasets with various b values, especially for images acquired with significant deviations from the PI-RADS recommended DWI protocol (e.g. with an extremely high b-value).
FastMRI Prostate: A Publicly Available, Biparametric MRI Dataset to Advance Machine Learning for Prostate Cancer Imaging
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:The fastMRI brain and knee dataset has enabled significant advances in exploring reconstruction methods for improving speed and image quality for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) via novel, clinically relevant reconstruction approaches. In this study, we describe the April 2023 expansion of the fastMRI dataset to include biparametric prostate MRI data acquired on a clinical population. The dataset consists of raw k-space and reconstructed images for T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted sequences along with slice-level labels that indicate the presence and grade of prostate cancer. As has been the case with fastMRI, increasing accessibility to raw prostate MRI data will further facilitate research in MR image reconstruction and evaluation with the larger goal of improving the utility of MRI for prostate cancer detection and evaluation. The dataset is available at https://fastmri.med.nyu.edu.
On the Feasibility of Machine Learning Augmented Magnetic Resonance for Point-of-Care Identification of Disease
Feb 02, 2023



Abstract:Early detection of many life-threatening diseases (e.g., prostate and breast cancer) within at-risk population can improve clinical outcomes and reduce cost of care. While numerous disease-specific "screening" tests that are closer to Point-of-Care (POC) are in use for this task, their low specificity results in unnecessary biopsies, leading to avoidable patient trauma and wasteful healthcare spending. On the other hand, despite the high accuracy of Magnetic Resonance (MR) imaging in disease diagnosis, it is not used as a POC disease identification tool because of poor accessibility. The root cause of poor accessibility of MR stems from the requirement to reconstruct high-fidelity images, as it necessitates a lengthy and complex process of acquiring large quantities of high-quality k-space measurements. In this study we explore the feasibility of an ML-augmented MR pipeline that directly infers the disease sidestepping the image reconstruction process. We hypothesise that the disease classification task can be solved using a very small tailored subset of k-space data, compared to image reconstruction. Towards that end, we propose a method that performs two tasks: 1) identifies a subset of the k-space that maximizes disease identification accuracy, and 2) infers the disease directly using the identified k-space subset, bypassing the image reconstruction step. We validate our hypothesis by measuring the performance of the proposed system across multiple diseases and anatomies. We show that comparable performance to image-based classifiers, trained on images reconstructed with full k-space data, can be achieved using small quantities of data: 8% of the data for detecting multiple abnormalities in prostate and brain scans, and 5% of the data for knee abnormalities. To better understand the proposed approach and instigate future research, we provide an extensive analysis and release code.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge