Alexander Trott
Modeling Bounded Rationality in Multi-Agent Simulations Using Rationally Inattentive Reinforcement Learning
Jan 18, 2022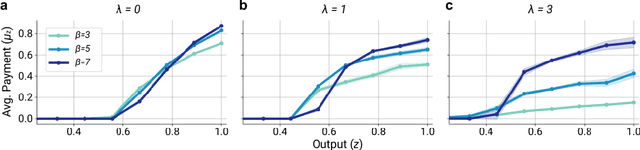
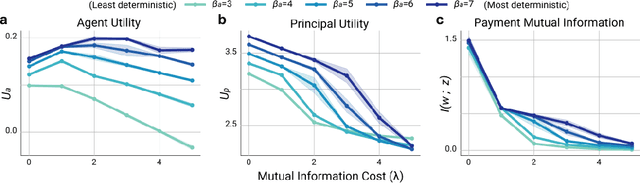
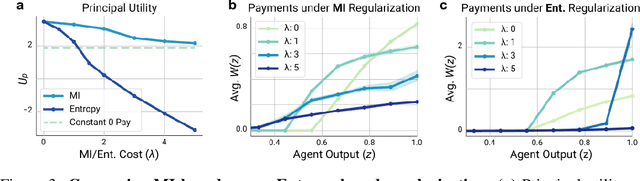
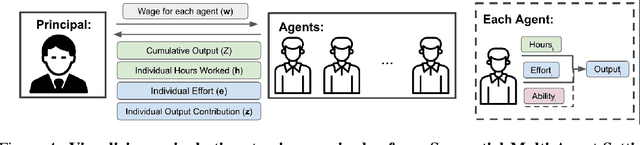
Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) is a powerful framework for studying emergent behavior in complex agent-based simulations. However, RL agents are often assumed to be rational and behave optimally, which does not fully reflect human behavior. Here, we study more human-like RL agents which incorporate an established model of human-irrationality, the Rational Inattention (RI) model. RI models the cost of cognitive information processing using mutual information. Our RIRL framework generalizes and is more flexible than prior work by allowing for multi-timestep dynamics and information channels with heterogeneous processing costs. We evaluate RIRL in Principal-Agent (specifically manager-employee relations) problem settings of varying complexity where RI models information asymmetry (e.g. it may be costly for the manager to observe certain information about the employees). We show that using RIRL yields a rich spectrum of new equilibrium behaviors that differ from those found under rational assumptions. For instance, some forms of a Principal's inattention can increase Agent welfare due to increased compensation, while other forms of inattention can decrease Agent welfare by encouraging extra work effort. Additionally, new strategies emerge compared to those under rationality assumptions, e.g., Agents are incentivized to increase work effort. These results suggest RIRL is a powerful tool towards building AI agents that can mimic real human behavior.
Finding General Equilibria in Many-Agent Economic Simulations Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jan 03, 2022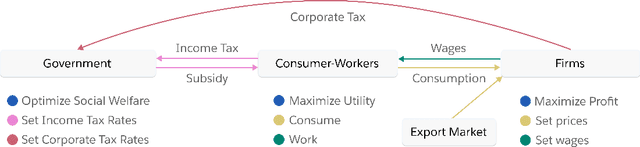

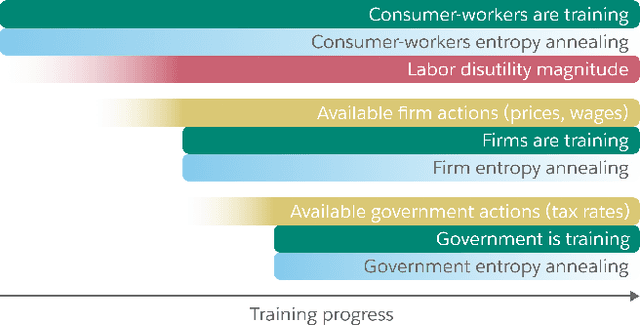
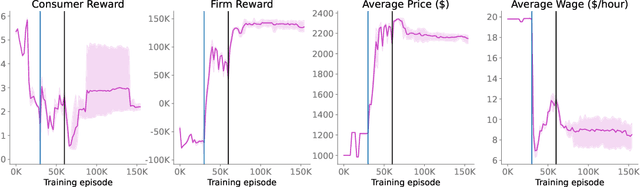
Abstract:Real economies can be seen as a sequential imperfect-information game with many heterogeneous, interacting strategic agents of various agent types, such as consumers, firms, and governments. Dynamic general equilibrium models are common economic tools to model the economic activity, interactions, and outcomes in such systems. However, existing analytical and computational methods struggle to find explicit equilibria when all agents are strategic and interact, while joint learning is unstable and challenging. Amongst others, a key reason is that the actions of one economic agent may change the reward function of another agent, e.g., a consumer's expendable income changes when firms change prices or governments change taxes. We show that multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (RL) can discover stable solutions that are epsilon-Nash equilibria for a meta-game over agent types, in economic simulations with many agents, through the use of structured learning curricula and efficient GPU-only simulation and training. Conceptually, our approach is more flexible and does not need unrealistic assumptions, e.g., market clearing, that are commonly used for analytical tractability. Our GPU implementation enables training and analyzing economies with a large number of agents within reasonable time frames, e.g., training completes within a day. We demonstrate our approach in real-business-cycle models, a representative family of DGE models, with 100 worker-consumers, 10 firms, and a government who taxes and redistributes. We validate the learned meta-game epsilon-Nash equilibria through approximate best-response analyses, show that RL policies align with economic intuitions, and that our approach is constructive, e.g., by explicitly learning a spectrum of meta-game epsilon-Nash equilibria in open RBC models.
Building a Foundation for Data-Driven, Interpretable, and Robust Policy Design using the AI Economist
Aug 06, 2021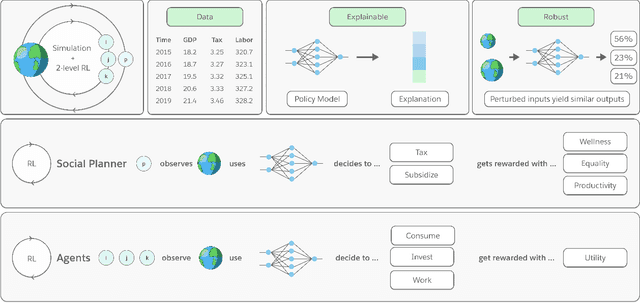
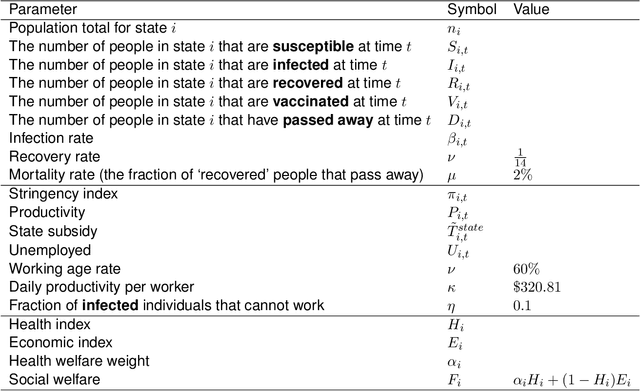
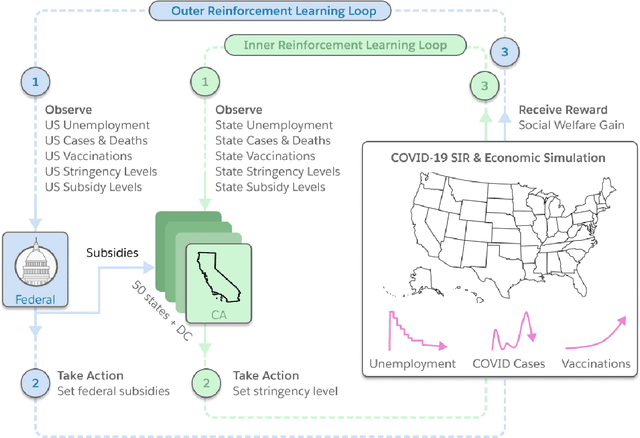
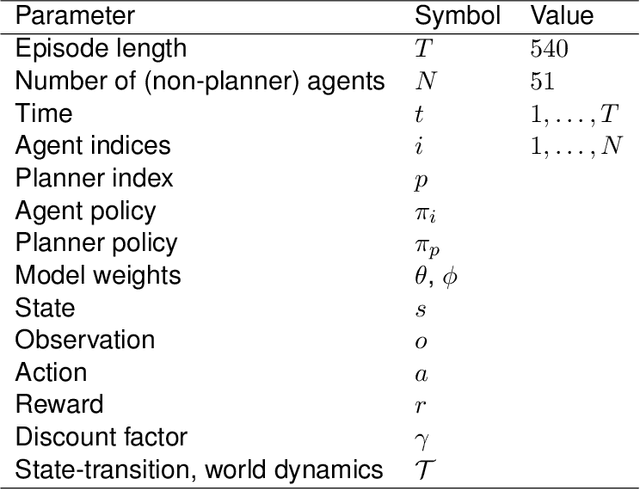
Abstract:Optimizing economic and public policy is critical to address socioeconomic issues and trade-offs, e.g., improving equality, productivity, or wellness, and poses a complex mechanism design problem. A policy designer needs to consider multiple objectives, policy levers, and behavioral responses from strategic actors who optimize for their individual objectives. Moreover, real-world policies should be explainable and robust to simulation-to-reality gaps, e.g., due to calibration issues. Existing approaches are often limited to a narrow set of policy levers or objectives that are hard to measure, do not yield explicit optimal policies, or do not consider strategic behavior, for example. Hence, it remains challenging to optimize policy in real-world scenarios. Here we show that the AI Economist framework enables effective, flexible, and interpretable policy design using two-level reinforcement learning (RL) and data-driven simulations. We validate our framework on optimizing the stringency of US state policies and Federal subsidies during a pandemic, e.g., COVID-19, using a simulation fitted to real data. We find that log-linear policies trained using RL significantly improve social welfare, based on both public health and economic outcomes, compared to past outcomes. Their behavior can be explained, e.g., well-performing policies respond strongly to changes in recovery and vaccination rates. They are also robust to calibration errors, e.g., infection rates that are over or underestimated. As of yet, real-world policymaking has not seen adoption of machine learning methods at large, including RL and AI-driven simulations. Our results show the potential of AI to guide policy design and improve social welfare amidst the complexity of the real world.
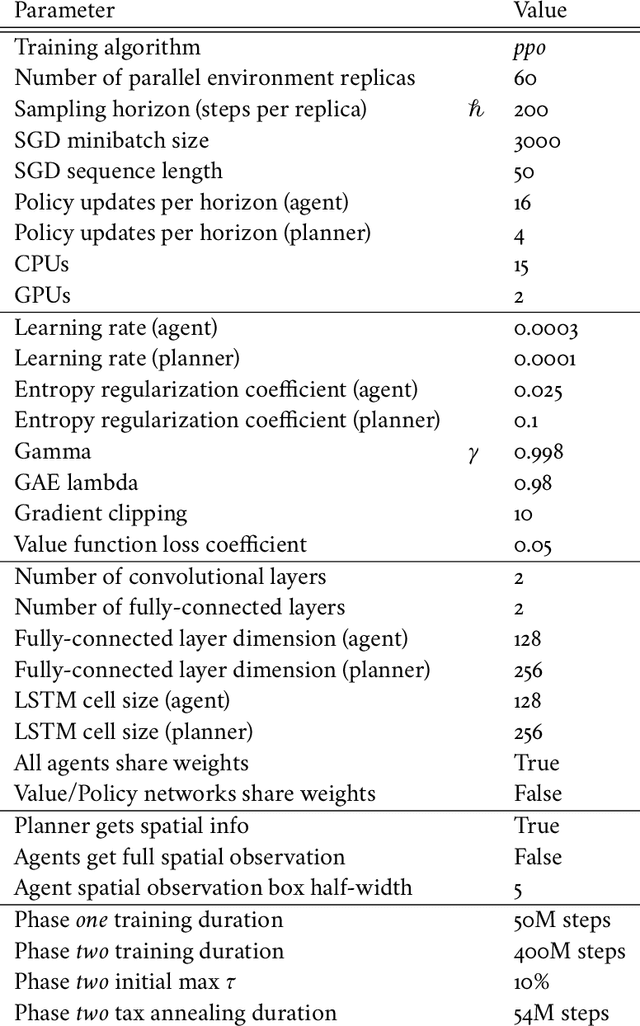
The AI Economist: Optimal Economic Policy Design via Two-level Deep Reinforcement Learning
Aug 05, 2021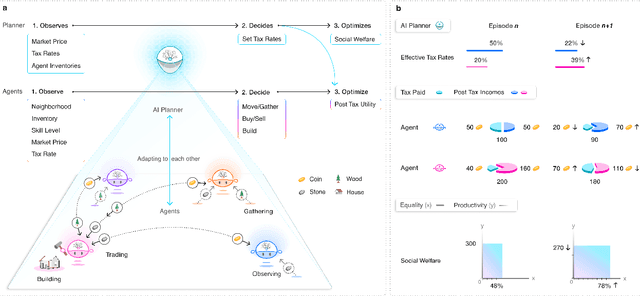
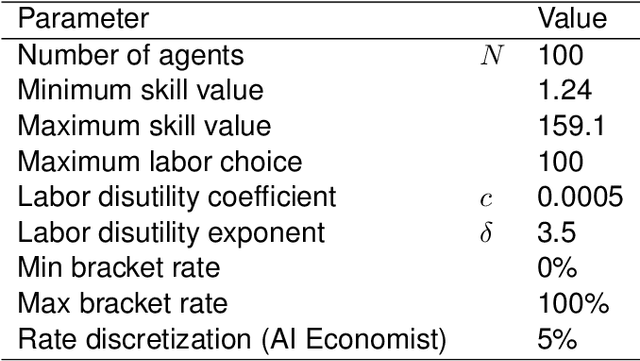
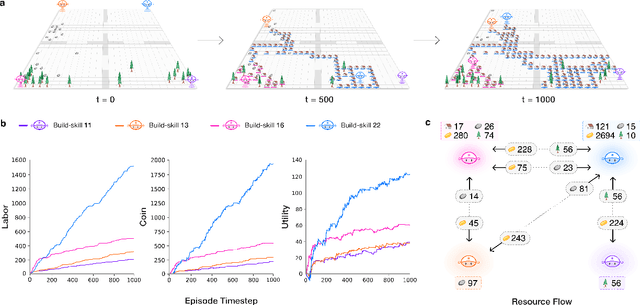
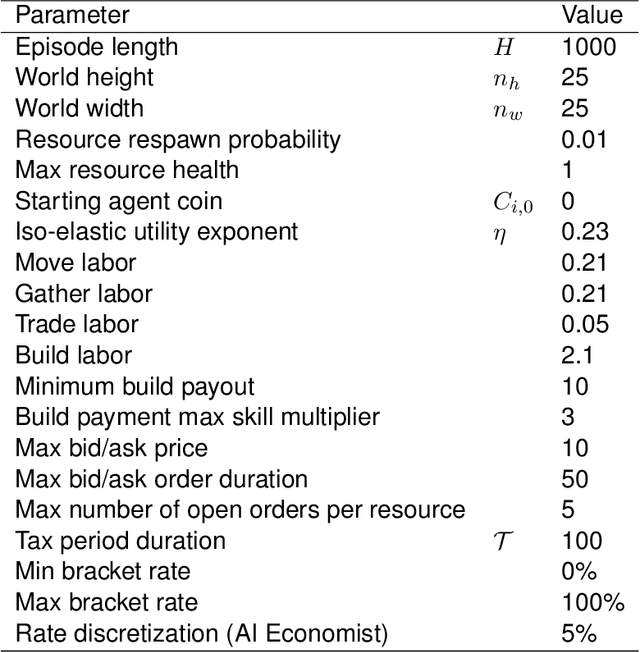
Abstract:AI and reinforcement learning (RL) have improved many areas, but are not yet widely adopted in economic policy design, mechanism design, or economics at large. At the same time, current economic methodology is limited by a lack of counterfactual data, simplistic behavioral models, and limited opportunities to experiment with policies and evaluate behavioral responses. Here we show that machine-learning-based economic simulation is a powerful policy and mechanism design framework to overcome these limitations. The AI Economist is a two-level, deep RL framework that trains both agents and a social planner who co-adapt, providing a tractable solution to the highly unstable and novel two-level RL challenge. From a simple specification of an economy, we learn rational agent behaviors that adapt to learned planner policies and vice versa. We demonstrate the efficacy of the AI Economist on the problem of optimal taxation. In simple one-step economies, the AI Economist recovers the optimal tax policy of economic theory. In complex, dynamic economies, the AI Economist substantially improves both utilitarian social welfare and the trade-off between equality and productivity over baselines. It does so despite emergent tax-gaming strategies, while accounting for agent interactions and behavioral change more accurately than economic theory. These results demonstrate for the first time that two-level, deep RL can be used for understanding and as a complement to theory for economic design, unlocking a new computational learning-based approach to understanding economic policy.
The AI Economist: Improving Equality and Productivity with AI-Driven Tax Policies
Apr 28, 2020
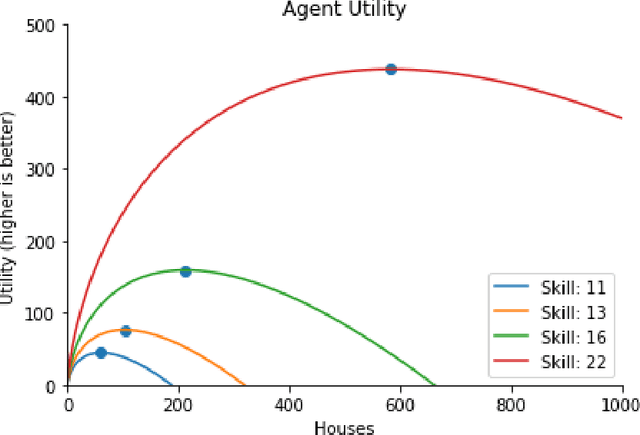
Abstract:Tackling real-world socio-economic challenges requires designing and testing economic policies. However, this is hard in practice, due to a lack of appropriate (micro-level) economic data and limited opportunity to experiment. In this work, we train social planners that discover tax policies in dynamic economies that can effectively trade-off economic equality and productivity. We propose a two-level deep reinforcement learning approach to learn dynamic tax policies, based on economic simulations in which both agents and a government learn and adapt. Our data-driven approach does not make use of economic modeling assumptions, and learns from observational data alone. We make four main contributions. First, we present an economic simulation environment that features competitive pressures and market dynamics. We validate the simulation by showing that baseline tax systems perform in a way that is consistent with economic theory, including in regard to learned agent behaviors and specializations. Second, we show that AI-driven tax policies improve the trade-off between equality and productivity by 16% over baseline policies, including the prominent Saez tax framework. Third, we showcase several emergent features: AI-driven tax policies are qualitatively different from baselines, setting a higher top tax rate and higher net subsidies for low incomes. Moreover, AI-driven tax policies perform strongly in the face of emergent tax-gaming strategies learned by AI agents. Lastly, AI-driven tax policies are also effective when used in experiments with human participants. In experiments conducted on MTurk, an AI tax policy provides an equality-productivity trade-off that is similar to that provided by the Saez framework along with higher inverse-income weighted social welfare.
Explore, Discover and Learn: Unsupervised Discovery of State-Covering Skills
Feb 14, 2020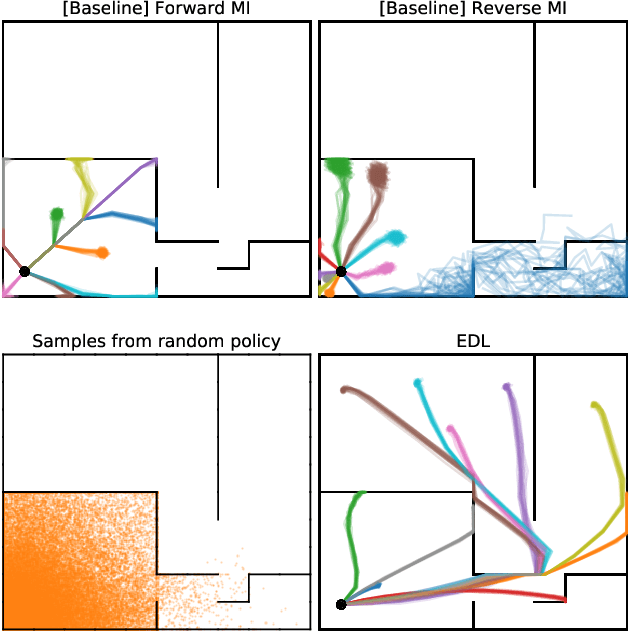
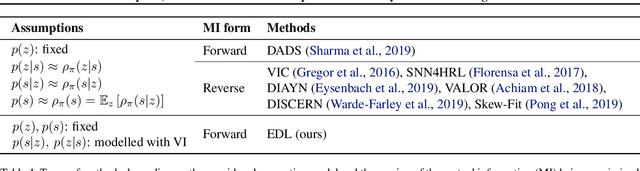
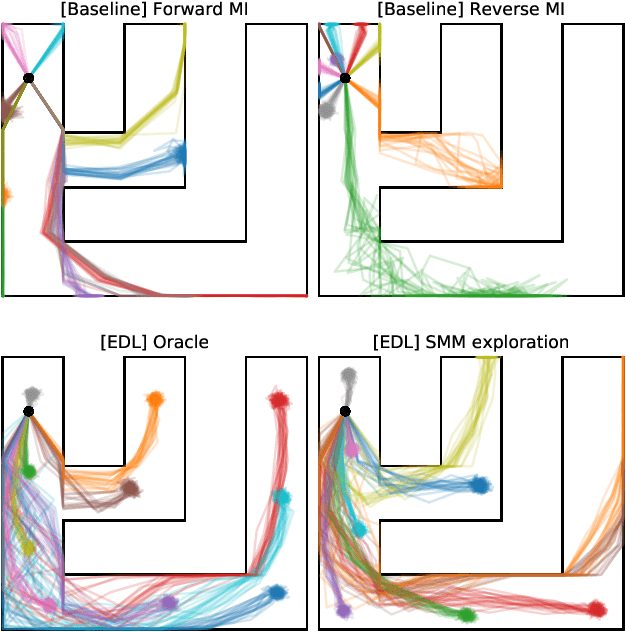
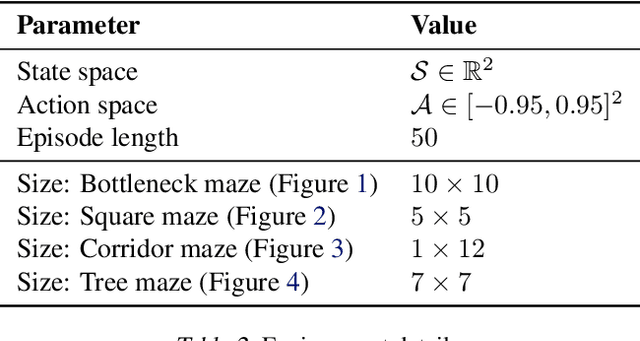
Abstract:Acquiring abilities in the absence of a task-oriented reward function is at the frontier of reinforcement learning research. This problem has been studied through the lens of empowerment, which draws a connection between option discovery and information theory. Information-theoretic skill discovery methods have garnered much interest from the community, but little research has been conducted in understanding their limitations. Through theoretical analysis and empirical evidence, we show that existing algorithms suffer from a common limitation -- they discover options that provide a poor coverage of the state space. In light of this, we propose 'Explore, Discover and Learn' (EDL), an alternative approach to information-theoretic skill discovery. Crucially, EDL optimizes the same information-theoretic objective derived from the empowerment literature, but addresses the optimization problem using different machinery. We perform an extensive evaluation of skill discovery methods on controlled environments and show that EDL offers significant advantages, such as overcoming the coverage problem, reducing the dependence of learned skills on the initial state, and allowing the user to define a prior over which behaviors should be learned.
Keeping Your Distance: Solving Sparse Reward Tasks Using Self-Balancing Shaped Rewards
Nov 04, 2019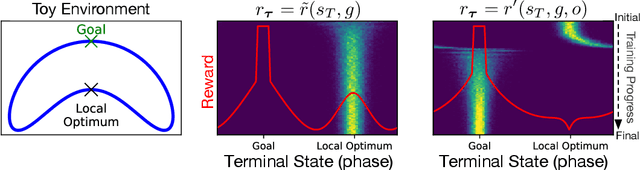
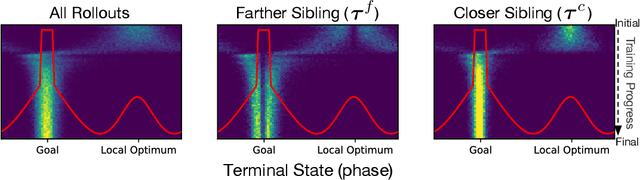
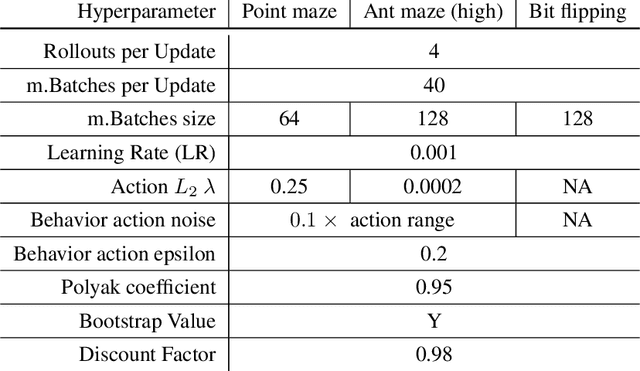
Abstract:While using shaped rewards can be beneficial when solving sparse reward tasks, their successful application often requires careful engineering and is problem specific. For instance, in tasks where the agent must achieve some goal state, simple distance-to-goal reward shaping often fails, as it renders learning vulnerable to local optima. We introduce a simple and effective model-free method to learn from shaped distance-to-goal rewards on tasks where success depends on reaching a goal state. Our method introduces an auxiliary distance-based reward based on pairs of rollouts to encourage diverse exploration. This approach effectively prevents learning dynamics from stabilizing around local optima induced by the naive distance-to-goal reward shaping and enables policies to efficiently solve sparse reward tasks. Our augmented objective does not require any additional reward engineering or domain expertise to implement and converges to the original sparse objective as the agent learns to solve the task. We demonstrate that our method successfully solves a variety of hard-exploration tasks (including maze navigation and 3D construction in a Minecraft environment), where naive distance-based reward shaping otherwise fails, and intrinsic curiosity and reward relabeling strategies exhibit poor performance.
Competitive Experience Replay
Feb 17, 2019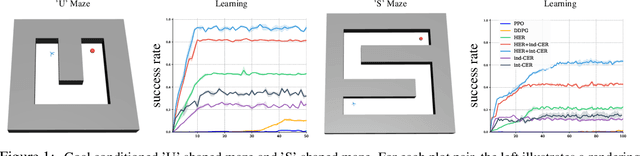
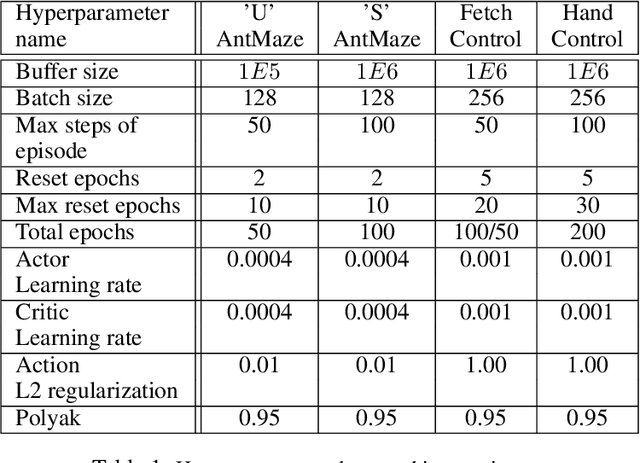
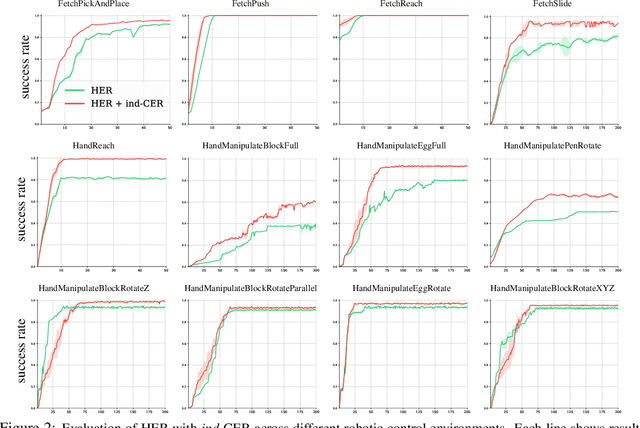
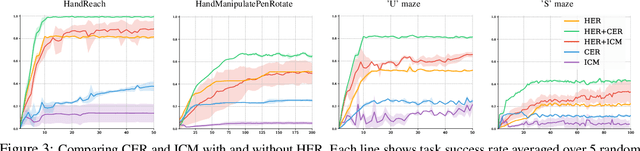
Abstract:Deep learning has achieved remarkable successes in solving challenging reinforcement learning (RL) problems when dense reward function is provided. However, in sparse reward environment it still often suffers from the need to carefully shape reward function to guide policy optimization. This limits the applicability of RL in the real world since both reinforcement learning and domain-specific knowledge are required. It is therefore of great practical importance to develop algorithms which can learn from a binary signal indicating successful task completion or other unshaped, sparse reward signals. We propose a novel method called competitive experience replay, which efficiently supplements a sparse reward by placing learning in the context of an exploration competition between a pair of agents. Our method complements the recently proposed hindsight experience replay (HER) by inducing an automatic exploratory curriculum. We evaluate our approach on the tasks of reaching various goal locations in an ant maze and manipulating objects with a robotic arm. Each task provides only binary rewards indicating whether or not the goal is achieved. Our method asymmetrically augments these sparse rewards for a pair of agents each learning the same task, creating a competitive game designed to drive exploration. Extensive experiments demonstrate that this method leads to faster converge and improved task performance.
Interpretable Counting for Visual Question Answering
Mar 02, 2018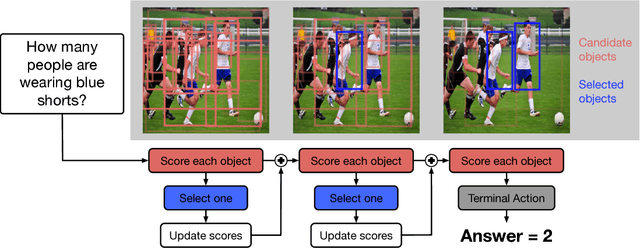
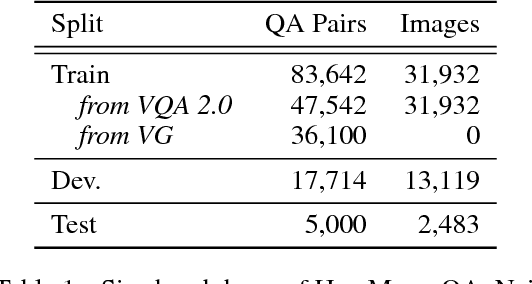

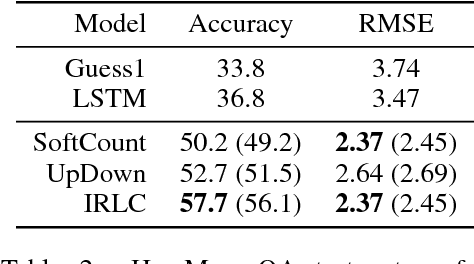
Abstract:Questions that require counting a variety of objects in images remain a major challenge in visual question answering (VQA). The most common approaches to VQA involve either classifying answers based on fixed length representations of both the image and question or summing fractional counts estimated from each section of the image. In contrast, we treat counting as a sequential decision process and force our model to make discrete choices of what to count. Specifically, the model sequentially selects from detected objects and learns interactions between objects that influence subsequent selections. A distinction of our approach is its intuitive and interpretable output, as discrete counts are automatically grounded in the image. Furthermore, our method outperforms the state of the art architecture for VQA on multiple metrics that evaluate counting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge