Jialun Kou
Dualband OFDM Delay Estimation for Multi-Target Localization
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Integrated localization and communication systems aim to reuse communication waveforms for simultaneous data transmission and localization, but delay resolution is fundamentally limited by the available bandwidth. In practice, large contiguous bandwidths are difficult to obtain due to hardware constraints and spectrum fragmentation. Aggregating non-contiguous narrow bands can increase the effective frequency span, but a non-contiguous frequency layout introduces challenges such as elevated sidelobes and ambiguity in delay estimation. This paper introduces a point-spread-function (PSF)-centric framework for dual-band OFDM delay estimation. We model the observed delay profile as the convolution of the true target response with a PSF determined by the dual-band subcarrier selection pattern, explicitly linking band configuration to resolution and ambiguity. To suppress PSF-induced artifacts, we adapt the RELAX algorithm for dual-band multi-target delay estimation. Simulations demonstrate improved robustness and accuracy in dual-band scenarios, supporting ILC under fragmented spectrum.
Distributed PMCW Radar Network in Presence of Phase Noise
May 15, 2024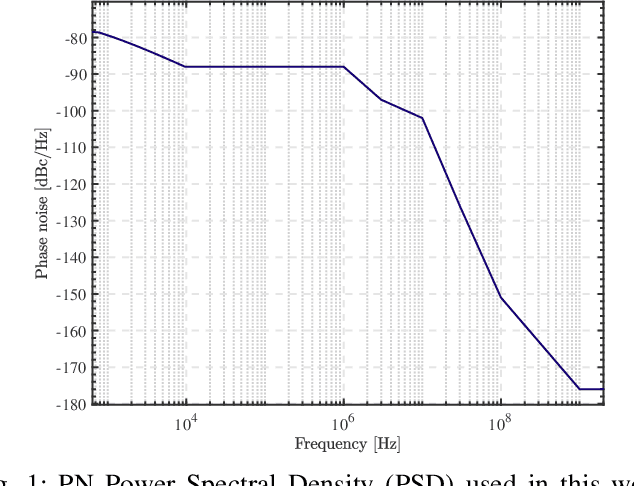
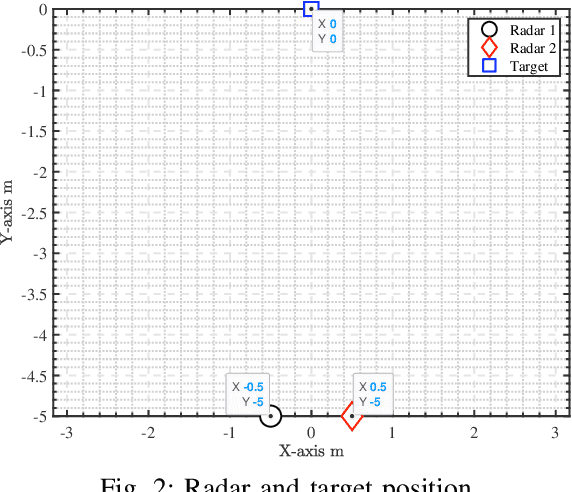
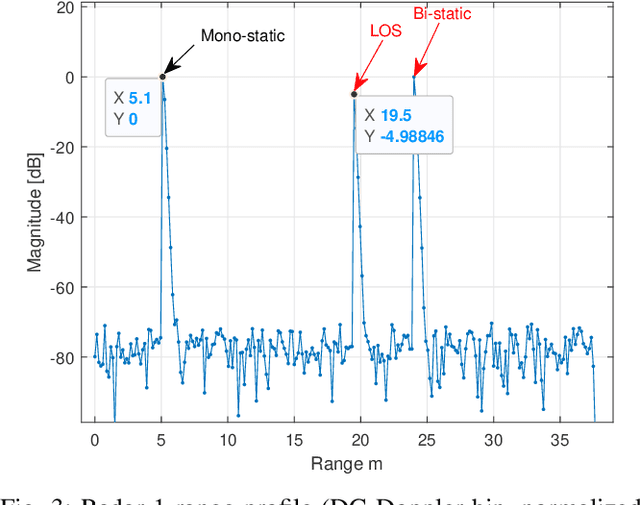
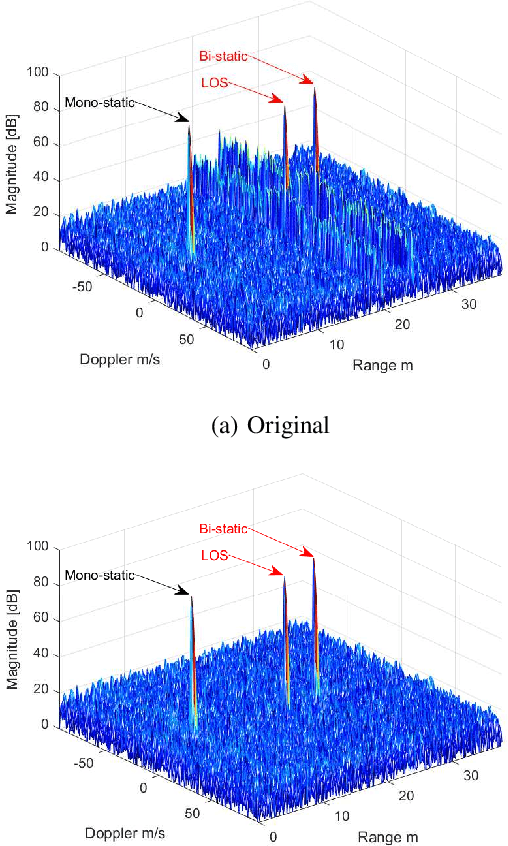
Abstract:In Frequency Modulated Continuous Waveform (FMCW) radar systems, the phase noise from the Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) can increase the noise floor in the Range-Doppler map. The adverse effects of phase noise on close targets can be mitigated if the transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx) employ the same chirp, a phenomenon known as the range correlation effect. In the context of a multi-static radar network, sharing the chirp between distant radars becomes challenging. Each radar generates its own chirp, leading to uncorrelated phase noise. Consequently, the system performance cannot benefit from the range correlation effect. Previous studies show that selecting a suitable code sequence for a Phase Modulated Continuous Waveform (PMCW) radar can reduce the impact of uncorrelated phase noise in the range dimension. In this paper, we demonstrate how to leverage this property to exploit both the mono- and multi-static signals of each radar in the network without having to share any signal at the carrier frequency. The paper introduces a detailed signal model for PMCW radar networks, analyzing both correlated and uncorrelated phase noise effects in the Doppler dimension. Additionally, a solution for compensating uncorrelated phase noise in Doppler is presented and supported by numerical results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge