André Bourdoux
Approximation of the Range Ambiguity Function in Near-field Sensing Systems
Sep 26, 2025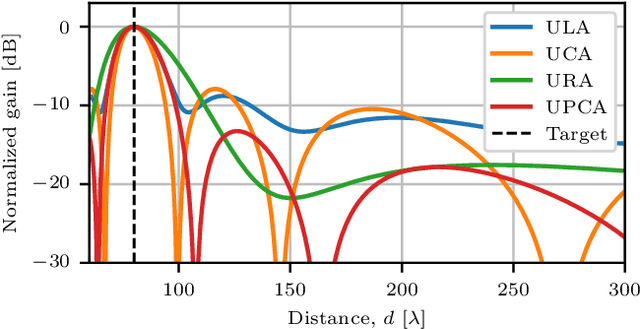
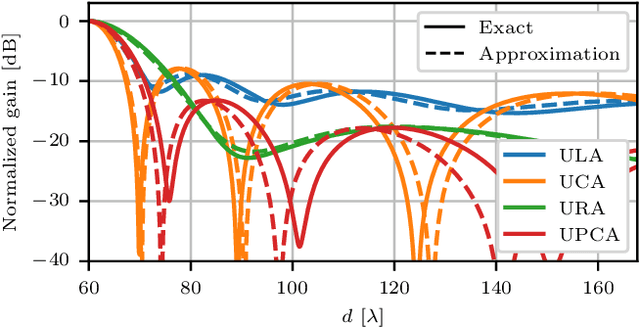
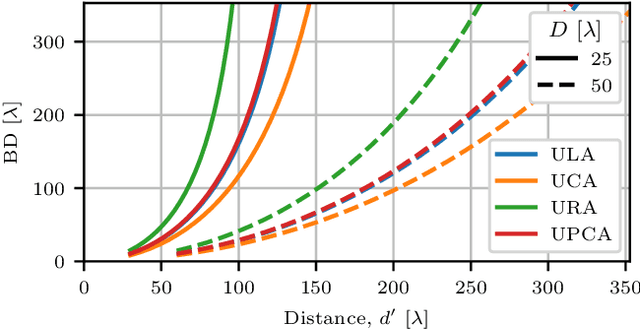
Abstract:This paper investigates the range ambiguity function of near-field systems where bandwidth and near-field beamfocusing jointly determine the resolution. First, the general matched filter ambiguity function is derived and the near-field array factors of different antenna array geometries are introduced. Next, the near-field ambiguity function is approximated as a product of the range-dependent near-field array factor and the ambiguity function due to the utilized bandwidth and waveform. An approximation criterion based on the aperture-bandwidth product is formulated, and its accuracy is examined. Finally, the improvements to the ambiguity function offered by the near-field beamfocusing, as compared to the far-field case, are presented. The performance gains are evaluated in terms of resolution improvement offered by beamfocusing, peak-to-sidelobe and integrated-sidelobe level improvement. The gains offered by the near-field regime are shown to be range-dependent and substantial only in close proximity to the array.
Range Resolution of Near-field MIMO Sensing
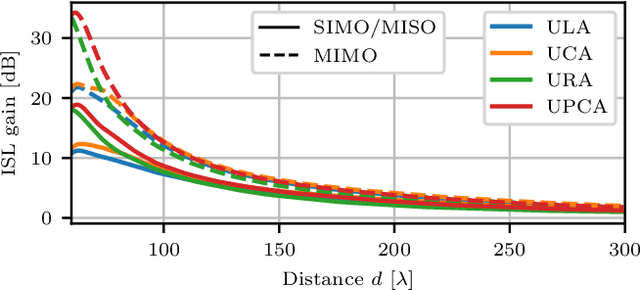
May 15, 2025Abstract:The radiative near-field and integration of sensing capabilities are seen as two key components of the next generation of wireless communication systems. In this paper, the sensing performance of a narrowband near-field system is investigated for several practical antenna array geometries and configurations, namely SIMO/MISO and MIMO. In the SIMO/MISO configuration, the antenna aperture is exploited only a single time for either transmit or receive signal processing, while the MIMO configuration exploits both TX and RX processing. Analytical derivations, supported by simulations, show that the MIMO processing improves the maximum near-field range and sensing resolution by approximately a factor of 1.4 as compared to single-aperture systems. The value of the improvement factor is consistent for all considered array geometries. Finally, using a quadratic approximation of the array factor, an analytical improvement factor of $\sqrt{2}$ is derived, clarifying the observed improvements and validating the numerical results.
Frequency Diverse Array OFDM Transmit System with Partial Overlap in Frequency
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Frequency-diverse array (FDA) is an alternative array architecture in which each antenna is preceded by a mixer instead of a phase shifter. The mixers introduce a frequency offset between signals transmitted by each antenna resulting in a time-varying beam pattern. However, time-dependent beamforming is not desirable for communication or sensing. In this paper, the FDA is combined with orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation. The proposed beamforming method splits the OFDM symbol transmitted by all antennas into subcarrier blocks, which are precoded differently. The selected frequency offset between the antennas results in overlap and coherent summation of the differently precoded subcarrier blocks. This allows to achieve fully digital beamforming over a single block with the use of a single digital-to-analog converter. The system's joint communication and sensing performance is evaluated and sensitivity to errors is studied.
Aliased Time-Modulated Array OFDM System
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:The time-modulated array is a simple array architecture in which each antenna is connected to an RF switch that serves as a modulator. The phase shift is achieved by digitally controlling the relative delay between the periodic modulating sequences of the antennas. The practical use of this architecture is limited by two factors. First, the switching frequency is high, as it must be a multiple of the sampling frequency. Second, the discrete modulating sequence introduces undesired harmonic replicas of the signal with non-negligible power. In this paper, aliasing is exploited to simultaneously reduce sideband radiation and switching frequency. To facilitate coherent combining of aliased signal blocks, the transmit signal has a repeated block structure in the frequency domain. As a result, a factor $A$ reduction in switching frequency is achieved at the cost of a factor $A$ reduction in communication capacity. Doubling $A$ reduces sideband radiation by around 2.9 dB.
Beamforming with Oversampled Time-Modulated Arrays
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:The time-modulated array (TMA) is a simple array architecture in which each antenna is connected via a multi-throw switch. The switch acts as a modulator switching state faster than the symbol rate. The phase shifting and beamforming is achieved by a cyclic shift of the periodical modulating signal across antennas. In this paper, the TMA mode of operation is proposed to improve the resolution of a conventional phase shifter. The TMAs are analyzed under constrained switching frequency being a small multiple of the symbol rate. The presented generic signal model gives insight into the magnitude, phase and spacing of the harmonic components generated by the quantized modulating sequence. It is shown that the effective phase-shifting resolution can be improved multiplicatively by the oversampling factor ($O$) at the cost of introducing harmonics. Finally, the array tapering with an oversampled modulating signal is proposed. The oversampling provides $O+1$ uniformly distributed tapering amplitudes.
Frequency Diverse Array OFDM System for Joint Communication and Sensing
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:The frequency-diverse array (FDA) offers a time-varying beamforming capability without the use of phase shifters. The autoscanning property is achieved by applying a frequency offset between the antennas. This paper analyzes the performance of an FDA joint communication and sensing system with the orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation. The performance of the system is evaluated against the scanning frequency, number of antennas and number of subcarriers. The utilized metrics; integrated sidelobe level (ISL) and error vector magnitude (EVM) allow for straightforward comparison with a standard single-input single-output (SISO) OFDM system.
Distributed PMCW Radar Network in Presence of Phase Noise
May 15, 2024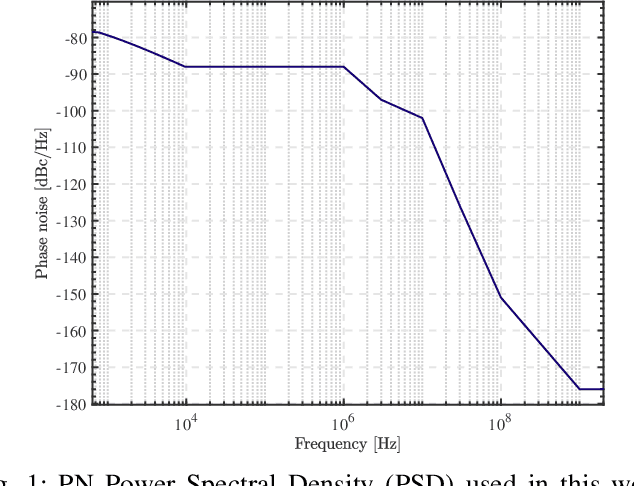
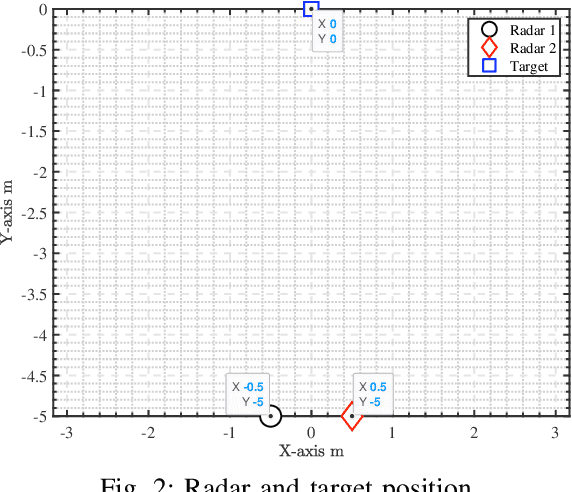
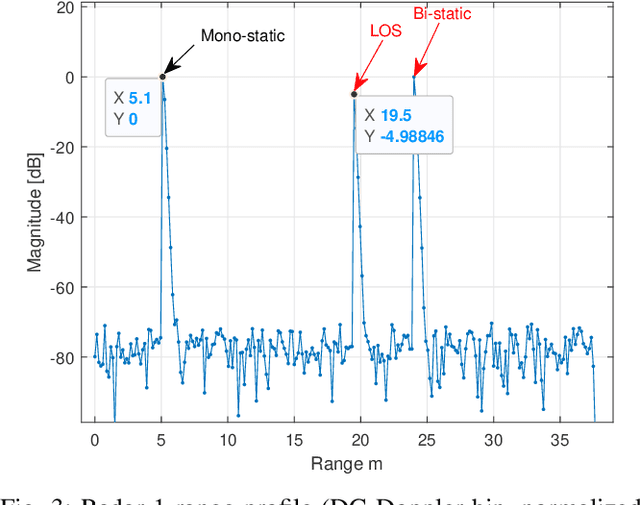
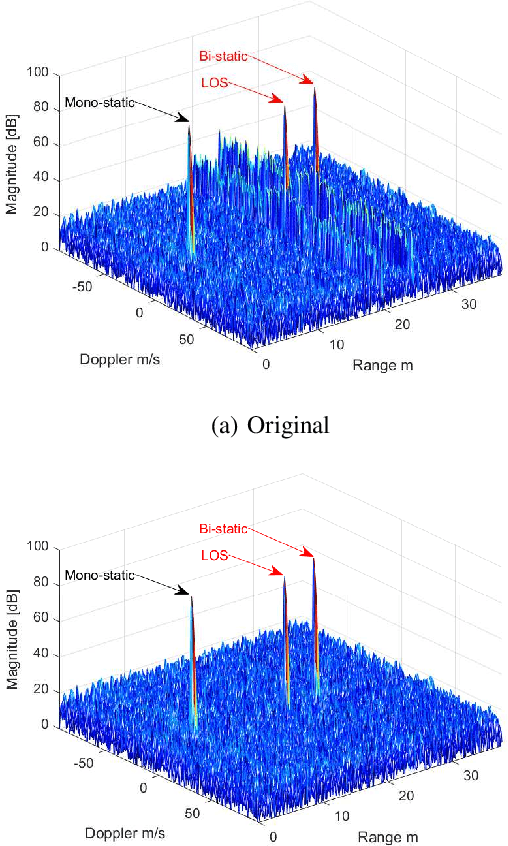
Abstract:In Frequency Modulated Continuous Waveform (FMCW) radar systems, the phase noise from the Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) can increase the noise floor in the Range-Doppler map. The adverse effects of phase noise on close targets can be mitigated if the transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx) employ the same chirp, a phenomenon known as the range correlation effect. In the context of a multi-static radar network, sharing the chirp between distant radars becomes challenging. Each radar generates its own chirp, leading to uncorrelated phase noise. Consequently, the system performance cannot benefit from the range correlation effect. Previous studies show that selecting a suitable code sequence for a Phase Modulated Continuous Waveform (PMCW) radar can reduce the impact of uncorrelated phase noise in the range dimension. In this paper, we demonstrate how to leverage this property to exploit both the mono- and multi-static signals of each radar in the network without having to share any signal at the carrier frequency. The paper introduces a detailed signal model for PMCW radar networks, analyzing both correlated and uncorrelated phase noise effects in the Doppler dimension. Additionally, a solution for compensating uncorrelated phase noise in Doppler is presented and supported by numerical results.
Active Inference in Hebbian Learning Networks
Jun 22, 2023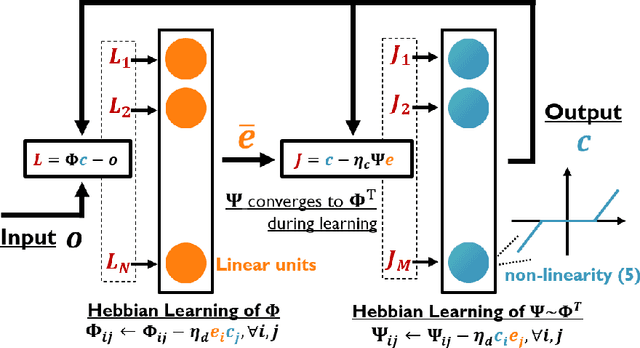
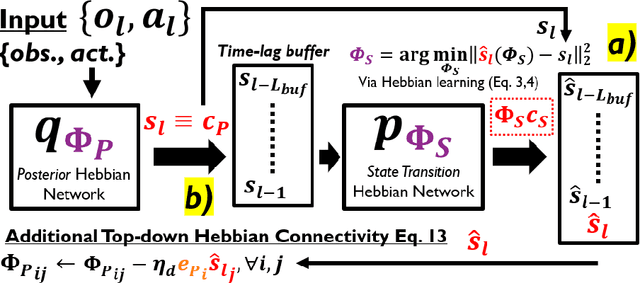
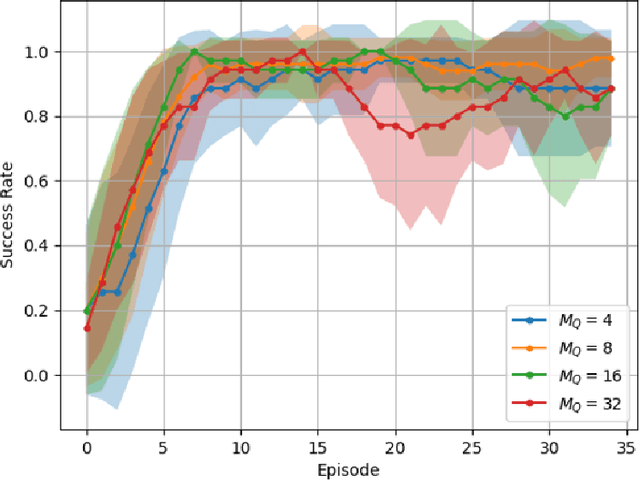
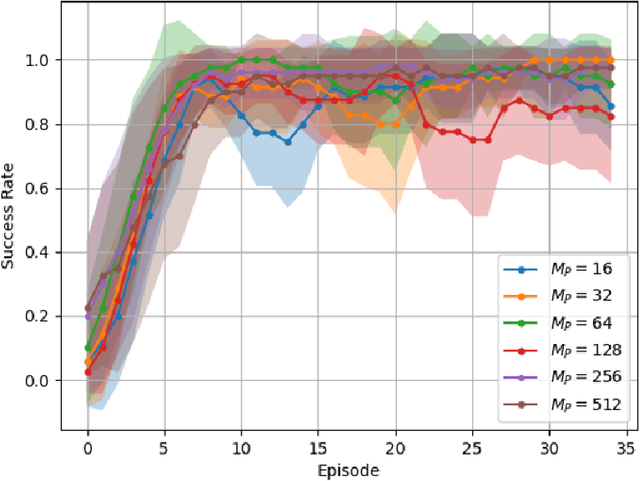
Abstract:This work studies how brain-inspired neural ensembles equipped with local Hebbian plasticity can perform active inference (AIF) in order to control dynamical agents. A generative model capturing the environment dynamics is learned by a network composed of two distinct Hebbian ensembles: a posterior network, which infers latent states given the observations, and a state transition network, which predicts the next expected latent state given current state-action pairs. Experimental studies are conducted using the Mountain Car environment from the OpenAI gym suite, to study the effect of the various Hebbian network parameters on the task performance. It is shown that the proposed Hebbian AIF approach outperforms the use of Q-learning, while not requiring any replay buffer, as in typical reinforcement learning systems. These results motivate further investigations of Hebbian learning for the design of AIF networks that can learn environment dynamics without the need for revisiting past buffered experiences.
FMCW Radar Sensing for Indoor Drones Using Learned Representations
Jan 06, 2023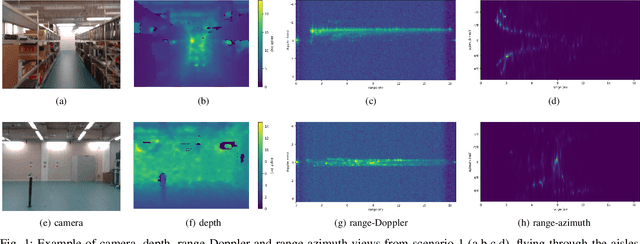
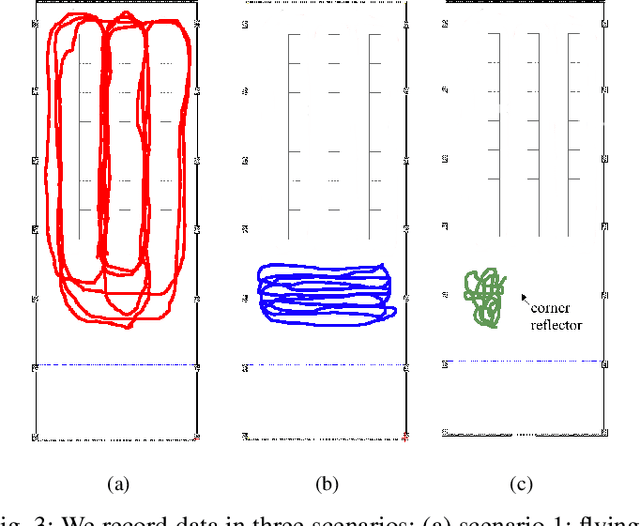
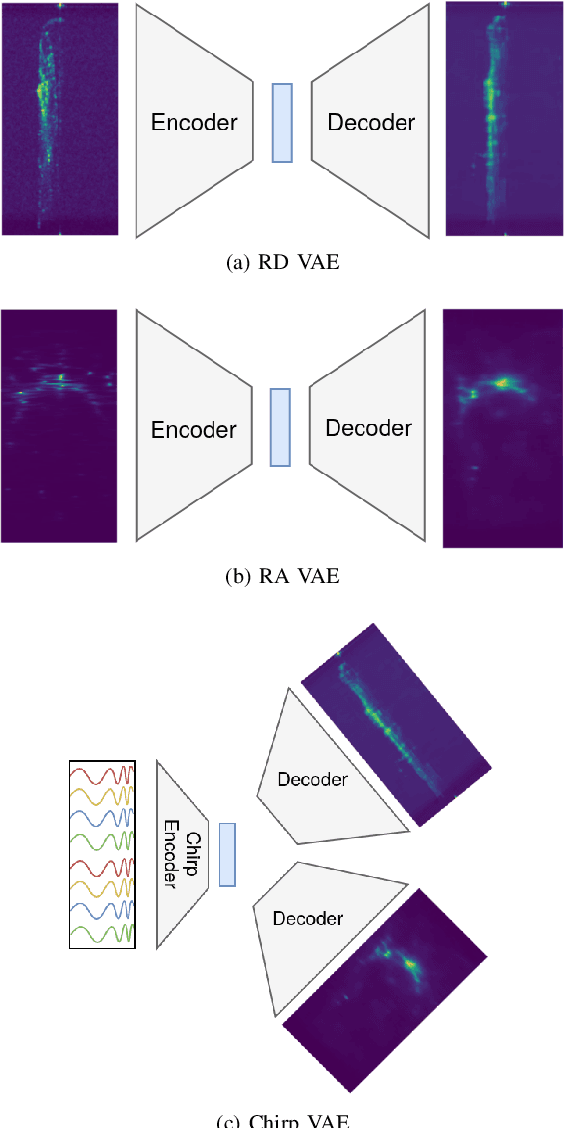
Abstract:Frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) radar is a promising sensor technology for indoor drones as it provides range, angular as well as Doppler-velocity information about obstacles in the environment. Recently, deep learning approaches have been proposed for processing FMCW data, outperforming traditional detection techniques on range-Doppler or range-azimuth maps. However, these techniques come at a cost; for each novel task a deep neural network architecture has to be trained on high-dimensional input data, stressing both data bandwidth and processing budget. In this paper, we investigate unsupervised learning techniques that generate low-dimensional representations from FMCW radar data, and evaluate to what extent these representations can be reused for multiple downstream tasks. To this end, we introduce a novel dataset of raw radar ADC data recorded from a radar mounted on a flying drone platform in an indoor environment, together with ground truth detection targets. We show with real radar data that, utilizing our learned representations, we match the performance of conventional radar processing techniques and that our model can be trained on different input modalities such as raw ADC samples of only two consecutively transmitted chirps.
Fusing Event-based Camera and Radar for SLAM Using Spiking Neural Networks with Continual STDP Learning
Oct 09, 2022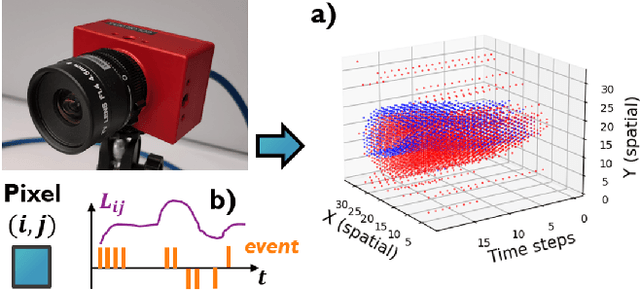
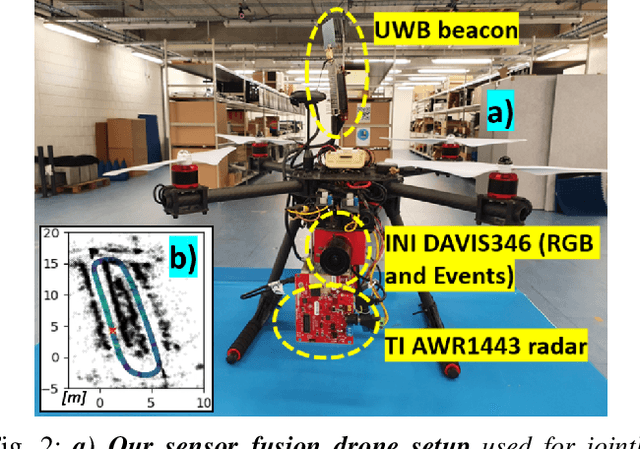
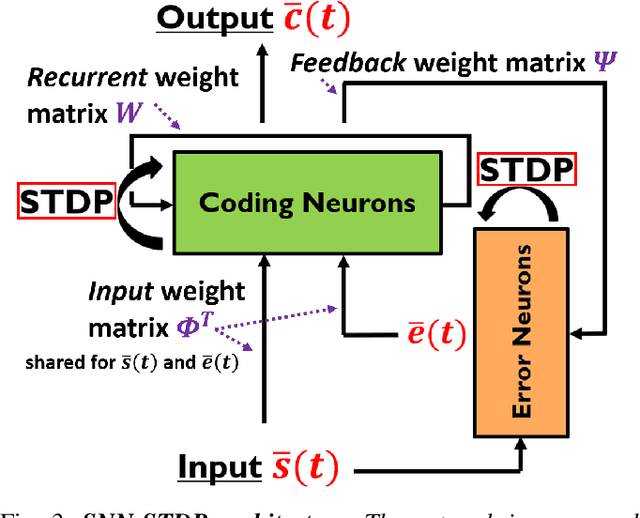
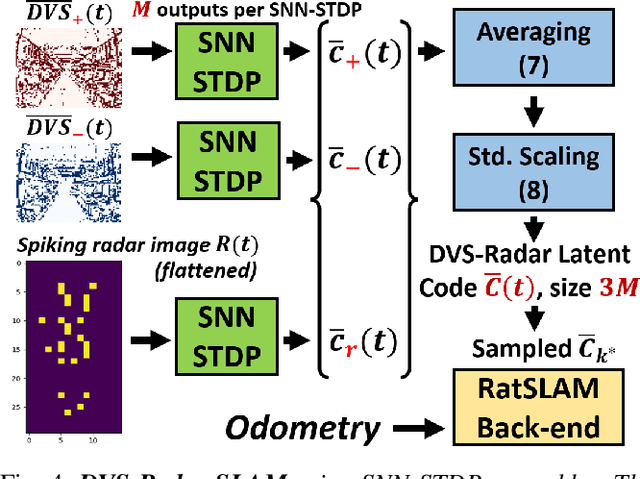
Abstract:This work proposes a first-of-its-kind SLAM architecture fusing an event-based camera and a Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) radar for drone navigation. Each sensor is processed by a bio-inspired Spiking Neural Network (SNN) with continual Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity (STDP) learning, as observed in the brain. In contrast to most learning-based SLAM systems%, which a) require the acquisition of a representative dataset of the environment in which navigation must be performed and b) require an off-line training phase, our method does not require any offline training phase, but rather the SNN continuously learns features from the input data on the fly via STDP. At the same time, the SNN outputs are used as feature descriptors for loop closure detection and map correction. We conduct numerous experiments to benchmark our system against state-of-the-art RGB methods and we demonstrate the robustness of our DVS-Radar SLAM approach under strong lighting variations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge