Aliasghar Khani
FunPhase: A Periodic Functional Autoencoder for Motion Generation via Phase Manifolds
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Learning natural body motion remains challenging due to the strong coupling between spatial geometry and temporal dynamics. Embedding motion in phase manifolds, latent spaces that capture local periodicity, has proven effective for motion prediction; however, existing approaches lack scalability and remain confined to specific settings. We introduce FunPhase, a functional periodic autoencoder that learns a phase manifold for motion and replaces discrete temporal decoding with a function-space formulation, enabling smooth trajectories that can be sampled at arbitrary temporal resolutions. FunPhase supports downstream tasks such as super-resolution and partial-body motion completion, generalizes across skeletons and datasets, and unifies motion prediction and generation within a single interpretable manifold. Our model achieves substantially lower reconstruction error than prior periodic autoencoder baselines while enabling a broader range of applications and performing on par with state-of-the-art motion generation methods.
UniMoGen: Universal Motion Generation
May 28, 2025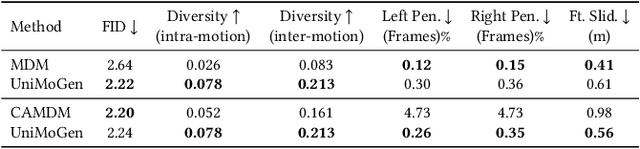
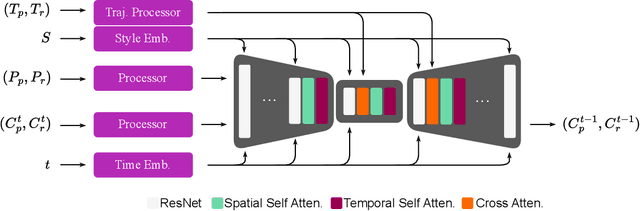
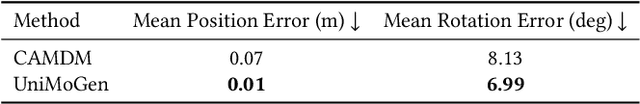
Abstract:Motion generation is a cornerstone of computer graphics, animation, gaming, and robotics, enabling the creation of realistic and varied character movements. A significant limitation of existing methods is their reliance on specific skeletal structures, which restricts their versatility across different characters. To overcome this, we introduce UniMoGen, a novel UNet-based diffusion model designed for skeleton-agnostic motion generation. UniMoGen can be trained on motion data from diverse characters, such as humans and animals, without the need for a predefined maximum number of joints. By dynamically processing only the necessary joints for each character, our model achieves both skeleton agnosticism and computational efficiency. Key features of UniMoGen include controllability via style and trajectory inputs, and the ability to continue motions from past frames. We demonstrate UniMoGen's effectiveness on the 100style dataset, where it outperforms state-of-the-art methods in diverse character motion generation. Furthermore, when trained on both the 100style and LAFAN1 datasets, which use different skeletons, UniMoGen achieves high performance and improved efficiency across both skeletons. These results highlight UniMoGen's potential to advance motion generation by providing a flexible, efficient, and controllable solution for a wide range of character animations.
Wavelet Latent Diffusion (Wala): Billion-Parameter 3D Generative Model with Compact Wavelet Encodings
Nov 12, 2024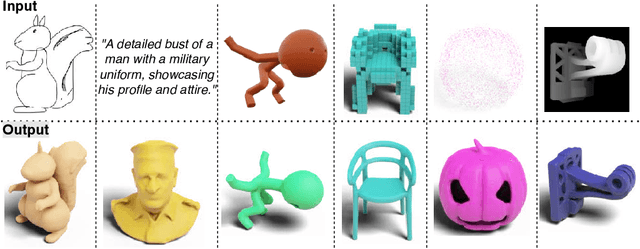

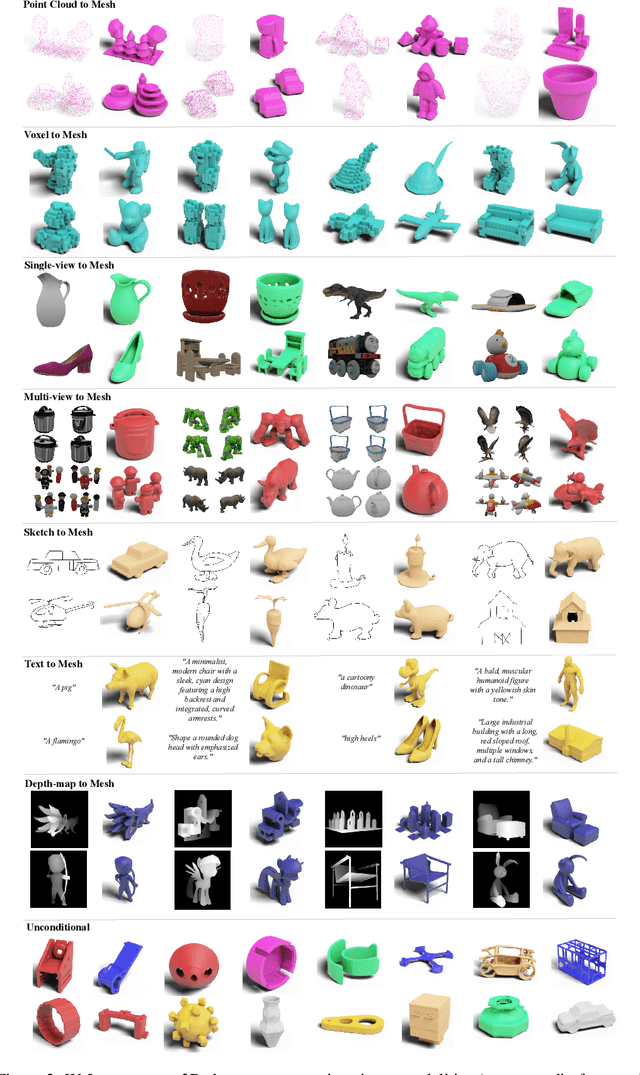
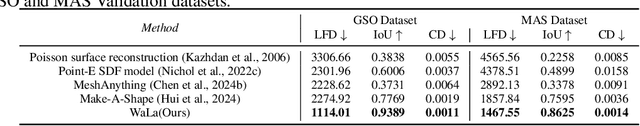
Abstract:Large-scale 3D generative models require substantial computational resources yet often fall short in capturing fine details and complex geometries at high resolutions. We attribute this limitation to the inefficiency of current representations, which lack the compactness required to model the generative models effectively. To address this, we introduce a novel approach called Wavelet Latent Diffusion, or WaLa, that encodes 3D shapes into wavelet-based, compact latent encodings. Specifically, we compress a $256^3$ signed distance field into a $12^3 \times 4$ latent grid, achieving an impressive 2427x compression ratio with minimal loss of detail. This high level of compression allows our method to efficiently train large-scale generative networks without increasing the inference time. Our models, both conditional and unconditional, contain approximately one billion parameters and successfully generate high-quality 3D shapes at $256^3$ resolution. Moreover, WaLa offers rapid inference, producing shapes within two to four seconds depending on the condition, despite the model's scale. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across multiple datasets, with significant improvements in generation quality, diversity, and computational efficiency. We open-source our code and, to the best of our knowledge, release the largest pretrained 3D generative models across different modalities.
SLiMe: Segment Like Me
Sep 06, 2023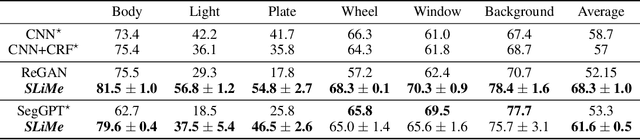

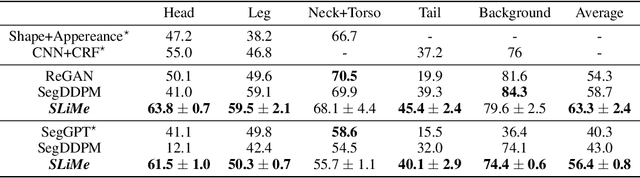

Abstract:Significant strides have been made using large vision-language models, like Stable Diffusion (SD), for a variety of downstream tasks, including image editing, image correspondence, and 3D shape generation. Inspired by these advancements, we explore leveraging these extensive vision-language models for segmenting images at any desired granularity using as few as one annotated sample by proposing SLiMe. SLiMe frames this problem as an optimization task. Specifically, given a single training image and its segmentation mask, we first extract attention maps, including our novel "weighted accumulated self-attention map" from the SD prior. Then, using the extracted attention maps, the text embeddings of Stable Diffusion are optimized such that, each of them, learn about a single segmented region from the training image. These learned embeddings then highlight the segmented region in the attention maps, which in turn can then be used to derive the segmentation map. This enables SLiMe to segment any real-world image during inference with the granularity of the segmented region in the training image, using just one example. Moreover, leveraging additional training data when available, i.e. few-shot, improves the performance of SLiMe. We carried out a knowledge-rich set of experiments examining various design factors and showed that SLiMe outperforms other existing one-shot and few-shot segmentation methods.
Learned Visual Features to Textual Explanations
Sep 01, 2023Abstract:Interpreting the learned features of vision models has posed a longstanding challenge in the field of machine learning. To address this issue, we propose a novel method that leverages the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to interpret the learned features of pre-trained image classifiers. Our method, called TExplain, tackles this task by training a neural network to establish a connection between the feature space of image classifiers and LLMs. Then, during inference, our approach generates a vast number of sentences to explain the features learned by the classifier for a given image. These sentences are then used to extract the most frequent words, providing a comprehensive understanding of the learned features and patterns within the classifier. Our method, for the first time, utilizes these frequent words corresponding to a visual representation to provide insights into the decision-making process of the independently trained classifier, enabling the detection of spurious correlations, biases, and a deeper comprehension of its behavior. To validate the effectiveness of our approach, we conduct experiments on diverse datasets, including ImageNet-9L and Waterbirds. The results demonstrate the potential of our method to enhance the interpretability and robustness of image classifiers.
MaskTune: Mitigating Spurious Correlations by Forcing to Explore
Oct 08, 2022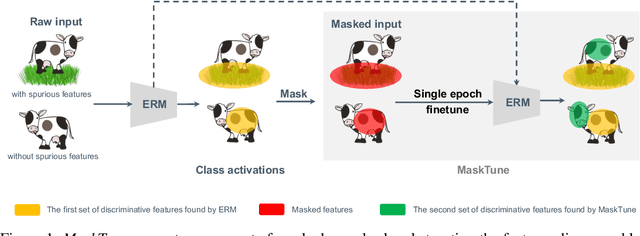
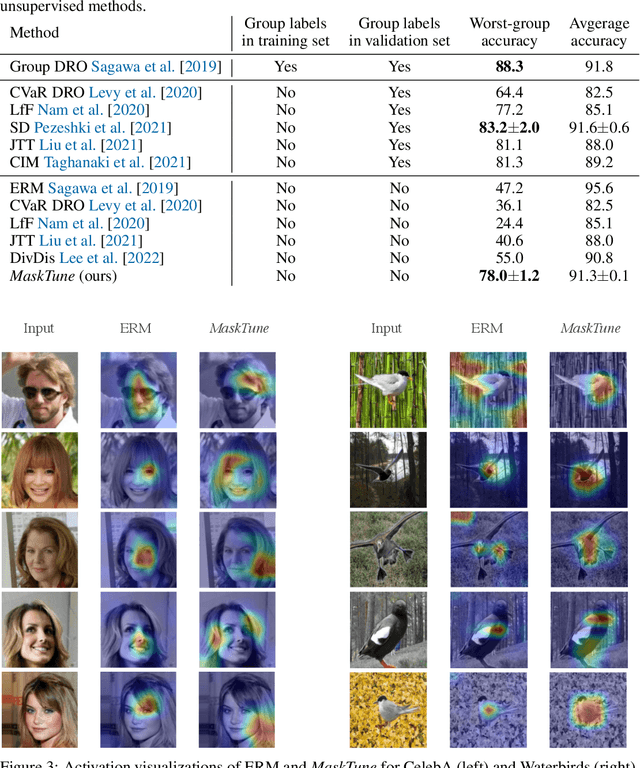
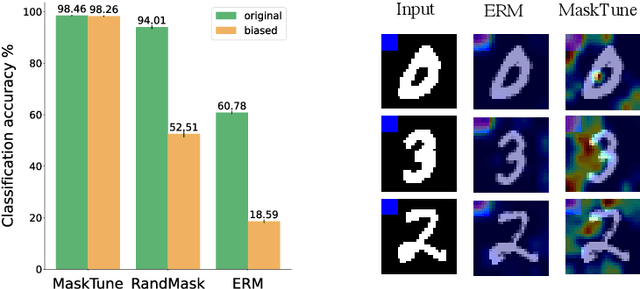
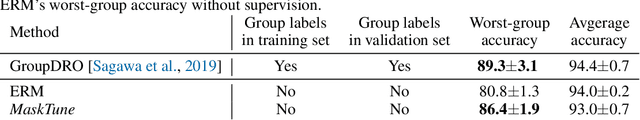
Abstract:A fundamental challenge of over-parameterized deep learning models is learning meaningful data representations that yield good performance on a downstream task without over-fitting spurious input features. This work proposes MaskTune, a masking strategy that prevents over-reliance on spurious (or a limited number of) features. MaskTune forces the trained model to explore new features during a single epoch finetuning by masking previously discovered features. MaskTune, unlike earlier approaches for mitigating shortcut learning, does not require any supervision, such as annotating spurious features or labels for subgroup samples in a dataset. Our empirical results on biased MNIST, CelebA, Waterbirds, and ImagenNet-9L datasets show that MaskTune is effective on tasks that often suffer from the existence of spurious correlations. Finally, we show that MaskTune outperforms or achieves similar performance to the competing methods when applied to the selective classification (classification with rejection option) task. Code for MaskTune is available at https://github.com/aliasgharkhani/Masktune.
Counterbalancing Teacher: Regularizing Batch Normalized Models for Robustness
Jul 04, 2022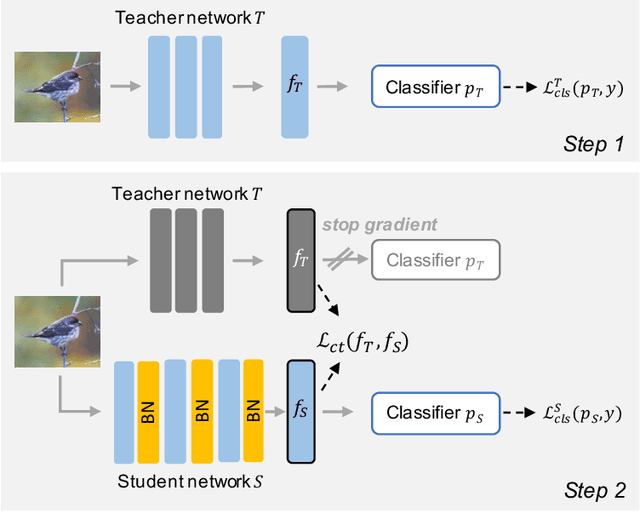
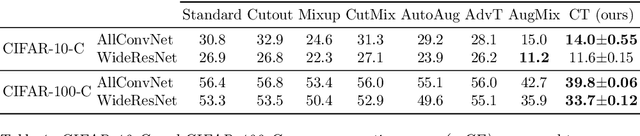
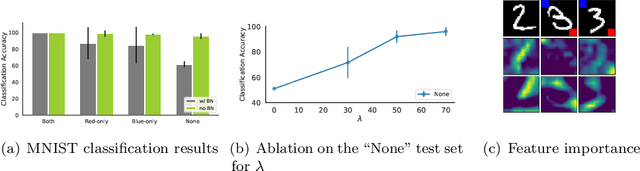
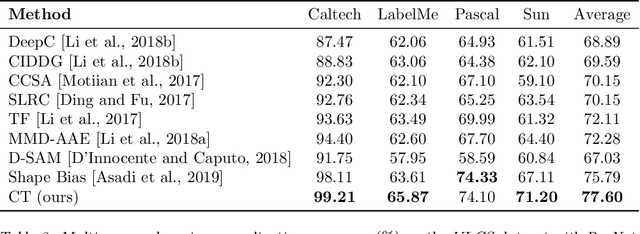
Abstract:Batch normalization (BN) is a ubiquitous technique for training deep neural networks that accelerates their convergence to reach higher accuracy. However, we demonstrate that BN comes with a fundamental drawback: it incentivizes the model to rely on low-variance features that are highly specific to the training (in-domain) data, hurting generalization performance on out-of-domain examples. In this work, we investigate this phenomenon by first showing that removing BN layers across a wide range of architectures leads to lower out-of-domain and corruption errors at the cost of higher in-domain errors. We then propose Counterbalancing Teacher (CT), a method which leverages a frozen copy of the same model without BN as a teacher to enforce the student network's learning of robust representations by substantially adapting its weights through a consistency loss function. This regularization signal helps CT perform well in unforeseen data shifts, even without information from the target domain as in prior works. We theoretically show in an overparameterized linear regression setting why normalization leads to a model's reliance on such in-domain features, and empirically demonstrate the efficacy of CT by outperforming several baselines on robustness benchmarks such as CIFAR-10-C, CIFAR-100-C, and VLCS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge