Andreas Wicki
Towards Scalable and Cross-Lingual Specialist Language Models for Oncology
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:Clinical oncology generates vast, unstructured data that often contain inconsistencies, missing information, and ambiguities, making it difficult to extract reliable insights for data-driven decision-making. General-purpose large language models (LLMs) struggle with these challenges due to their lack of domain-specific reasoning, including specialized clinical terminology, context-dependent interpretations, and multi-modal data integration. We address these issues with an oncology-specialized, efficient, and adaptable NLP framework that combines instruction tuning, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and graph-based knowledge integration. Our lightweight models prove effective at oncology-specific tasks, such as named entity recognition (e.g., identifying cancer diagnoses), entity linking (e.g., linking entities to standardized ontologies), TNM staging, document classification (e.g., cancer subtype classification from pathology reports), and treatment response prediction. Our framework emphasizes adaptability and resource efficiency. We include minimal German instructions, collected at the University Hospital Zurich (USZ), to test whether small amounts of non-English language data can effectively transfer knowledge across languages. This approach mirrors our motivation for lightweight models, which balance strong performance with reduced computational costs, making them suitable for resource-limited healthcare settings. We validated our models on oncology datasets, demonstrating strong results in named entity recognition, relation extraction, and document classification.
AI-powered virtual tissues from spatial proteomics for clinical diagnostics and biomedical discovery
Jan 10, 2025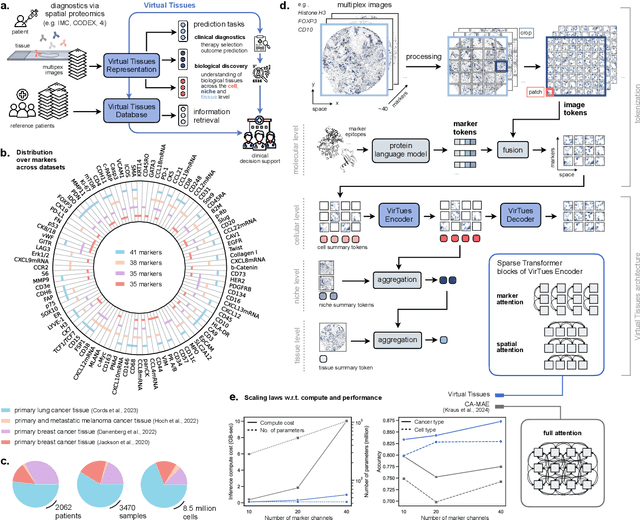
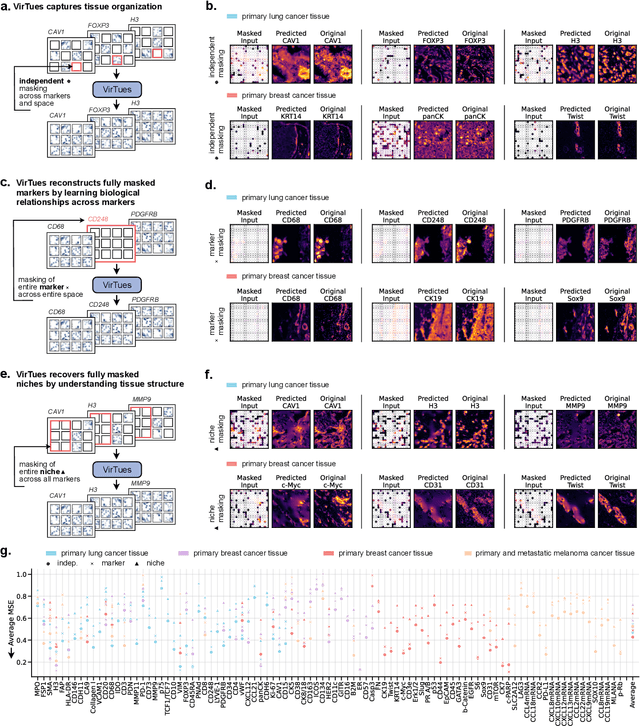
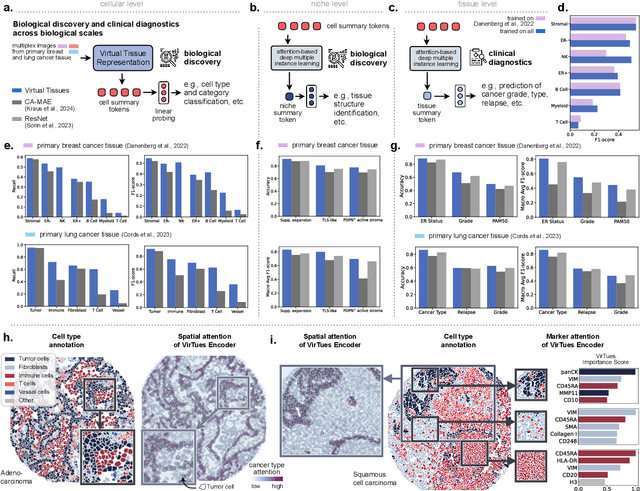
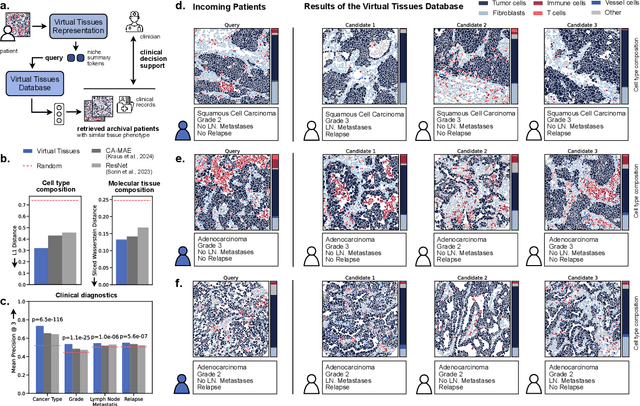
Abstract:Spatial proteomics technologies have transformed our understanding of complex tissue architectures by enabling simultaneous analysis of multiple molecular markers and their spatial organization. The high dimensionality of these data, varying marker combinations across experiments and heterogeneous study designs pose unique challenges for computational analysis. Here, we present Virtual Tissues (VirTues), a foundation model framework for biological tissues that operates across the molecular, cellular and tissue scale. VirTues introduces innovations in transformer architecture design, including a novel tokenization scheme that captures both spatial and marker dimensions, and attention mechanisms that scale to high-dimensional multiplex data while maintaining interpretability. Trained on diverse cancer and non-cancer tissue datasets, VirTues demonstrates strong generalization capabilities without task-specific fine-tuning, enabling cross-study analysis and novel marker integration. As a generalist model, VirTues outperforms existing approaches across clinical diagnostics, biological discovery and patient case retrieval tasks, while providing insights into tissue function and disease mechanisms.
Learning Personalized Treatment Decisions in Precision Medicine: Disentangling Treatment Assignment Bias in Counterfactual Outcome Prediction and Biomarker Identification
Oct 01, 2024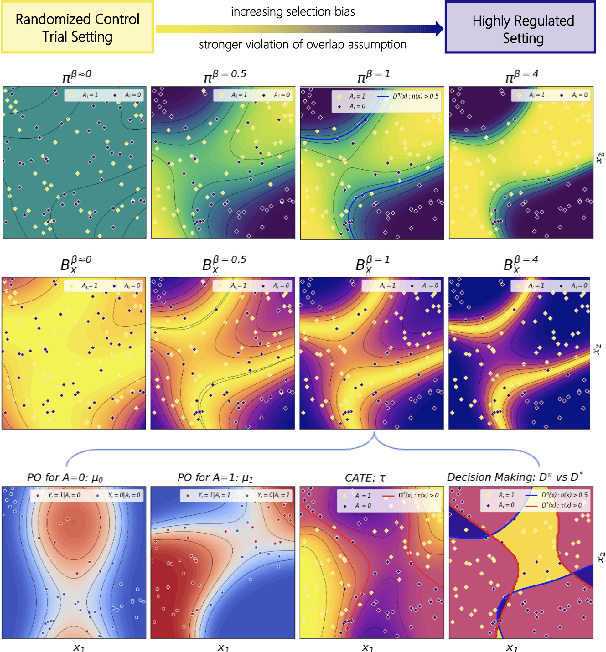
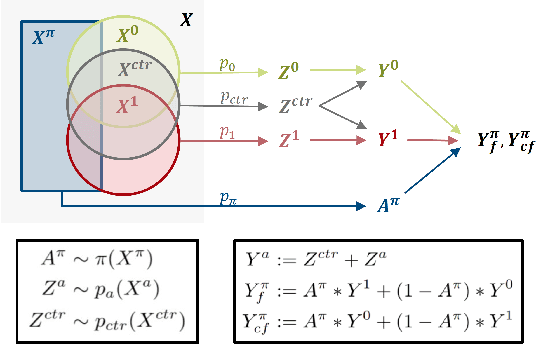
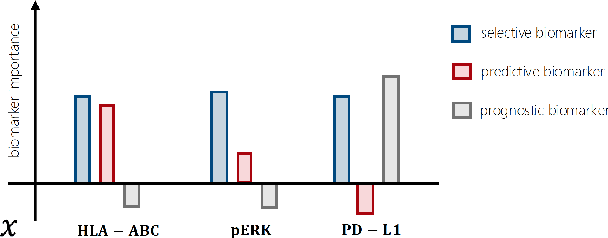
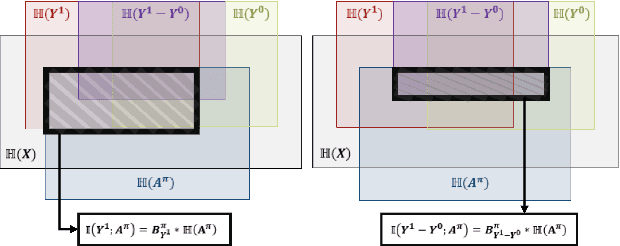
Abstract:Precision medicine offers the potential to tailor treatment decisions to individual patients, yet it faces significant challenges due to the complex biases in clinical observational data and the high-dimensional nature of biological data. This study models various types of treatment assignment biases using mutual information and investigates their impact on machine learning (ML) models for counterfactual prediction and biomarker identification. Unlike traditional counterfactual benchmarks that rely on fixed treatment policies, our work focuses on modeling different characteristics of the underlying observational treatment policy in distinct clinical settings. We validate our approach through experiments on toy datasets, semi-synthetic tumor cancer genome atlas (TCGA) data, and real-world biological outcomes from drug and CRISPR screens. By incorporating empirical biological mechanisms, we create a more realistic benchmark that reflects the complexities of real-world data. Our analysis reveals that different biases lead to varying model performances, with some biases, especially those unrelated to outcome mechanisms, having minimal effect on prediction accuracy. This highlights the crucial need to account for specific biases in clinical observational data in counterfactual ML model development, ultimately enhancing the personalization of treatment decisions in precision medicine.
Towards AI-Based Precision Oncology: A Machine Learning Framework for Personalized Counterfactual Treatment Suggestions based on Multi-Omics Data
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:AI-driven precision oncology has the transformative potential to reshape cancer treatment by leveraging the power of AI models to analyze the interaction between complex patient characteristics and their corresponding treatment outcomes. New technological platforms have facilitated the timely acquisition of multimodal data on tumor biology at an unprecedented resolution, such as single-cell multi-omics data, making this quality and quantity of data available for data-driven improved clinical decision-making. In this work, we propose a modular machine learning framework designed for personalized counterfactual cancer treatment suggestions based on an ensemble of machine learning experts trained on diverse multi-omics technologies. These specialized counterfactual experts per technology are consistently aggregated into a more powerful expert with superior performance and can provide both confidence and an explanation of its decision. The framework is tailored to address critical challenges inherent in data-driven cancer research, including the high-dimensional nature of the data, and the presence of treatment assignment bias in the retrospective observational data. The framework is showcased through comprehensive demonstrations using data from in-vitro and in-vivo treatment responses from a cohort of patients with ovarian cancer. Our method aims to empower clinicians with a reality-centric decision-support tool including probabilistic treatment suggestions with calibrated confidence and personalized explanations for tailoring treatment strategies to multi-omics characteristics of individual cancer patients.
Unsupervised Extraction of Phenotypes from Cancer Clinical Notes for Association Studies
May 03, 2019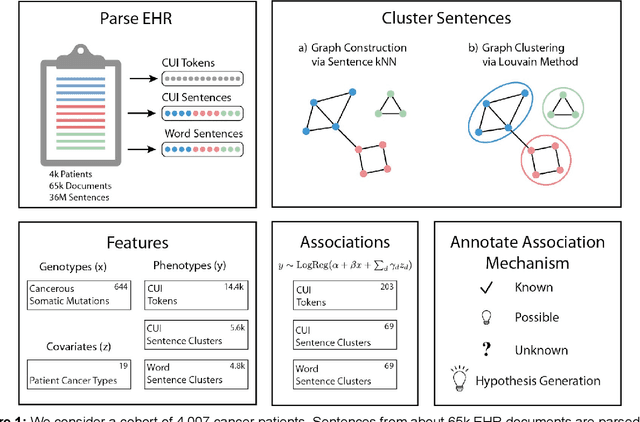


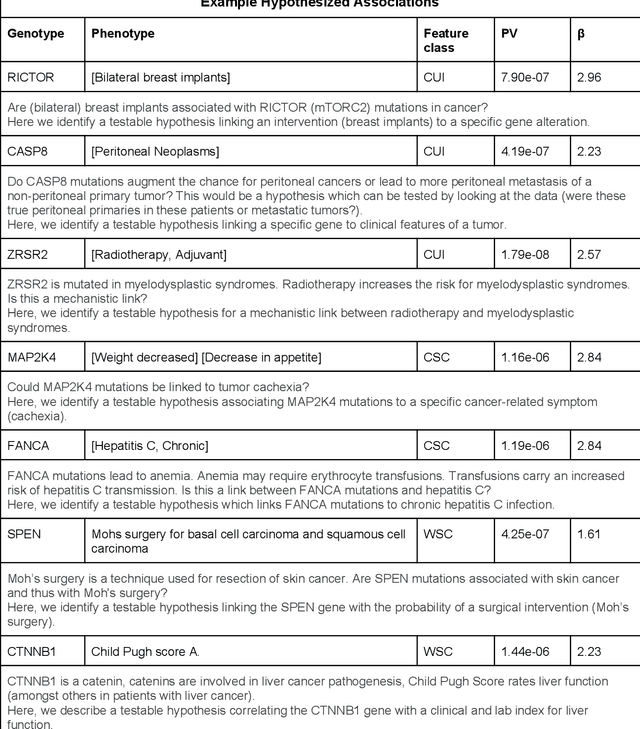
Abstract:The recent adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) by health care providers has introduced an important source of data that provides detailed and highly specific insights into patient phenotypes over large cohorts. These datasets, in combination with machine learning and statistical approaches, generate new opportunities for research and clinical care. However, many methods require the patient representations to be in structured formats, while the information in the EHR is often locked in unstructured texts designed for human readability. In this work, we develop the methodology to automatically extract clinical features from clinical narratives from large EHR corpora without the need for prior knowledge. We consider medical terms and sentences appearing in clinical narratives as atomic information units. We propose an efficient clustering strategy suitable for the analysis of large text corpora and to utilize the clusters to represent information about the patient compactly. To demonstrate the utility of our approach, we perform an association study of clinical features with somatic mutation profiles from 4,007 cancer patients and their tumors. We apply the proposed algorithm to a dataset consisting of about 65 thousand documents with a total of about 3.2 million sentences. We identify 341 significant statistical associations between the presence of somatic mutations and clinical features. We annotated these associations according to their novelty, and report several known associations. We also propose 32 testable hypotheses where the underlying biological mechanism does not appear to be known but plausible. These results illustrate that the automated discovery of clinical features is possible and the joint analysis of clinical and genetic datasets can generate appealing new hypotheses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge